 |
PDBsum entry 2bnf

|

|

|
|
 |
Contents |
 |
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
* Residue conservation analysis
|
|
|

|
|
PDB id:
|
 |
|
 |
| Name: |
 |
Transferase
|
 |
|
Title:
|
 |
The structure of e. Coli ump kinase in complex with utp
|
|
Structure:
|
 |
Uridylate kinase. Chain: a, b. Synonym: ump kinase, uk, uridine monophosphate kinase. Engineered: yes. Mutation: yes
|
|
Source:
|
 |
Escherichia coli. Organism_taxid: 83333. Strain: k12. Expressed in: escherichia coli. Expression_system_taxid: 562
|
|
Biol. unit:
|
 |
 Hexamer (from PDB file)
Hexamer (from PDB file)
|
|
Resolution:
|
 |
|
2.45Å
|
R-factor:
|
0.184
|
R-free:
|
0.231
|
|
|
Authors:
|
 |
P.Briozzo,C.Evrin,P.Meyer,L.Assairi,N.Joly,O.Barzu,A.M.Gilles
|
Key ref:

|
 |
P.Briozzo
et al.
(2005).
Structure of Escherichia coli UMP kinase differs from that of other nucleoside monophosphate kinases and sheds new light on enzyme regulation.
J Biol Chem,
280,
25533-25540.
PubMed id:
DOI:

|
 |
|
Date:
|
 |
|
23-Mar-05
|
Release date:
|
27-Apr-05
|
|
|

|

|
|
PROCHECK
|

|

|
|
|
Headers
|
 |
|
|
References
|
|
|
|

|

|
|
P0A7E9
(PYRH_ECOLI) -
Uridylate kinase from Escherichia coli (strain K12)
|
|

|

|
Seq:
Struc:
|
 |
 |
 |
241 a.a.
236 a.a.*
|

|

|

|

|
|

|

|

|
 |
 |

|
|
Key: |
 |
PfamA domain |
 |
 |
 |
Secondary structure |
 |
 |
CATH domain |
 |
|
*
PDB and UniProt seqs differ
at 1 residue position (black
cross)
|
|

|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
E.C.2.7.4.22
- Ump kinase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
UMP + ATP = UDP + ADP
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
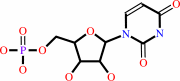 UMP
UMP
|
+
|
 ATP
ATP
|
=
|
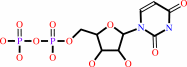 UDP
UDP
|
+
|
ADP
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
matches with 86.21% similarity
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
J Biol Chem
280:25533-25540
(2005)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Structure of Escherichia coli UMP kinase differs from that of other nucleoside monophosphate kinases and sheds new light on enzyme regulation.
|
|
P.Briozzo,
C.Evrin,
P.Meyer,
L.Assairi,
N.Joly,
O.Barzu,
A.M.Gilles.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
Bacterial UMP kinases are essential enzymes involved in the multistep synthesis
of nucleoside triphosphates. They are hexamers regulated by the allosteric
activator GTP and inhibited by UTP. We solved the crystal structure of
Escherichia coli UMP kinase bound to the UMP substrate (2.3 A resolution), the
UDP product (2.6 A), or UTP (2.45 A). The monomer fold, unrelated to that of
other nucleoside monophosphate kinases, belongs to the carbamate kinase-like
superfamily. However, the phosphate acceptor binding cleft and subunit assembly
are characteristic of UMP kinase. Interactions with UMP explain the high
specificity for this natural substrate. UTP, previously described as an
allosteric inhibitor, was unexpectedly found in the phosphate acceptor site,
suggesting that it acts as a competitive inhibitor. Site-directed mutagenesis of
residues Thr-138 and Asn-140, involved in both uracil recognition and active
site interaction within the hexamer, decreased the activation by GTP and
inhibition by UTP. These experiments suggest a cross-talk mechanism between
enzyme subunits involved in cooperative binding at the phosphate acceptor site
and in allosteric regulation by GTP. As bacterial UMP kinases have no
counterpart in eukaryotes, the information provided here could help the design
of new antibiotics.

|

|
|
|

|
| |
Selected figure(s)
|
|

|
| |
 |
 |

|
 |

|
 |
Figure 2.
FIG. 2. Overall fold and quaternary structure. A, ribbon
representation of the UMPKeco monomer fold (using the
UMP-containing complex).  -strands (yellow) and
helices (blue, except -strands (yellow) and
helices (blue, except  3, pink) are numbered.
A stick model of UMP is shown in magenta. The cross-talk loop
(green) is labeled CT. The loops are smoothed for clarity. A
gray line connects residues that delimit a segment in which no
clear density can be seen. B, the dimer constituted by the two
molecules of an asymmetric unit. View along the
non-crystallographic two-fold axis (indicated by a black ellipse
symbol). The blue subunit orientation is close to that in panel
A. C, ribbon representation of the hexamer viewed along the
three-fold crystallographic axis (indicated by a black
triangle). A particular color is used for each subunit. For the
blue and green dimer, 3, pink) are numbered.
A stick model of UMP is shown in magenta. The cross-talk loop
(green) is labeled CT. The loops are smoothed for clarity. A
gray line connects residues that delimit a segment in which no
clear density can be seen. B, the dimer constituted by the two
molecules of an asymmetric unit. View along the
non-crystallographic two-fold axis (indicated by a black ellipse
symbol). The blue subunit orientation is close to that in panel
A. C, ribbon representation of the hexamer viewed along the
three-fold crystallographic axis (indicated by a black
triangle). A particular color is used for each subunit. For the
blue and green dimer,  3 helices are pink.
Corey-Pauling-Koltun space-filling models of UMP are magenta.
The three non-crystallographic two-fold axes are shown by dotted
lines; they are perpendicular to the three-fold axis. D,
magnification of the dimer-dimer interface emphasizing the 2
residues (shown in sticks and labeled) from the cross-talk loop
that interact both with their homologues from the facing dimer
and with UMP (stick model with carbon atoms in magenta).
Hydrogen bonds are shown as red dots. 3 helices are pink.
Corey-Pauling-Koltun space-filling models of UMP are magenta.
The three non-crystallographic two-fold axes are shown by dotted
lines; they are perpendicular to the three-fold axis. D,
magnification of the dimer-dimer interface emphasizing the 2
residues (shown in sticks and labeled) from the cross-talk loop
that interact both with their homologues from the facing dimer
and with UMP (stick model with carbon atoms in magenta).
Hydrogen bonds are shown as red dots.  -helices are
transparized for clarity. The figure was drawn with PyMOL,
Version 0.97 (38). -helices are
transparized for clarity. The figure was drawn with PyMOL,
Version 0.97 (38).
|
 |
Figure 3.
FIG. 3. Comparison with NAGK structure. A, superposition of
the ribbon representations of the monomers of UMPKeco (blue,
with a stick model of UMP in cyan) and NAGK (yellow, with
N-acetyl glutamine and ADPNP in red; the helix homologous to
 3
is pink). The cross-talk loop of UMPKeco is green, the flexible
loops close to ADPNP are magenta, and the extra 3
is pink). The cross-talk loop of UMPKeco is green, the flexible
loops close to ADPNP are magenta, and the extra  -hairpins
of NAGK are orange. The orientation is close to that in Fig. 2A
but slightly modified to better see all ligands. B, the dimer of
NAGK. The orientation is slightly different from that in Fig. 2B
to give a better view of the interface. -hairpins
of NAGK are orange. The orientation is close to that in Fig. 2A
but slightly modified to better see all ligands. B, the dimer of
NAGK. The orientation is slightly different from that in Fig. 2B
to give a better view of the interface.
|
 |
|
|

|
| |
The above figures are
reprinted
by permission from the ASBMB:
J Biol Chem
(2005,
280,
25533-25540)
copyright 2005.
|
|
| |
Figures were
selected
by the author.
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Literature references that cite this PDB file's key reference
|
|
 |
| |
PubMed id
|
 |
Reference
|
 |
|
|
|
 |
G.Labesse,
K.Benkali,
I.Salard-Arnaud,
A.M.Gilles,
and
H.Munier-Lehmann
(2011).
Structural and functional characterization of the Mycobacterium tuberculosis uridine monophosphate kinase: insights into the allosteric regulation.
|
| |
Nucleic Acids Res,
39,
3458-3472.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
M.J.Lee,
L.Chien-Liang,
J.Y.Tsai,
W.T.Sue,
W.S.Hsia,
and
H.Huang
(2010).
Identification and biochemical characterization of a unique Mn2+-dependent UMP kinase from Helicobacter pylori.
|
| |
Arch Microbiol,
192,
739-746.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
N.Dellas,
and
J.P.Noel
(2010).
Mutation of archaeal isopentenyl phosphate kinase highlights mechanism and guides phosphorylation of additional isoprenoid monophosphates.
|
| |
ACS Chem Biol,
5,
589-601.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
P.Hein,
J.Stöckel,
S.Bennewitz,
and
R.Oelmüller
(2009).
A protein related to prokaryotic UMP kinases is involved in psaA/B transcript accumulation in Arabidopsis.
|
| |
Plant Mol Biol,
69,
517-528.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
P.N.Minh,
N.Devroede,
J.Massant,
D.Maes,
and
D.Charlier
(2009).
Insights into the architecture and stoichiometry of Escherichia coli PepA*DNA complexes involved in transcriptional control and site-specific DNA recombination by atomic force microscopy.
|
| |
Nucleic Acids Res,
37,
1463-1476.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
J.Schemberg,
K.Schneider,
D.Fenske,
and
A.Müller
(2008).
Azotobacter vinelandii metal storage protein: "classical" inorganic chemistry involved in Mo/W uptake and release processes.
|
| |
Chembiochem,
9,
595-602.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
S.Pakhomova,
S.G.Bartlett,
A.Augustus,
T.Kuzuyama,
and
M.E.Newcomer
(2008).
Crystal structure of fosfomycin resistance kinase FomA from Streptomyces wedmorensis.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
283,
28518-28526.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
J.L.Tu,
K.H.Chin,
A.H.Wang,
and
S.H.Chou
(2007).
The crystallization of apo-form UMP kinase from Xanthomonas campestris is significantly improved in a strong magnetic field.
|
| |
Acta Crystallogr Sect F Struct Biol Cryst Commun,
63,
438-442.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
S.E.Lee,
S.Y.Kim,
C.M.Kim,
M.K.Kim,
Y.R.Kim,
K.Jeong,
H.J.Ryu,
Y.S.Lee,
S.S.Chung,
H.E.Choy,
and
J.H.Rhee
(2007).
The pyrH gene of Vibrio vulnificus is an essential in vivo survival factor.
|
| |
Infect Immun,
75,
2795-2801.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
B.Dhaliwal,
J.Ren,
M.Lockyer,
I.Charles,
A.R.Hawkins,
and
D.K.Stammers
(2006).
Structure of Staphylococcus aureus cytidine monophosphate kinase in complex with cytidine 5'-monophosphate.
|
| |
Acta Crystallogr Sect F Struct Biol Cryst Commun,
62,
710-715.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
G.Hible,
P.Christova,
L.Renault,
E.Seclaman,
A.Thompson,
E.Girard,
H.Munier-Lehmann,
and
J.Cherfils
(2006).
Unique GMP-binding site in Mycobacterium tuberculosis guanosine monophosphate kinase.
|
| |
Proteins,
62,
489-500.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
N.Devroede,
N.Huysveld,
and
D.Charlier
(2006).
Mutational analysis of intervening sequences connecting the binding sites for integration host factor, PepA, PurR, and RNA polymerase in the control region of the Escherichia coli carAB operon, encoding carbamoylphosphate synthase.
|
| |
J Bacteriol,
188,
3236-3245.
|
 |
|
 |
 |
|
The most recent references are shown first.
Citation data come partly from CiteXplore and partly
from an automated harvesting procedure. Note that this is likely to be
only a partial list as not all journals are covered by
either method. However, we are continually building up the citation data
so more and more references will be included with time.
Where a reference describes a PDB structure, the PDB
code is
shown on the right.
|
 |

