 |
PDBsum entry 5kjd

|
|
|

|
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
 |

|

|

|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
Oxidoreductase
|
PDB id
|
|

|

|
5kjd
|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
|

|
|
PDB id:
|
 |
|
 |
| Name: |
 |
Oxidoreductase
|
 |
|
Title:
|
 |
Synechocystis apocarotenoid oxygenase (aco) mutant - glu150gln
|
|
Structure:
|
 |
Apocarotenoid-15,15'-oxygenase. Chain: a, b, c, d, e. Synonym: aco,8'-apo-beta-carotenal 15,15'-oxygenase,diox1. Engineered: yes. Mutation: yes
|
|
Source:
|
 |
Synechocystis sp. (Strain pcc 6803 / kazusa). Organism_taxid: 1111708. Strain: pcc 6803 / kazusa. Gene: sll1541. Expressed in: escherichia coli. Expression_system_taxid: 562
|
|
Resolution:
|
 |
|
2.75Å
|
R-factor:
|
0.213
|
R-free:
|
0.247
|
|
|
Authors:
|
 |
X.Sui,P.D.Kiser,K.Palczewski
|
|
Key ref:
|
 |
X.Sui
et al.
(2016).
Key Residues for Catalytic Function and Metal Coordination in a Carotenoid Cleavage Dioxygenase.
J Biol Chem,
291,
19401-19412.
PubMed id:
DOI:
|
 |
|
Date:
|
 |
|
18-Jun-16
|
Release date:
|
03-Aug-16
|
|
|

|

|
|
PROCHECK
|

|

|
|
|
Headers
|
 |
|
|
References
|
|
|
|

|

|
|
P74334
(ACOX_SYNY3) -
Apocarotenoid-15,15'-oxygenase from Synechocystis sp. (strain PCC 6803 / Kazusa)
|
|

|

|
Seq:
Struc:
|
 |
 |
 |
490 a.a.
479 a.a.*
|

|

|

|

|
|

|

|

|
 |
 |

|
|
Key: |
 |
PfamA domain |
 |
 |
 |
Secondary structure |
 |
|
*
PDB and UniProt seqs differ
at 1 residue position (black
cross)
|
|

|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
E.C.1.13.11.75
- all-trans-8'-apo-beta-carotenal 15,15'-oxygenase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
all-trans-8'-apo-beta-carotenal + O2 = (2E,4E,6E)-2,6-dimethylocta-2,4,6- trienedial + all-trans-retinal
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
all-trans-8'-apo-beta-carotenal
|
+
|
 O2
O2
|
=
|
(2E,4E,6E)-2,6-dimethylocta-2,4,6- trienedial
|
+
|
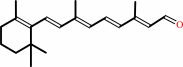 all-trans-retinal
all-trans-retinal
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Cofactor:
|
 |
Fe(2+)
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
J Biol Chem
291:19401-19412
(2016)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Key Residues for Catalytic Function and Metal Coordination in a Carotenoid Cleavage Dioxygenase.
|
|
X.Sui,
J.Zhang,
M.Golczak,
K.Palczewski,
P.D.Kiser.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
Carotenoid cleavage dioxygenases (CCDs) are non-heme iron-containing enzymes
found in all domains of life that generate biologically important
apocarotenoids. Prior studies have revealed a critical role for a conserved
4-His motif in forming the CCD iron center. By contrast, the roles of other
active site residues in catalytic function, including maintenance of the
stringent regio- and stereo-selective cleavage activity, typically exhibited by
these enzymes have not been thoroughly investigated. Here, we examined the
functional and structural importance of active site residues in an
apocarotenoid-cleaving oxygenase (ACO) from Synechocystis Most active site
substitutions variably lowered maximal catalytic activity without markedly
affecting the Km value for the all-trans-8'-apocarotenol substrate. Native
C15-C15' cleavage activity was retained in all ACO variants examined suggesting
that multiple active site residues contribute to the enzyme's regioselectivity.
Crystallographic analysis of a nearly inactive W149A-substituted ACO revealed
marked disruption of the active site structure, including loss of iron
coordination by His-238 apparently from an altered conformation of the conserved
second sphere Glu-150 residue. Gln- and Asp-150-substituted versions of ACO
further confirmed the structural/functional requirement for a Glu side chain at
this position, which is homologous to Glu-148 in RPE65, a site in which
substitution to Asp has been associated with loss of enzymatic function in Leber
congenital amaurosis. The novel links shown here between ACO active site
structure and catalytic activity could be broadly applicable to other CCD
members and provide insights into the molecular pathogenesis of vision loss
associated with an RPE65 point mutation.

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

