 |
PDBsum entry 1ekf

|

|

|
|
 |
Contents |
 |
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
* Residue conservation analysis
|
|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
E.C.2.6.1.42
- branched-chain-amino-acid transaminase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

Pathway:
|
 |
Leucine Biosynthesis
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
L-leucine + 2-oxoglutarate = 4-methyl-2-oxopentanoate + L-glutamate
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
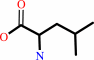 L-leucine
L-leucine
|
+
|
 2-oxoglutarate
2-oxoglutarate
|
=
|
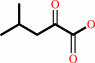 4-methyl-2-oxopentanoate
4-methyl-2-oxopentanoate
|
+
|
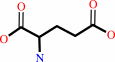 L-glutamate
L-glutamate
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Cofactor:
|
 |
Pyridoxal 5'-phosphate
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Pyridoxal 5'-phosphate
Bound ligand (Het Group name =
PLP)
matches with 93.75% similarity
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr
57:506-515
(2001)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
The structure of human mitochondrial branched-chain aminotransferase.
|
|
N.Yennawar,
J.Dunbar,
M.Conway,
S.Hutson,
G.Farber.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
X-ray crystal structures of three forms of human mitochondrial branched-chain
aminotransferase (BCAT) were solved by molecular-replacement methods, using
Escherichia coli BCAT as the search model. The enzyme is a homodimer and the
polypeptide chain of each monomer has two domains. The small domain is composed
of residues 1--175 and the large domain is composed of residues 176--365. The
active site is close to the dimer interface. The 4'-aldehyde of the PLP cofactor
is covalently linked to the epsilon-amino group of the active-site lysine,
Lys202, via a Schiff-base linkage in two of the structures. In the third
structure, the enzyme is irreversibly inactivated by Tris. The overall fold of
the dimer in human mitochondrial BCAT is similar to the structure of two
bacterial enzymes, E. coli BCAT and D-amino acid aminotransferase (D-AAT). The
residues lining the putative substrate-binding pocket of human BCAT and D-AAT
are completely rearranged to allow catalysis with substrates of opposite
stereochemistry. In the case of human mitochondrial branched-chain
aminotransferase, a hydrogen-bond interaction between the guanidinium group of
Arg143 in the first monomer with the side-chain hydroxyl of Tyr70 in the second
monomer is important in the formation of the substrate-binding pocket.

|

|
|
|

|
| |
Selected figure(s)
|
|

|
| |
 |
 |

|
 |

|
 |
Figure 2.
Figure 2 Active-site density of BCAT inhibited by Tris. The map
was calculated from a structure that does not contain Tris. This
is the first example in the Protein Data Bank where a buffer has
formed a covalent intermediate with an enzyme active site.
|
 |
Figure 6.
Figure 6 (a) Active-site superposition of E. coli BCAT (thinner
bonds and smaller residue labels) with human BCATm (thicker
bonds and larger residue labels). The side chains are conserved
and their orientation is very similar. (b) Active-site
superposition of D-AAT (thinner bonds and smaller residue
labels) with human BCATm (thicker bonds and larger residue
labels). Only the side chains interacting with the PLP are
similar in nature and have comparable conformation.
|
 |
|
|

|
| |
The above figures are
reprinted
by permission from the IUCr:
Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr
(2001,
57,
506-515)
copyright 2001.
|
|
| |
Figures were
selected
by the author.
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Literature references that cite this PDB file's key reference
|
|
 |
| |
PubMed id
|
 |
Reference
|
 |
|
|
|
 |
M.Colón,
F.Hernández,
K.López,
H.Quezada,
J.González,
G.López,
C.Aranda,
and
A.González
(2011).
Saccharomyces cerevisiae Bat1 and Bat2 Aminotransferases Have Functionally Diverged from the Ancestral-Like Kluyveromyces lactis Orthologous Enzyme.
|
| |
PLoS One,
6,
e16099.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
A.Castell,
C.Mille,
and
T.Unge
(2010).
Structural analysis of mycobacterial branched-chain aminotransferase: implications for inhibitor design.
|
| |
Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr,
66,
549-557.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
M.M.Islam,
M.Nautiyal,
R.M.Wynn,
J.A.Mobley,
D.T.Chuang,
and
S.M.Hutson
(2010).
Branched-chain amino acid metabolon: interaction of glutamate dehydrogenase with the mitochondrial branched-chain aminotransferase (BCATm).
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
285,
265-276.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
F.Gao,
C.Wang,
C.Wei,
and
Y.Li
(2009).
A branched-chain aminotransferase may regulate hormone levels by affecting KNOX genes in plants.
|
| |
Planta,
230,
611-623.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
Q.Han,
H.Robinson,
T.Cai,
D.A.Tagle,
and
J.Li
(2009).
Structural insight into the inhibition of human kynurenine aminotransferase I/glutamine transaminase K.
|
| |
J Med Chem,
52,
2786-2793.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
F.R.Salsbury,
S.T.Knutson,
L.B.Poole,
and
J.S.Fetrow
(2008).
Functional site profiling and electrostatic analysis of cysteines modifiable to cysteine sulfenic acid.
|
| |
Protein Sci,
17,
299-312.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
M.M.Islam,
R.Wallin,
R.M.Wynn,
M.Conway,
H.Fujii,
J.A.Mobley,
D.T.Chuang,
and
S.M.Hutson
(2007).
A novel branched-chain amino acid metabolon. Protein-protein interactions in a supramolecular complex.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
282,
11893-11903.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
N.H.Yennawar,
M.M.Islam,
M.Conway,
R.Wallin,
and
S.M.Hutson
(2006).
Human mitochondrial branched chain aminotransferase isozyme: structural role of the CXXC center in catalysis.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
281,
39660-39671.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
M.Goto,
I.Miyahara,
K.Hirotsu,
M.Conway,
N.Yennawar,
M.M.Islam,
and
S.M.Hutson
(2005).
Structural determinants for branched-chain aminotransferase isozyme-specific inhibition by the anticonvulsant drug gabapentin.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
280,
37246-37256.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
|
The most recent references are shown first.
Citation data come partly from CiteXplore and partly
from an automated harvesting procedure. Note that this is likely to be
only a partial list as not all journals are covered by
either method. However, we are continually building up the citation data
so more and more references will be included with time.
Where a reference describes a PDB structure, the PDB
codes are
shown on the right.
|
 |

