 |
PDBsum entry 1bjo

|
|
|

|
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
 |

|

|

|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
Aminotransferase
|
PDB id
|
|

|

|
1bjo
|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
 |
Contents |
 |
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
* Residue conservation analysis
|
|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
E.C.2.6.1.52
- phosphoserine transaminase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
|
1.
|
O-phospho-L-serine + 2-oxoglutarate = 3-phosphooxypyruvate + L-glutamate
|
|
2.
|
4-(phosphooxy)-L-threonine + 2-oxoglutarate = (R)-3-hydroxy-2-oxo-4- phosphooxybutanoate + L-glutamate
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
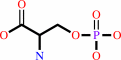 O-phospho-L-serine
O-phospho-L-serine
|
+
|
 2-oxoglutarate
2-oxoglutarate
|
=
|
3-phosphooxypyruvate
|
+
|
L-glutamate
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
matches with 90.91% similarity
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
4-(phosphooxy)-L-threonine
|
+
|
 2-oxoglutarate
2-oxoglutarate
|
=
|
(R)-3-hydroxy-2-oxo-4- phosphooxybutanoate
|
+
|
L-glutamate
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
matches with 90.91% similarity
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Cofactor:
|
 |
Pyridoxal 5'-phosphate
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Pyridoxal 5'-phosphate
Bound ligand (Het Group name =
PLP)
matches with 93.75% similarity
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
J Mol Biol
286:829-850
(1999)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Crystal structure of phosphoserine aminotransferase from Escherichia coli at 2.3 A resolution: comparison of the unligated enzyme and a complex with alpha-methyl-l-glutamate.
|
|
G.Hester,
W.Stark,
M.Moser,
J.Kallen,
Z.Marković-Housley,
J.N.Jansonius.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
Phosphoserine aminotransferase (PSAT; EC 2.6.1.52), a member of subgroup IV of
the aminotransferases, catalyses the conversion of 3-phosphohydroxypyruvate to
l-phosphoserine. The crystal structure of PSAT from Escherichia coli has been
solved in space group P212121 using MIRAS phases in combination with density
modification and was refined to an R-factor of 17.5% (Rfree=20.1 %) at 2.3 A
resolution. In addition, the structure of PSAT in complex with
alpha-methyl-l-glutamate (AMG) has been refined to an R-factor of 18.5%
(Rfree=25.1%) at 2.8 A resolution. Each subunit (361 residues) of the PSAT
homodimer is composed of a large pyridoxal-5'-phosphate binding domain (residues
16-268), consisting of a seven-stranded mainly parallel beta-sheet, two
additional beta-strands and seven alpha-helices, and a small C-terminal domain,
which incorporates a five-stranded beta-sheet and two alpha-helices. A
three-dimensional structural comparison to four other vitamin B6-dependent
enzymes reveals that three alpha-helices of the large domain, as well as an
N-terminal domain (subgroup II) or subdomain (subgroup I) are absent in PSAT.
Its only 15 N-terminal residues form a single beta-strand, which participates in
the beta-sheet of the C-terminal domain. The cofactor is bound through an
aldimine linkage to Lys198 in the active site. In the PSAT-AMG complex Ser9 and
Arg335 bind the AMG alpha-carboxylate group while His41, Arg42 and His328 are
involved in binding the AMG side-chain. Arg77 binds the AMG side-chain
indirectly through a solvent molecule and is expected to position itself during
catalysis between the PLP phosphate group and the substrate side-chain.
Comparison of the active sites of PSAT and aspartate aminotransferase suggests a
similar catalytic mechanism, except for the transaldimination step, since in
PSAT the Schiff base is protonated. Correlation of the PSAT crystal structure to
a published profile sequence analysis of all subgroup IV members allows active
site modelling of nifs and the proposal of a likely molecular reaction mechanism.

|

|
|
|

|
| |
Selected figure(s)
|
|

|
| |
 |
 |

|
 |

|
 |
Figure 1.
Figure 1. Nomenclature of atoms for PLP-Lys198 aldimine and
for the external aldimine with AMG.
|
 |
Figure 5.
Figure 5. Comparison of structure topologies by
superpositions of C^α traces of PSAT with those of DGD and E.
coli AAT, respectively, using DALI algorithm [Holm and Sander
1993]. In both stereo diagrams PSAT is displayed in fat lines
while the superimposed molecule is displayed in thin lines. N
and C termini are labelled. (a) Stereo diagram of superimposed
C^α traces of closed form of AAT and PSAT-AMG complex. (b)
Stereo diagram of superimposed C^α traces of DGD and native
PSAT. Pictures generated using program BOBSCRIPT [Kraulis 1991
and Esnouf 1998]. Program RASTER3D was used additionally to
generate (b) [Bacon and Anderson 1988 and Merrit and Murphy
1994].
|
 |
|
|

|
| |
The above figures are
reprinted
by permission from Elsevier:
J Mol Biol
(1999,
286,
829-850)
copyright 1999.
|
|
| |
Figures were
selected
by an automated process.
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Literature references that cite this PDB file's key reference
|
 Google scholar
Google scholar
|
|
 |
| |
PubMed id
|
 |
Reference
|
 |
|
|
|
 |
V.Mishra,
V.Ali,
T.Nozaki,
and
V.Bhakuni
(2011).
Biophysical characterization of Entamoeba histolytica phosphoserine aminotransferase (EhPSAT): role of cofactor and domains in stability and subunit assembly.
|
| |
Eur Biophys J,
40,
599-610.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
J.E.Antflick,
G.B.Baker,
and
D.R.Hampson
(2010).
The effects of a low protein diet on amino acids and enzymes in the serine synthesis pathway in mice.
|
| |
Amino Acids,
39,
145-153.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
M.Kameya,
H.Arai,
M.Ishii,
and
Y.Igarashi
(2010).
Purification of three aminotransferases from Hydrogenobacter thermophilus TK-6--novel types of alanine or glycine aminotransferase: enzymes and catalysis.
|
| |
FEBS J,
277,
1876-1885.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
V.Mishra,
V.Ali,
T.Nozaki,
and
V.Bhakuni
(2010).
Entamoeba histolytica Phosphoserine aminotransferase (EhPSAT): insights into the structure-function relationship.
|
| |
BMC Res Notes,
3,
52.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
O.M.Ganichkin,
X.M.Xu,
B.A.Carlson,
H.Mix,
D.L.Hatfield,
V.N.Gladyshev,
and
M.C.Wahl
(2008).
Structure and catalytic mechanism of eukaryotic selenocysteine synthase.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
283,
5849-5865.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
Y.Yoshikane,
N.Yokochi,
M.Yamasaki,
K.Mizutani,
K.Ohnishi,
B.Mikami,
H.Hayashi,
and
T.Yagi
(2008).
Crystal structure of pyridoxamine-pyruvate aminotransferase from Mesorhizobium loti MAFF303099.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
283,
1120-1127.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
C.E.Hart,
V.Race,
Y.Achouri,
E.Wiame,
M.Sharrard,
S.E.Olpin,
J.Watkinson,
J.R.Bonham,
J.Jaeken,
G.Matthijs,
and
E.Van Schaftingen
(2007).
Phosphoserine aminotransferase deficiency: a novel disorder of the serine biosynthesis pathway.
|
| |
Am J Hum Genet,
80,
931-937.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
B.Campanini,
F.Schiaretti,
S.Abbruzzetti,
D.Kessler,
and
A.Mozzarelli
(2006).
Sulfur mobilization in cyanobacteria: the catalytic mechanism of L-cystine C-S lyase (C-DES) from synechocystis.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
281,
38769-38780.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
E.G.Kapetaniou,
A.Thanassoulas,
A.P.Dubnovitsky,
G.Nounesis,
and
A.C.Papageorgiou
(2006).
Effect of pH on the structure and stability of Bacillus circulans ssp. alkalophilus phosphoserine aminotransferase: thermodynamic and crystallographic studies.
|
| |
Proteins,
63,
742-753.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
A.P.Dubnovitsky,
E.G.Kapetaniou,
and
A.C.Papageorgiou
(2005).
Enzyme adaptation to alkaline pH: atomic resolution (1.08 A) structure of phosphoserine aminotransferase from Bacillus alcalophilus.
|
| |
Protein Sci,
14,
97.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
A.P.Dubnovitsky,
R.B.Ravelli,
A.N.Popov,
and
A.C.Papageorgiou
(2005).
Strain relief at the active site of phosphoserine aminotransferase induced by radiation damage.
|
| |
Protein Sci,
14,
1498-1507.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
P.Peters-Wendisch,
M.Stolz,
H.Etterich,
N.Kennerknecht,
H.Sahm,
and
L.Eggeling
(2005).
Metabolic engineering of Corynebacterium glutamicum for L-serine production.
|
| |
Appl Environ Microbiol,
71,
7139-7144.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
A.C.Eliot,
and
J.F.Kirsch
(2004).
Pyridoxal phosphate enzymes: mechanistic, structural, and evolutionary considerations.
|
| |
Annu Rev Biochem,
73,
383-415.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
A.Paiardini,
F.Bossa,
and
S.Pascarella
(2004).
Evolutionarily conserved regions and hydrophobic contacts at the superfamily level: The case of the fold-type I, pyridoxal-5'-phosphate-dependent enzymes.
|
| |
Protein Sci,
13,
2992-3005.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
E.Y.Seo,
W.H.Lee,
Y.J.Piao,
K.H.Kim,
K.M.Lee,
K.S.Ahn,
J.M.Yang,
Y.J.Seo,
C.D.Kim,
J.K.Park,
and
J.H.Lee
(2004).
Identification of calcium-inducible genes in primary keratinocytes using suppression-subtractive hybridization.
|
| |
Exp Dermatol,
13,
163-169.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
Y.Katsura,
M.Shirouzu,
H.Yamaguchi,
R.Ishitani,
O.Nureki,
S.Kuramitsu,
H.Hayashi,
and
S.Yokoyama
(2004).
Crystal structure of a putative aspartate aminotransferase belonging to subgroup IV.
|
| |
Proteins,
55,
487-492.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
R.Contestabile,
A.Paiardini,
S.Pascarella,
M.L.di Salvo,
S.D'Aguanno,
and
F.Bossa
(2001).
l-Threonine aldolase, serine hydroxymethyltransferase and fungal alanine racemase. A subgroup of strictly related enzymes specialized for different functions.
|
| |
Eur J Biochem,
268,
6508-6525.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
G.Schneider,
H.Käck,
and
Y.Lindqvist
(2000).
The manifold of vitamin B6 dependent enzymes.
|
| |
Structure,
8,
R1-R6.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
T.Fujii,
M.Maeda,
H.Mihara,
T.Kurihara,
N.Esaki,
and
Y.Hata
(2000).
Structure of a NifS homologue: X-ray structure analysis of CsdB, an Escherichia coli counterpart of mammalian selenocysteine lyase.
|
| |
Biochemistry,
39,
1263-1273.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
W.Blankenfeldt,
C.Nowicki,
M.Montemartini-Kalisz,
H.M.Kalisz,
and
H.J.Hecht
(1999).
Crystal structure of Trypanosoma cruzi tyrosine aminotransferase: substrate specificity is influenced by cofactor binding mode.
|
| |
Protein Sci,
8,
2406-2417.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
|
The most recent references are shown first.
Citation data come partly from CiteXplore and partly
from an automated harvesting procedure. Note that this is likely to be
only a partial list as not all journals are covered by
either method. However, we are continually building up the citation data
so more and more references will be included with time.
Where a reference describes a PDB structure, the PDB
codes are
shown on the right.
|
 |

