 |
PDBsum entry 3d04

|

|

|
|
 |
Contents |
 |
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
* Residue conservation analysis
|
|
|

|
|
PDB id:
|
 |
|
 |
| Name: |
 |
Lyase
|
 |
|
Title:
|
 |
Crystal structure of (3r)-hydroxyacyl-acyl carrier protein dehydratase (fabz) from helicobacter pylori in complex with sakuranetin
|
|
Structure:
|
 |
(3r)-hydroxymyristoyl-acyl carrier protein dehydratase. Chain: a, b, c, d, e, f. Engineered: yes
|
|
Source:
|
 |
Helicobacter pylori. Organism_taxid: 210. Strain: ss1. Gene: fabz. Expressed in: escherichia coli. Expression_system_taxid: 562.
|
|
Resolution:
|
 |
|
2.40Å
|
R-factor:
|
0.191
|
R-free:
|
0.212
|
|
|
Authors:
|
 |
L.Zhang,Y.Kong,D.Wu,X.Shen,H.Jiang
|
Key ref:

|
 |
L.Zhang
et al.
(2008).
Three flavonoids targeting the beta-hydroxyacyl-acyl carrier protein dehydratase from Helicobacter pylori: crystal structure characterization with enzymatic inhibition assay.
Protein Sci,
17,
1971-1978.
PubMed id:
DOI:

|
 |
|
Date:
|
 |
|
01-May-08
|
Release date:
|
09-Dec-08
|
|
|

|

|
|
PROCHECK
|

|

|
|
|
Headers
|
 |
|
|
References
|
|
|
|

|

|
|
Q5G940
(Q5G940_HELPX) -
3-hydroxyacyl-[acyl-carrier-protein] dehydratase FabZ from Helicobacter pylori
|
|

|

|
Seq:
Struc:
|
 |
 |
 |
159 a.a.
152 a.a.
|

|

|

|

|
|

|

|

|
 |
 |

|
|
Key: |
 |
PfamA domain |
 |
 |
 |
Secondary structure |
 |
 |
CATH domain |
 |
|

|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
E.C.4.2.1.59
- 3-hydroxyacyl-[acyl-carrier-protein] dehydratase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
a (3R)-hydroxyacyl-[ACP] = a (2E)-enoyl-[ACP] + H2O
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
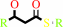 (3R)-3-hydroxyacyl-[acyl-carrier protein]
(3R)-3-hydroxyacyl-[acyl-carrier protein]
|
=
|
trans-2-enoyl-[acyl- carrier protein]
|
+
|
H(2)O
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
Protein Sci
17:1971-1978
(2008)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Three flavonoids targeting the beta-hydroxyacyl-acyl carrier protein dehydratase from Helicobacter pylori: crystal structure characterization with enzymatic inhibition assay.
|
|
L.Zhang,
Y.Kong,
D.Wu,
H.Zhang,
J.Wu,
J.Chen,
J.Ding,
L.Hu,
H.Jiang,
X.Shen.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
Flavonoids are the major functional components of many herbal and insect
preparations and demonstrate varied pharmacological functions including
antibacterial activity. Here by enzymatic assay and crystal structure analysis,
we studied the inhibition of three flavonoids (quercetin, apigenin, and
(S)-sakuranetin) against the beta-hydroxyacyl-acyl carrier protein dehydratase
from Helicobacter pylori (HpFabZ). These three flavonoids are all competitive
inhibitors against HpFabZ by either binding to the entrance of substrate tunnel
B (binding model A) or plugging into the tunnel C near the catalytic residues
(binding model B) mainly by hydrophobic interaction and hydrogen-bond pattern.
Surrounded by hydrophobic residues of HpFabZ at both positions of models A and
B, the methoxy group at C-7 of (S)-sakuranetin seems to play an important role
for the inhibitor's binding to HpFabZ, partly responsible for the higher
inhibitory activity of (S)-sakuranetin than those of quercetin and apigenin
against HpFabZ (IC(50) in microM: (S)-sakuranetin, 2.0 +/- 0.1; quercetin: 39.3
+/- 2.7; apigenin, 11.0 +/- 2.5). Our work is expected to supply useful
information for understanding the potential antibacterial mechanism of
flavonoids.

|

|
|
|

|
| |
Selected figure(s)
|
|

|
| |
 |
 |

|
 |

|
 |
Figure 2.
Stereoview of the omit electron density maps contoured at 1.0
[sigma] around quercetin (A,B), apigenin (C,D), and
(S)-sakuranetin (E,F). Quercetin, apigenin, and (S)-sakuranetin
are shown as sticks and colored in wheat, yellow, and olive,
respectively. Monomers A, B, C, and D are colored in green,
cyan, magenta, and orange, respectively. The pictures were
generated using the program PyMOL (DeLano Scientific).
|
 |
Figure 3.
The interaction between HpFabZ and inhibitors. (A,B) Binding
positions of quercetin (salmon), apigenin (yellow), and
(S)-sakuranetin (purple-blue) around the tunnel entrance (model
A) or near the catalytic residues (model B) are shown. In model
A, the inhibitors bind to the entrance of tunnel B linearly
through hydrophobic interactions and are stacked between
residues Tyr100 and Pro112[prime prime or minute]. In model B,
inhibitors embed into tunnel C near the catalytic residues and
are located in the hydrophobic pocket. The electrostatic surface
of the active tunnel is rendered by a color ramp from red to
blue. (C --H) Quercetin colored in wheat (C,D), apigenin colored
in yellow (E,F), and (S)-sakuranetin colored in olive (G,H)
interact with surrounding residues and water molecules in
HpFabZ. Hydrogen bonds are shown as black dashes. Residues are
labeled and colored in green, cyan, magenta, and orange for
monomers A, B, C, and D, respectively.
|
 |
|
|

|
| |
The above figures are
reprinted
from an Open Access publication published by the Protein Society:
Protein Sci
(2008,
17,
1971-1978)
copyright 2008.
|
|
| |
Figures were
selected
by an automated process.
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Literature references that cite this PDB file's key reference
|
|
 |
| |
PubMed id
|
 |
Reference
|
 |
|
|
|
 |
J.Chen,
L.Zhang,
Y.Zhang,
H.Zhang,
J.Du,
J.Ding,
Y.Guo,
H.Jiang,
and
X.Shen
(2009).
Emodin targets the beta-hydroxyacyl-acyl carrier protein dehydratase from Helicobacter pylori: enzymatic inhibition assay with crystal structural and thermodynamic characterization.
|
| |
BMC Microbiol,
9,
91.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
|
The most recent references are shown first.
Citation data come partly from CiteXplore and partly
from an automated harvesting procedure. Note that this is likely to be
only a partial list as not all journals are covered by
either method. However, we are continually building up the citation data
so more and more references will be included with time.
Where a reference describes a PDB structure, the PDB
code is
shown on the right.
|
 |

