 |
PDBsum entry 3d40

|

|

|
|
 |
Contents |
 |
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
* Residue conservation analysis
|
|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
E.C.2.7.4.26
- isopentenyl phosphate kinase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
isopentenyl phosphate + ATP = isopentenyl diphosphate + ADP
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
isopentenyl phosphate
|
+
|
 ATP
ATP
|
=
|
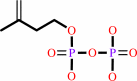 isopentenyl diphosphate
isopentenyl diphosphate
|
+
|
ADP
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
matches with 64.29% similarity
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
J Biol Chem
283:28518-28526
(2008)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Crystal Structure of Fosfomycin Resistance Kinase FomA from Streptomyces wedmorensis.
|
|
S.Pakhomova,
S.G.Bartlett,
A.Augustus,
T.Kuzuyama,
M.E.Newcomer.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
The fosfomycin resistance protein FomA inactivates fosfomycin by phosphorylation
of the phosphonate group of the antibiotic in the presence of ATP and Mg(II). We
report the crystal structure of FomA from the fosfomycin biosynthetic gene
cluster of Streptomyces wedmorensis in complex with diphosphate and in ternary
complex with the nonhydrolyzable ATP analog adenosine
5'-(beta,gamma-imido)-triphosphate (AMPPNP), Mg(II), and fosfomycin, at 1.53 and
2.2A resolution, respectively. The polypeptide exhibits an open alphabetaalpha
sandwich fold characteristic for the amino acid kinase family of enzymes. The
diphosphate complex shows significant disorder in loops surrounding the active
site. As a result, the nucleotide-binding site is wide open. Binding of the
substrates is followed by the partial closure of the active site and ordering of
the alpha2-helix. Structural comparison with N-acetyl-l-glutamate kinase shows
several similarities in the site of phosphoryl transfer: 1) preservation of
architecture of the catalytical amino acids of N-acetyl-l-glutamate kinase
(Lys(9), Lys(216), and Asp(150) in FomA); 2) good superposition of the phosphate
acceptor groups of the substrates, and 3) good superposition of the diphosphate
molecule with the beta- and gamma-phosphates of AMPPNP, suggesting that the
reaction could proceed by an associative in-line mechanism. However, differences
in conformations of the triphosphate moiety of AMPPNP molecules, the long
distance (5.1A) between the phosphate acceptor and donor groups in FomA, and
involvement of Lys(18) instead of Lys(9) in binding with the gamma-phosphate may
indicate a different reaction mechanism. The present work identifies the active
site residues of FomA responsible for substrate binding and specificity and
proposes their roles in catalysis.

|

|
|
|

|
| |
Selected figure(s)
|
|

|
| |
 |
 |

|
 |

|
 |
Figure 2.
F[o] - F[c] electron density omit map contoured at 3 σ for
DPO in the FomA·DPO complex (A) and MgAMPPNP and
fosfomycin in the FomA·MgAMPPNP·fosfomycin complex
(B). Mg^2+ cation is shown as a sphere.
|
 |
Figure 5.
Stereo views of the active site. A, FomA·DPO complex.
B, FomA·MgAMPPNP·fosfomycin complex. The ligand
molecules are shown in ball-and-stick format. The Mg^2+ (green)
and coordinated water molecules are represented as spheres. The
interacting protein residues are shown in stick format. C, a
stereo view of the superposition of the AMPPNP binding sites in
FomA·MgAMPPNP·fosfomycin (blue) and
NAGK·MgAMPPNP·NAD (red) structures. Mg^2+ cations
are shown as spheres, and water molecules are shown as crosses.
|
 |
|
|

|
| |
The above figures are
reprinted
from an Open Access publication published by the ASBMB:
J Biol Chem
(2008,
283,
28518-28526)
copyright 2008.
|
|
| |
Figures were
selected
by an automated process.
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Literature references that cite this PDB file's key reference
|
|
 |
| |
PubMed id
|
 |
Reference
|
 |
|
|
|
 |
M.F.Mabanglo,
H.L.Schubert,
M.Chen,
C.P.Hill,
and
C.D.Poulter
(2010).
X-ray structures of isopentenyl phosphate kinase.
|
| |
ACS Chem Biol,
5,
517-527.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
N.Dellas,
and
J.P.Noel
(2010).
Mutation of archaeal isopentenyl phosphate kinase highlights mechanism and guides phosphorylation of additional isoprenoid monophosphates.
|
| |
ACS Chem Biol,
5,
589-601.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
|
The most recent references are shown first.
Citation data come partly from CiteXplore and partly
from an automated harvesting procedure. Note that this is likely to be
only a partial list as not all journals are covered by
either method. However, we are continually building up the citation data
so more and more references will be included with time.
Where a reference describes a PDB structure, the PDB
codes are
shown on the right.
|
 |

