 |
PDBsum entry 1vdr

|
|
|

|
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
 |

|

|

|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
Oxidoreductase
|
PDB id
|
|

|

|
1vdr
|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
 |
Contents |
 |
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
* Residue conservation analysis
|
|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
E.C.1.5.1.3
- dihydrofolate reductase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

Pathway:
|
 |
Folate Coenzymes
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
(6S)-5,6,7,8-tetrahydrofolate + NADP+ = 7,8-dihydrofolate + NADPH + H+
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
(6S)-5,6,7,8-tetrahydrofolate
|
+
|
 NADP(+)
NADP(+)
|
=
|
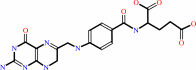 7,8-dihydrofolate
7,8-dihydrofolate
|
+
|
 NADPH
NADPH
|
+
|
H(+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
Structure
6:75-88
(1998)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Structural features of halophilicity derived from the crystal structure of dihydrofolate reductase from the Dead Sea halophilic archaeon, Haloferax volcanii.
|
|
U.Pieper,
G.Kapadia,
M.Mevarech,
O.Herzberg.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
BACKGROUND: The proteins of halophilic archaea require high salt concentrations
both for stability and for activity, whereas they denature at low ionic
strength. The structural basis for this phenomenon is not yet well understood.
The crystal structure of dihydrofolate reductase (DHFR) from Haloferax volcanii
(hv-DHFR) reported here provides the third example of a structure of a protein
from a halophilic organism. The enzyme is considered moderately halophilic, as
it retains activity and secondary structure at monovalent salt concentrations as
low as 0.5 M. RESULTS: The crystal structure of hv-DHFR has been determined at
2.6 A resolution and reveals the same overall fold as that of other DHFRs. The
structure is in the apo state, with an open conformation of the active-site
gully different from the open conformation seen in other DHFR structures. The
unique feature of hv-DHFR is a shift of the alpha helix encompassing residues
46-51 and an accompanied altered conformation of the ensuing loop relative to
other DHFRs. Analysis of the charge distribution, amino acid composition,
packing and hydrogen-bonding pattern in hv-DHFR and its non-halophilic homologs
has been performed. CONCLUSIONS: The moderately halophilic behavior of hv-DHFR
is consistent with the lack of striking structural features expected to occur in
extremely halophilic proteins. The most notable feature of halophilicity is the
presence of clusters of non-interacting negatively charged residues. Such
clusters are associated with unfavorable electrostatic energy at low salt
concentrations, and may account for the instability of hv-DHFR at salt
concentrations lower than 0.5 M. With respect to catalysis, the open
conformation seen here is indicative of a conformational transition not reported
previously. The impact of this conformation on function and/or halophilicity is
unknown.

|

|
|
|

|
| |
Selected figure(s)
|
|

|
| |
 |
 |

|
 |

|
 |
Figure 3.
Figure 3. Superposition of the Cα trace of hv-DHFR (solid
line), ec-DHFR in the closed conformation (long dashes; PDB
entry code 1rx9) and ec-DHFR in the occluded conformation (short
dashes; PDB entry code 1rx5). Every tenth residue of hv-DHFR is
labeled.
|
 |
Figure 6.
Figure 6. Stereo representation of two clusters of negatively
charged residues in hv-DHFR. Water molecules are depicted as
black spheres and hydrogen bonds as dashed lines. (a)
Intramolecular cluster; (b) intermolecular cluster at the
interface of three molecules.
|
 |
|
|

|
| |
The above figures are
reprinted
by permission from Cell Press:
Structure
(1998,
6,
75-88)
copyright 1998.
|
|
| |
Figures were
selected
by an automated process.
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Literature references that cite this PDB file's key reference
|
|
 |
| |
PubMed id
|
 |
Reference
|
 |
|
|
|
 |
F.Liu,
J.Xiong,
S.Kumar,
C.Yang,
S.Ge,
S.Li,
N.Xia,
and
K.Swaminathan
(2011).
Structural and biophysical characterization of Mycobacterium tuberculosis dodecin Rv1498A.
|
| |
J Struct Biol,
175,
31-38.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
A.F.Boroujerdi,
and
J.K.Young
(2009).
NMR-derived folate-bound structure of dihydrofolate reductase 1 from the halophile Haloferax volcanii.
|
| |
Biopolymers,
91,
140-144.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
J.A.Winter,
P.Christofi,
S.Morroll,
and
K.A.Bunting
(2009).
The crystal structure of Haloferax volcanii proliferating cell nuclear antigen reveals unique surface charge characteristics due to halophilic adaptation.
|
| |
BMC Struct Biol,
9,
55.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
J.Domenech,
P.J.Baker,
S.E.Sedelnikova,
H.F.Rodgers,
D.W.Rice,
and
J.Ferrer
(2009).
Crystallization and preliminary X-ray analysis of D-2-hydroxyacid dehydrogenase from Haloferax mediterranei.
|
| |
Acta Crystallogr Sect F Struct Biol Cryst Commun,
65,
415-418.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
L.Malki,
M.Yanku,
I.Borovok,
G.Cohen,
M.Mevarech,
and
Y.Aharonowitz
(2009).
Identification and characterization of gshA, a gene encoding the glutamate-cysteine ligase in the halophilic archaeon Haloferax volcanii.
|
| |
J Bacteriol,
191,
5196-5204.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
S.Hay,
R.M.Evans,
C.Levy,
E.J.Loveridge,
X.Wang,
D.Leys,
R.K.Allemann,
and
N.S.Scrutton
(2009).
Are the catalytic properties of enzymes from piezophilic organisms pressure adapted?
|
| |
Chembiochem,
10,
2348-2353.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
X.Tadeo,
B.López-Méndez,
T.Trigueros,
A.Laín,
D.Castaño,
and
O.Millet
(2009).
Structural basis for the aminoacid composition of proteins from halophilic archea.
|
| |
PLoS Biol,
7,
e1000257.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
Y.Cao,
L.Liao,
X.W.Xu,
A.Oren,
C.Wang,
X.F.Zhu,
and
M.Wu
(2008).
Characterization of alcohol dehydrogenase from the haloalkaliphilic archaeon Natronomonas pharaonis.
|
| |
Extremophiles,
12,
471-476.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
B.Binbuga,
A.F.Boroujerdi,
and
J.K.Young
(2007).
Structure in an extreme environment: NMR at high salt.
|
| |
Protein Sci,
16,
1783-1787.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
L.Redecke,
M.A.Brehm,
and
R.Bredehorst
(2007).
Cloning and characterization of dihydrofolate reductase from a facultative alkaliphilic and halotolerant bacillus strain.
|
| |
Extremophiles,
11,
75-83.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
D.Madern,
M.Camacho,
A.Rodríguez-Arnedo,
M.J.Bonete,
and
G.Zaccai
(2004).
Salt-dependent studies of NADP-dependent isocitrate dehydrogenase from the halophilic archaeon Haloferax volcanii.
|
| |
Extremophiles,
8,
377-384.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
J.Yuvaniyama,
P.Chitnumsub,
S.Kamchonwongpaisan,
J.Vanichtanankul,
W.Sirawaraporn,
P.Taylor,
M.D.Walkinshaw,
and
Y.Yuthavong
(2003).
Insights into antifolate resistance from malarial DHFR-TS structures.
|
| |
Nat Struct Biol,
10,
357-365.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
P.Chantawannakul,
K.Yoshimune,
Y.Shirakihara,
A.Shiratori,
M.Wakayama,
and
M.Moriguchi
(2003).
Crystallization and preliminary X-ray crystallographic studies of salt-tolerant glutaminase from Micrococcus luteus K-3.
|
| |
Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr,
59,
566-568.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
B.Franzetti,
G.Schoehn,
D.Garcia,
R.W.Ruigrok,
and
G.Zaccai
(2002).
Characterization of the proteasome from the extremely halophilic archaeon Haloarcula marismortui.
|
| |
Archaea,
1,
53-61.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
A.K.Bandyopadhyay,
G.Krishnamoorthy,
and
H.M.Sonawat
(2001).
Structural stabilization of [2Fe-2S] ferredoxin from Halobacterium salinarum.
|
| |
Biochemistry,
40,
1284-1292.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
R.J.Read
(2001).
Pushing the boundaries of molecular replacement with maximum likelihood.
|
| |
Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr,
57,
1373-1382.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
A.K.Bandyopadhyay,
and
H.M.Sonawat
(2000).
Salt dependent stability and unfolding of [Fe2-S2] ferredoxin of Halobacterium salinarum: spectroscopic investigations.
|
| |
Biophys J,
79,
501-510.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
K.Yoshimatsu,
T.Sakurai,
and
T.Fujiwara
(2000).
Purification and characterization of dissimilatory nitrate reductase from a denitrifying halophilic archaeon, Haloarcula marismortui.
|
| |
FEBS Lett,
470,
216-220.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
R.Ortenberg,
O.Rozenblatt-Rosen,
and
M.Mevarech
(2000).
The extremely halophilic archaeon Haloferax volcanii has two very different dihydrofolate reductases.
|
| |
Mol Microbiol,
35,
1493-1505.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
S.B.Richard,
D.Madern,
E.Garcin,
and
G.Zaccai
(2000).
Halophilic adaptation: novel solvent protein interactions observed in the 2.9 and 2.6 A resolution structures of the wild type and a mutant of malate dehydrogenase from Haloarcula marismortui.
|
| |
Biochemistry,
39,
992.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
Y.H.Kao,
C.A.Fitch,
S.Bhattacharya,
C.J.Sarkisian,
J.T.Lecomte,
and
B.García-Moreno E
(2000).
Salt effects on ionization equilibria of histidines in myoglobin.
|
| |
Biophys J,
79,
1637-1654.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
C.Ebel,
P.Faou,
B.Kernel,
and
G.Zaccai
(1999).
Relative role of anions and cations in the stabilization of halophilic malate dehydrogenase.
|
| |
Biochemistry,
38,
9039-9047.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
C.Wanner,
and
J.Soppa
(1999).
Genetic identification of three ABC transporters as essential elements for nitrate respiration in Haloferax volcanii.
|
| |
Genetics,
152,
1417-1428.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
M.T.Madigan,
and
A.Oren
(1999).
Thermophilic and halophilic extremophiles.
|
| |
Curr Opin Microbiol,
2,
265-269.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
W.Grabarse,
M.Vaupel,
J.A.Vorholt,
S.Shima,
R.K.Thauer,
A.Wittershagen,
G.Bourenkov,
H.D.Bartunik,
and
U.Ermler
(1999).
The crystal structure of methenyltetrahydromethanopterin cyclohydrolase from the hyperthermophilic archaeon Methanopyrus kandleri.
|
| |
Structure,
7,
1257-1268.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
R.Jaenicke,
and
G.Böhm
(1998).
The stability of proteins in extreme environments.
|
| |
Curr Opin Struct Biol,
8,
738-748.
|
 |
|
 |
 |
|
The most recent references are shown first.
Citation data come partly from CiteXplore and partly
from an automated harvesting procedure. Note that this is likely to be
only a partial list as not all journals are covered by
either method. However, we are continually building up the citation data
so more and more references will be included with time.
Where a reference describes a PDB structure, the PDB
code is
shown on the right.
|
 |

