 |
PDBsum entry 5ecm

|
|
|

|
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
 |

|

|

|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
Ligase/transferase
|
PDB id
|
|

|

|
5ecm
|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
|

|
|
PDB id:
|
 |
|
 |
| Name: |
 |
Ligase/transferase
|
 |
|
Title:
|
 |
Crystal structure of fin219-fip1 complex with ja and leu
|
|
Structure:
|
 |
Jasmonic acid-amido synthetase jar1. Chain: a, d. Synonym: jasmonate-amino acid synthetase jar1,protein far-red insensitive 219,protein jasmonate resistant 1. Engineered: yes. Glutathione s-transferase u20. Chain: b, c, e, f. Synonym: atgstu20,fin219-interacting protein 1,gst class-tau member 20.
|
|
Source:
|
 |
Arabidopsis thaliana. Mouse-ear cress. Organism_taxid: 3702. Gene: jar1, fin219, at2g46370, f11c10.6. Expressed in: escherichia coli bl21(de3). Expression_system_taxid: 469008. Gene: gstu20, fip1, at1g78370, f3f9.11. Expressed in: escherichia coli. Expression_system_taxid: 562.
|
|
Resolution:
|
 |
|
1.60Å
|
R-factor:
|
0.233
|
R-free:
|
0.246
|
|
|
Authors:
|
 |
C.Y.Chen,Y.S.Cheng
|
|
Key ref:
|
 |
C.Y.Chen
et al.
(2017).
Structural basis of jasmonate-amido synthetase FIN219 in complex with glutathione S-transferase FIP1 during the JA signal regulation.
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A,
114,
E1815.
PubMed id:
DOI:
|
 |
|
Date:
|
 |
|
20-Oct-15
|
Release date:
|
02-Nov-16
|
|
|

|

|
|
PROCHECK
|

|

|
|
|
Headers
|
 |
|
|
References
|
|
|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class 2:
|
 |
Chains A, D:
E.C.6.3.2.52
- jasmonoyl--L-amino acid ligase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
a jasmonate + an L-alpha-amino acid + ATP = a jasmonyl-L-amino acid + AMP + diphosphate + H+
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
jasmonate
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
corresponds exactly
|
+
|
L-alpha-amino acid
|
+
|
 ATP
ATP
|
=
|
jasmonyl-L-amino acid
|
+
|
 AMP
AMP
|
+
|
 diphosphate
diphosphate
|
+
|
H(+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class 3:
|
 |
Chains B, C, E, F:
E.C.2.5.1.18
- glutathione transferase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
RX + glutathione = an S-substituted glutathione + a halide anion + H+
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
RX
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
corresponds exactly
|
+
|
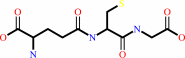 glutathione
glutathione
|
=
|
S-substituted glutathione
|
+
|
halide anion
|
+
|
H(+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Note, where more than one E.C. class is given (as above), each may
correspond to a different protein domain or, in the case of polyprotein
precursors, to a different mature protein.
|
|
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A
114:E1815
(2017)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Structural basis of jasmonate-amido synthetase FIN219 in complex with glutathione S-transferase FIP1 during the JA signal regulation.
|
|
C.Y.Chen,
S.S.Ho,
T.Y.Kuo,
H.L.Hsieh,
Y.S.Cheng.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
Far-red (FR) light-coupled jasmonate (JA) signaling is necessary for plant
defense and development. FR insensitive 219 (FIN219) is a member of the Gretchen
Hagen 3 (GH3) family of proteins in Arabidopsis and belongs to the
adenylate-forming family of enzymes. It directly controls biosynthesis of
jasmonoyl-isoleucine in JA-mediated defense responses and interacts with
FIN219-interacting protein 1 (FIP1) under FR light conditions. FIN219 and FIP1
are involved in FR light signaling and are regulators of the interplay between
light and JA signaling. However, how their interactions affect plant
physiological functions remains unclear. Here, we demonstrate the crystal
structures of FIN219-FIP1 while binding with substrates at atomic resolution.
Our results show an unexpected FIN219 conformation and demonstrate various
differences between this protein and other members of the GH3 family. We show
that the rotated C-terminal domain of FIN219 alters ATP binding and the core
structure of the active site. We further demonstrate that this unique
FIN219-FIP1 structure is crucial for increasing FIN219 activity and determines
the priority of substrate binding. We suggest that the increased FIN219 activity
resulting from the complex form, a conformation for domain switching, allows
FIN219 to switch to its high-affinity mode and thereby enhances JA signaling
under continuous FR light conditions.

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|

