 |
PDBsum entry 1vkh

|

|

|
|
 |
Contents |
 |
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
* Residue conservation analysis
|
|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
E.C.3.5.1.9
- arylformamidase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

Pathway:
|
 |
Tryptophan Catabolism
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
N-formyl-L-kynurenine + H2O = L-kynurenine + formate + H+
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
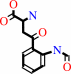 N-formyl-L-kynurenine
N-formyl-L-kynurenine
|
+
|
H2O
|
=
|
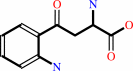 L-kynurenine
L-kynurenine
|
+
|
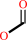 formate
formate
|
+
|
H(+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
Proteins
58:755-758
(2005)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Crystal structure of an alpha/beta serine hydrolase (YDR428C) from Saccharomyces cerevisiae at 1.85 A resolution.
|
|
J.W.Arndt,
R.Schwarzenbacher,
R.Page,
P.Abdubek,
E.Ambing,
T.Biorac,
J.M.Canaves,
H.J.Chiu,
X.Dai,
A.M.Deacon,
M.DiDonato,
M.A.Elsliger,
A.Godzik,
C.Grittini,
S.K.Grzechnik,
J.Hale,
E.Hampton,
G.W.Han,
J.Haugen,
M.Hornsby,
H.E.Klock,
E.Koesema,
A.Kreusch,
P.Kuhn,
L.Jaroszewski,
S.A.Lesley,
I.Levin,
D.McMullan,
T.M.McPhillips,
M.D.Miller,
A.Morse,
K.Moy,
E.Nigoghossian,
J.Ouyang,
W.S.Peti,
K.Quijano,
R.Reyes,
E.Sims,
G.Spraggon,
R.C.Stevens,
H.van den Bedem,
J.Velasquez,
J.Vincent,
F.von Delft,
X.Wang,
B.West,
A.White,
G.Wolf,
Q.Xu,
O.Zagnitko,
K.O.Hodgson,
J.Wooley,
I.A.Wilson.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |
|
|

|
| |
Selected figure(s)
|
|

|
| |
 |
 |

|
 |

|
 |
Figure 1.
Figure 1. Crystal structure of YDR428C. A: Stereoview of ribbon
diagram of Saccharomyces cerevisiae YDR428C color coded from
N-terminus (blue) to C-terminus (red) showing the domain
organization.  -Helices
H1-H12, and -Helices
H1-H12, and  -strands
( -strands
(  1- 1-
 7)
are indicated. B: Diagram showing the secondary structure
elements in YDR428C superimposed on its primary sequence. The 7)
are indicated. B: Diagram showing the secondary structure
elements in YDR428C superimposed on its primary sequence. The
 -helices,
3[10]-helices, -helices,
3[10]-helices,  -sheet
strands (red A), -sheet
strands (red A),  -bulges,
and -bulges,
and  -turns
are indicated. The disordered regions are depicted by a dashed
line with the corresponding sequence in brackets. -turns
are indicated. The disordered regions are depicted by a dashed
line with the corresponding sequence in brackets.
|
 |
Figure 2.
Figure 2. A: Ribbon diagram of a superposition of YDR428C
(blue) and P. fluorescens carboxylesterase (grey). Residues of
the catalytic triad, shown in ball and stick, indicate the
active site location. B: Same as A, but a close up view of the
catalytic triad. Active site residues as observed in P.
fluorescens carboxylesterase (PDB 1auo; grey; P. fluorescens
residues shown in parenthesis) and their counterparts in YDR428C
(blue) are shown in ball and stick. Hydrogen bond interactions
and distances are indicated. C: Ribbon diagram of the YDR428C
dimer.  7
strands and helices H10 and H12 forming part of the dimer
interface and locations of active sites (arrow) are indicated. 7
strands and helices H10 and H12 forming part of the dimer
interface and locations of active sites (arrow) are indicated.
|
 |
|
|

|
| |
The above figures are
reprinted
by permission from John Wiley & Sons, Inc.:
Proteins
(2005,
58,
755-758)
copyright 2005.
|
|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Literature references that cite this PDB file's key reference
|
|
 |
| |
PubMed id
|
 |
Reference
|
 |
|
|
|
 |
C.Y.Yang,
K.H.Chin,
C.C.Chou,
A.H.Wang,
and
S.H.Chou
(2006).
Structure of XC6422 from Xanthomonas campestris at 1.6 A resolution: a small serine alpha/beta-hydrolase.
|
| |
Acta Crystallogr Sect F Struct Biol Cryst Commun,
62,
498-503.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
|
The most recent references are shown first.
Citation data come partly from CiteXplore and partly
from an automated harvesting procedure. Note that this is likely to be
only a partial list as not all journals are covered by
either method. However, we are continually building up the citation data
so more and more references will be included with time.
Where a reference describes a PDB structure, the PDB
code is
shown on the right.
|
 |

