
|

|

|
|
 |
Contents |
 |
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
* Residue conservation analysis
|
|
|

|
|
PDB id:
|
 |
|
 |
| Name: |
 |
Transcription activator/inhibitor
|
 |
|
Title:
|
 |
Factor inhibiting hif-1 alpha in complex with hif-1 alpha fragment peptide
|
|
Structure:
|
 |
Factor inhibiting hif1. Chain: a. Engineered: yes. Hypoxia-inducible factor 1 alpha. Chain: s. Fragment: c-terminal transactivation domain fragment, residues 786- 826. Synonym: hif-1 alpha, arnt interacting protein, member of pas protein 1.
|
|
Source:
|
 |
Homo sapiens. Human. Organism_taxid: 9606. Expressed in: escherichia coli. Expression_system_taxid: 469008.
|
|
Biol. unit:
|
 |
 Tetramer (from PDB file)
Tetramer (from PDB file)
|
|
Resolution:
|
 |
|
2.15Å
|
R-factor:
|
0.180
|
R-free:
|
0.213
|
|
|
Authors:
|
 |
J.M.Elkins,K.S.Hewitson,L.A.Mcneill,I.Schlemminger,J.F.Seibel, C.J.Schofield
|
Key ref:

|
 |
J.M.Elkins
et al.
(2003).
Structure of factor-inhibiting hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF) reveals mechanism of oxidative modification of HIF-1 alpha.
J Biol Chem,
278,
1802-1806.
PubMed id:
DOI:

|
 |
|
Date:
|
 |
|
12-Aug-02
|
Release date:
|
28-Nov-02
|
|
|

|

|
|
PROCHECK
|

|

|
|
|
Headers
|
 |
|
|
References
|
|
|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class 1:
|
 |
Chain A:
E.C.1.14.11.30
- hypoxia-inducible factor-asparagine dioxygenase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
L-asparaginyl-[hypoxia-inducible factor alpha subunit] + 2-oxoglutarate + O2 = (3S)-3-hydroxy-L-asparaginyl-[hypoxia-inducible factor alpha subunit] + succinate + CO2
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
L-asparaginyl-[hypoxia-inducible factor alpha subunit]
|
+
|
 2-oxoglutarate
2-oxoglutarate
|
+
|
 O2
O2
|
=
|
(3S)-3-hydroxy-L-asparaginyl-[hypoxia-inducible factor alpha subunit]
|
+
|
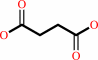 succinate
succinate
|
+
|
 CO2
CO2
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Cofactor:
|
 |
Fe(2+); L-ascorbate
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Fe(2+)
|
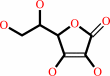 L-ascorbate
L-ascorbate
|
|
 |
 |
Enzyme class 2:
|
 |
Chain A:
E.C.1.14.11.n4
- ?????
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class 3:
|
 |
Chain S:
E.C.?
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Note, where more than one E.C. class is given (as above), each may
correspond to a different protein domain or, in the case of polyprotein
precursors, to a different mature protein.
|
|
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
J Biol Chem
278:1802-1806
(2003)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Structure of factor-inhibiting hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF) reveals mechanism of oxidative modification of HIF-1 alpha.
|
|
J.M.Elkins,
K.S.Hewitson,
L.A.McNeill,
J.F.Seibel,
I.Schlemminger,
C.W.Pugh,
P.J.Ratcliffe,
C.J.Schofield.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
The activity of the transcription factor hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF) is
regulated by oxygen-dependent hydroxylation. Under normoxic conditions,
hydroxylation of proline residues triggers destruction of its alpha-subunit
while hydroxylation of Asn(803) in the C-terminal transactivation domain of
HIF-1 alpha (CAD) prevents its interaction with p300. Here we report crystal
structures of the asparagine hydroxylase (factor-inhibiting HIF, FIH) complexed
with Fe((II)), 2-oxoglutarate cosubstrate, and CAD fragments, which reveal the
structural basis of HIF modification. CAD binding to FIH occurs via an induced
fit process at two distinct interaction sites. At the hydroxylation site CAD
adopts a loop conformation, contrasting with a helical conformation for the same
residues when bound to p300. Asn(803) of CAD is buried and precisely orientated
in the active site such that hydroxylation occurs at its beta-carbon. Together
with structures with the inhibitors Zn((II)) and N-oxaloylglycine, analysis of
the FIH-CAD complexes will assist design of hydroxylase inhibitors with
proangiogenic properties. Conserved structural motifs within FIH imply it is one
of an extended family of Fe((II)) oxygenases involved in gene regulation.

|

|
|
|

|
| |
Selected figure(s)
|
|

|
| |
 |
 |

|
 |

|
 |
Figure 1.
Fig. 1. The FIH-CAD complex (a-c, structure 1; d,
structure 2). a, FIH monomer. The CAD peptide is shown as a
ball-and-stick representation in red and the DSBH motif in
green. b, FIH dimer. The two molecules of FIH are in dark and
light blue, the DSBH motif is in green, and the CAD peptide is
in red. c, the 2OG binding site with bound NOG is shown in
yellow. The Fe^(II) is colored pink, and the 2mF[o]  DF[c]
electron density map is contoured at 1.5 DF[c]
electron density map is contoured at 1.5  . d,
orientation of CAD Asn803 at the FIH active site. The 2OG and
CAD peptide are shown in yellow. . d,
orientation of CAD Asn803 at the FIH active site. The 2OG and
CAD peptide are shown in yellow.
|
 |
Figure 2.
Fig. 2. FIH-CAD interactions. a, CAD fragments are shown
as stick models in yellow above a van der Waals surface of FIH.
FIH residues beneath the surface are colored green. Dotted red
lines represent electrostatic bonds. b, alternative view of site
1. Note Asn803 is deeply buried. c, electron density for the
bound CAD peptide (structure 1). CAD residues 795-806 (site 1,
left) and 812-823 (site 2, right) are shown as ball-and-stick
representations in yellow. The difference electron density,
contoured at 2.2  (left) and
1.5 (left) and
1.5  (right),
was calculated after random model perturbation and refinement
with CAD omitted to remove model bias. (right),
was calculated after random model perturbation and refinement
with CAD omitted to remove model bias.
|
 |
|
|

|
| |
The above figures are
reprinted
by permission from the ASBMB:
J Biol Chem
(2003,
278,
1802-1806)
copyright 2003.
|
|
| |
Figures were
selected
by an automated process.
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Literature references that cite this PDB file's key reference
|
|
 |
| |
PubMed id
|
 |
Reference
|
 |
|
|
|
 |
J.Cassavaugh,
and
K.M.Lounsbury
(2011).
Hypoxia-mediated biological control.
|
| |
J Cell Biochem,
112,
735-744.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
M.Kato,
Y.Araiso,
A.Noma,
A.Nagao,
T.Suzuki,
R.Ishitani,
and
O.Nureki
(2011).
Crystal structure of a novel JmjC-domain-containing protein, TYW5, involved in tRNA modification.
|
| |
Nucleic Acids Res,
39,
1576-1585.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
M.N.Khan,
T.Bhattacharyya,
P.Andrikopoulos,
M.A.Esteban,
R.Barod,
T.Connor,
M.Ashcroft,
P.H.Maxwell,
and
S.Kiriakidis
(2011).
Factor inhibiting HIF (FIH-1) promotes renal cancer cell survival by protecting cells from HIF-1α-mediated apoptosis.
|
| |
Br J Cancer,
104,
1151-1159.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
M.Yang,
R.Chowdhury,
W.Ge,
R.B.Hamed,
M.A.McDonough,
T.D.Claridge,
B.M.Kessler,
M.E.Cockman,
P.J.Ratcliffe,
and
C.J.Schofield
(2011).
Factor-inhibiting hypoxia-inducible factor (FIH) catalyses the post-translational hydroxylation of histidinyl residues within ankyrin repeat domains.
|
| |
FEBS J,
278,
1086-1097.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
M.Yang,
W.Ge,
R.Chowdhury,
T.D.Claridge,
H.B.Kramer,
B.Schmierer,
M.A.McDonough,
L.Gong,
B.M.Kessler,
P.J.Ratcliffe,
M.L.Coleman,
and
C.J.Schofield
(2011).
Asparagine and Aspartate Hydroxylation of the Cytoskeletal Ankyrin Family Is Catalyzed by Factor-inhibiting Hypoxia-inducible Factor.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
286,
7648-7660.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
R.Chowdhury,
K.K.Yeoh,
Y.M.Tian,
L.Hillringhaus,
E.A.Bagg,
N.R.Rose,
I.K.Leung,
X.S.Li,
E.C.Woon,
M.Yang,
M.A.McDonough,
O.N.King,
I.J.Clifton,
R.J.Klose,
T.D.Claridge,
P.J.Ratcliffe,
C.J.Schofield,
and
A.Kawamura
(2011).
The oncometabolite 2-hydroxyglutarate inhibits histone lysine demethylases.
|
| |
EMBO Rep,
12,
463-469.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
Y.Xia,
Y.Jin,
N.Kaur,
Y.Choi,
and
K.Lee
(2011).
HIF-1α inhibitors: synthesis and biological evaluation of novel moracin O and P analogues.
|
| |
Eur J Med Chem,
46,
2386-2396.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
Z.Geng,
J.Zhu,
J.Cao,
J.Geng,
X.Song,
Z.Zhang,
N.Bian,
and
Z.Wang
(2011).
Effects of polynitrogen compounds on the activity of recombinant human HIF-1α prolyl hydroxylase 3 in E. coli.
|
| |
J Inorg Biochem,
105,
391-399.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
D.R.Mole
(2010).
Iron homeostasis and its interaction with prolyl hydroxylases.
|
| |
Antioxid Redox Signal,
12,
445-458.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
H.Moon,
S.Han,
H.Park,
and
J.Choe
(2010).
Crystal structures of human FIH-1 in complex with quinol family inhibitors.
|
| |
Mol Cells,
29,
471-474.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
H.S.Kim,
H.L.Kim,
K.H.Kim,
d.o. .J.Kim,
S.J.Lee,
J.Y.Yoon,
H.J.Yoon,
H.Y.Lee,
S.B.Park,
S.J.Kim,
J.Y.Lee,
and
S.W.Suh
(2010).
Crystal structure of Tpa1 from Saccharomyces cerevisiae, a component of the messenger ribonucleoprotein complex.
|
| |
Nucleic Acids Res,
38,
2099-2110.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
K.L.Gorres,
and
R.T.Raines
(2010).
Prolyl 4-hydroxylase.
|
| |
Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol,
45,
106-124.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
L.Yu,
Y.Wang,
S.Huang,
J.Wang,
Z.Deng,
Q.Zhang,
W.Wu,
X.Zhang,
Z.Liu,
W.Gong,
and
Z.Chen
(2010).
Structural insights into a novel histone demethylase PHF8.
|
| |
Cell Res,
20,
166-173.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
S.Nagel,
N.P.Talbot,
J.Mecinović,
T.G.Smith,
A.M.Buchan,
and
C.J.Schofield
(2010).
Therapeutic manipulation of the HIF hydroxylases.
|
| |
Antioxid Redox Signal,
12,
481-501.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
X.Hong,
J.Zang,
J.White,
C.Wang,
C.H.Pan,
R.Zhao,
R.C.Murphy,
S.Dai,
P.Henson,
J.W.Kappler,
J.Hagman,
and
G.Zhang
(2010).
Interaction of JMJD6 with single-stranded RNA.
|
| |
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A,
107,
14568-14572.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
A.D.Gultice,
K.Kulkarni-Datar,
and
T.L.Brown
(2009).
Hypoxia-inducible factor 1alpha (HIF1A) mediates distinct steps of rat trophoblast differentiation in gradient oxygen.
|
| |
Biol Reprod,
80,
184-193.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
B.Muz,
M.N.Khan,
S.Kiriakidis,
and
E.M.Paleolog
(2009).
The role of hypoxia and HIF-dependent signalling events in rheumatoid arthritis.
|
| |
Arthritis Res Ther,
11,
201.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
L.Kelly,
M.A.McDonough,
M.L.Coleman,
P.J.Ratcliffe,
and
C.J.Schofield
(2009).
Asparagine beta-hydroxylation stabilizes the ankyrin repeat domain fold.
|
| |
Mol Biosyst,
5,
52-58.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
M.E.Cockman,
J.D.Webb,
and
P.J.Ratcliffe
(2009).
FIH-dependent asparaginyl hydroxylation of ankyrin repeat domain-containing proteins.
|
| |
Ann N Y Acad Sci,
1177,
9.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
M.F.Muñoz-Guerra,
M.E.Fernández-Contreras,
A.L.Moreno,
I.D.Martín,
B.Herráez,
and
C.Gamallo
(2009).
Polymorphisms in the hypoxia inducible factor 1-alpha and the impact on the prognosis of early stages of oral cancer.
|
| |
Ann Surg Oncol,
16,
2351-2358.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
M.K.Koski,
R.Hieta,
M.Hirsilä,
A.Rönkä,
J.Myllyharju,
and
R.K.Wierenga
(2009).
The crystal structure of an algal prolyl 4-hydroxylase complexed with a proline-rich peptide reveals a novel buried tripeptide binding motif.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
284,
25290-25301.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
M.Okamoto,
M.Van Stry,
L.Chung,
M.Koyanagi,
X.Sun,
Y.Suzuki,
O.Ohara,
H.Kitamura,
A.Hijikata,
M.Kubo,
and
M.Bix
(2009).
Mina, an Il4 repressor, controls T helper type 2 bias.
|
| |
Nat Immunol,
10,
872-879.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
R.Chowdhury,
M.A.McDonough,
J.Mecinović,
C.Loenarz,
E.Flashman,
K.S.Hewitson,
C.Domene,
and
C.J.Schofield
(2009).
Structural basis for binding of hypoxia-inducible factor to the oxygen-sensing prolyl hydroxylases.
|
| |
Structure,
17,
981-989.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
S.Lakhal,
N.P.Talbot,
A.Crosby,
C.Stoepker,
A.R.Townsend,
P.A.Robbins,
C.W.Pugh,
P.J.Ratcliffe,
and
D.R.Mole
(2009).
Regulation of growth differentiation factor 15 expression by intracellular iron.
|
| |
Blood,
113,
1555-1563.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
D.R.Mole,
and
P.J.Ratcliffe
(2008).
Cellular oxygen sensing in health and disease.
|
| |
Pediatr Nephrol,
23,
681-694.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
F.S.Lee
(2008).
Genetic causes of erythrocytosis and the oxygen-sensing pathway.
|
| |
Blood Rev,
22,
321-332.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
J.M.Simmons,
T.A.Müller,
and
R.P.Hausinger
(2008).
Fe(II)/alpha-ketoglutarate hydroxylases involved in nucleobase, nucleoside, nucleotide, and chromatin metabolism.
|
| |
Dalton Trans,
(),
5132-5142.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
K.Lisy,
and
D.J.Peet
(2008).
Turn me on: regulating HIF transcriptional activity.
|
| |
Cell Death Differ,
15,
642-649.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
P.Hahn,
J.Böse,
S.Edler,
and
A.Lengeling
(2008).
Genomic structure and expression of Jmjd6 and evolutionary analysis in the context of related JmjC domain containing proteins.
|
| |
BMC Genomics,
9,
293.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
R.Chowdhury,
A.Hardy,
and
C.J.Schofield
(2008).
The human oxygen sensing machinery and its manipulation.
|
| |
Chem Soc Rev,
37,
1308-1319.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
T.G.Smith,
G.M.Balanos,
Q.P.Croft,
N.P.Talbot,
K.L.Dorrington,
P.J.Ratcliffe,
and
P.A.Robbins
(2008).
The increase in pulmonary arterial pressure caused by hypoxia depends on iron status.
|
| |
J Physiol,
586,
5999-6005.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
Y.H.Chen,
L.M.Comeaux,
R.W.Herbst,
E.Saban,
D.C.Kennedy,
M.J.Maroney,
and
M.J.Knapp
(2008).
Coordination changes and auto-hydroxylation of FIH-1: uncoupled O2-activation in a human hypoxia sensor.
|
| |
J Inorg Biochem,
102,
2120-2129.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
Y.H.Chen,
L.M.Comeaux,
S.J.Eyles,
and
M.J.Knapp
(2008).
Auto-hydroxylation of FIH-1: an Fe(ii), alpha-ketoglutarate-dependent human hypoxia sensor.
|
| |
Chem Commun (Camb),
(),
4768-4770.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
A.Ozer,
and
R.K.Bruick
(2007).
Non-heme dioxygenases: cellular sensors and regulators jelly rolled into one?
|
| |
Nat Chem Biol,
3,
144-153.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
A.Siddiq,
L.R.Aminova,
and
R.R.Ratan
(2007).
Hypoxia inducible factor prolyl 4-hydroxylase enzymes: center stage in the battle against hypoxia, metabolic compromise and oxidative stress.
|
| |
Neurochem Res,
32,
931-946.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
A.Wolf,
C.Schmitz,
and
A.Böttger
(2007).
Changing story of the receptor for phosphatidylserine-dependent clearance of apoptotic cells.
|
| |
EMBO Rep,
8,
465-469.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
B.Chang,
Y.Chen,
Y.Zhao,
and
R.K.Bruick
(2007).
JMJD6 is a histone arginine demethylase.
|
| |
Science,
318,
444-447.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
J.E.Ferguson,
Y.Wu,
K.Smith,
P.Charles,
K.Powers,
H.Wang,
and
C.Patterson
(2007).
ASB4 is a hydroxylation substrate of FIH and promotes vascular differentiation via an oxygen-dependent mechanism.
|
| |
Mol Cell Biol,
27,
6407-6419.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
J.Li,
E.Wang,
S.Dutta,
J.S.Lau,
S.W.Jiang,
K.Datta,
and
D.Mukhopadhyay
(2007).
Protein kinase C-mediated modulation of FIH-1 expression by the homeodomain protein CDP/Cut/Cux.
|
| |
Mol Cell Biol,
27,
7345-7353.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
M.L.Neidig,
C.D.Brown,
K.M.Light,
D.G.Fujimori,
E.M.Nolan,
J.C.Price,
E.W.Barr,
J.M.Bollinger,
C.Krebs,
C.T.Walsh,
and
E.I.Solomon
(2007).
CD and MCD of CytC3 and taurine dioxygenase: role of the facial triad in alpha-KG-dependent oxygenases.
|
| |
J Am Chem Soc,
129,
14224-14231.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
Q.Yan,
S.Bartz,
M.Mao,
L.Li,
and
W.G.Kaelin
(2007).
The hypoxia-inducible factor 2alpha N-terminal and C-terminal transactivation domains cooperate to promote renal tumorigenesis in vivo.
|
| |
Mol Cell Biol,
27,
2092-2102.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
S.S.Ng,
K.L.Kavanagh,
M.A.McDonough,
D.Butler,
E.S.Pilka,
B.M.Lienard,
J.E.Bray,
P.Savitsky,
O.Gileadi,
F.von Delft,
N.R.Rose,
J.Offer,
J.C.Scheinost,
T.Borowski,
M.Sundstrom,
C.J.Schofield,
and
U.Oppermann
(2007).
Crystal structures of histone demethylase JMJD2A reveal basis for substrate specificity.
|
| |
Nature,
448,
87-91.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
V.Purpero,
and
G.R.Moran
(2007).
The diverse and pervasive chemistries of the alpha-keto acid dependent enzymes.
|
| |
J Biol Inorg Chem,
12,
587-601.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
X.Cheng,
and
X.Zhang
(2007).
Structural dynamics of protein lysine methylation and demethylation.
|
| |
Mutat Res,
618,
102-115.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
Z.Chen,
J.Zang,
J.Kappler,
X.Hong,
F.Crawford,
Q.Wang,
F.Lan,
C.Jiang,
J.Whetstine,
S.Dai,
K.Hansen,
Y.Shi,
and
G.Zhang
(2007).
Structural basis of the recognition of a methylated histone tail by JMJD2A.
|
| |
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A,
104,
10818-10823.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
C.Hebert,
K.Norris,
P.Parashar,
R.A.Ord,
N.G.Nikitakis,
and
J.J.Sauk
(2006).
Hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha polymorphisms and TSC1/2 mutations are complementary in head and neck cancers.
|
| |
Mol Cancer,
5,
3.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
D.G.Nagle,
and
Y.D.Zhou
(2006).
Natural product-derived small molecule activators of hypoxia-inducible factor-1 (HIF-1).
|
| |
Curr Pharm Des,
12,
2673-2688.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
H.Skarpos,
D.V.Vorob'eva,
S.N.Osipov,
I.L.Odinets,
E.Breuer,
and
G.V.Röschenthaler
(2006).
Methyltrifluoropyruvate imines possessing N-oxalyl and N-phosphonoformyl groups--precursors to a variety of alpha-CF3-alpha-amino acid derivatives.
|
| |
Org Biomol Chem,
4,
3669-3674.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
K.Hirota,
and
G.L.Semenza
(2006).
Regulation of angiogenesis by hypoxia-inducible factor 1.
|
| |
Crit Rev Oncol Hematol,
59,
15-26.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
K.Yamane,
C.Toumazou,
Y.Tsukada,
H.Erdjument-Bromage,
P.Tempst,
J.Wong,
and
Y.Zhang
(2006).
JHDM2A, a JmjC-containing H3K9 demethylase, facilitates transcription activation by androgen receptor.
|
| |
Cell,
125,
483-495.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
M.A.McDonough,
V.Li,
E.Flashman,
R.Chowdhury,
C.Mohr,
B.M.Liénard,
J.Zondlo,
N.J.Oldham,
I.J.Clifton,
J.Lewis,
L.A.McNeill,
R.J.Kurzeja,
K.S.Hewitson,
E.Yang,
S.Jordan,
R.S.Syed,
and
C.J.Schofield
(2006).
Cellular oxygen sensing: Crystal structure of hypoxia-inducible factor prolyl hydroxylase (PHD2).
|
| |
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A,
103,
9814-9819.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
M.J.Percy,
Q.Zhao,
A.Flores,
C.Harrison,
T.R.Lappin,
P.H.Maxwell,
M.F.McMullin,
and
F.S.Lee
(2006).
A family with erythrocytosis establishes a role for prolyl hydroxylase domain protein 2 in oxygen homeostasis.
|
| |
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A,
103,
654-659.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
P.A.Cloos,
J.Christensen,
K.Agger,
A.Maiolica,
J.Rappsilber,
T.Antal,
K.H.Hansen,
and
K.Helin
(2006).
The putative oncogene GASC1 demethylates tri- and dimethylated lysine 9 on histone H3.
|
| |
Nature,
442,
307-311.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
R.J.Klose,
E.M.Kallin,
and
Y.Zhang
(2006).
JmjC-domain-containing proteins and histone demethylation.
|
| |
Nat Rev Genet,
7,
715-727.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
T.A.Müller,
M.I.Zavodszky,
M.Feig,
L.A.Kuhn,
and
R.P.Hausinger
(2006).
Structural basis for the enantiospecificities of R- and S-specific phenoxypropionate/alpha-ketoglutarate dioxygenases.
|
| |
Protein Sci,
15,
1356-1368.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
T.L.Davidson,
H.Chen,
D.M.Di Toro,
G.D'Angelo,
and
M.Costa
(2006).
Soluble nickel inhibits HIF-prolyl-hydroxylases creating persistent hypoxic signaling in A549 cells.
|
| |
Mol Carcinog,
45,
479-489.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
T.Takeuchi,
Y.Watanabe,
T.Takano-Shimizu,
and
S.Kondo
(2006).
Roles of jumonji and jumonji family genes in chromatin regulation and development.
|
| |
Dev Dyn,
235,
2449-2459.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
Y.Tsukada,
J.Fang,
H.Erdjument-Bromage,
M.E.Warren,
C.H.Borchers,
P.Tempst,
and
Y.Zhang
(2006).
Histone demethylation by a family of JmjC domain-containing proteins.
|
| |
Nature,
439,
811-816.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
Z.Chen,
J.Zang,
J.Whetstine,
X.Hong,
F.Davrazou,
T.G.Kutateladze,
M.Simpson,
Q.Mao,
C.H.Pan,
S.Dai,
J.Hagman,
K.Hansen,
Y.Shi,
and
G.Zhang
(2006).
Structural insights into histone demethylation by JMJD2 family members.
|
| |
Cell,
125,
691-702.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
B.Banerji,
A.Conejo-Garcia,
L.A.McNeill,
M.A.McDonough,
M.R.Buck,
K.S.Hewitson,
N.J.Oldham,
and
C.J.Schofield
(2005).
The inhibition of factor inhibiting hypoxia-inducible factor (FIH) by beta-oxocarboxylic acids.
|
| |
Chem Commun (Camb),
(),
5438-5440.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
H.J.Dyson,
and
P.E.Wright
(2005).
Intrinsically unstructured proteins and their functions.
|
| |
Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol,
6,
197-208.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
K.K.To,
and
L.E.Huang
(2005).
Suppression of hypoxia-inducible factor 1alpha (HIF-1alpha) transcriptional activity by the HIF prolyl hydroxylase EGLN1.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
280,
38102-38107.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
M.L.Neidig,
and
E.I.Solomon
(2005).
Structure-function correlations in oxygen activating non-heme iron enzymes.
|
| |
Chem Commun (Camb),
(),
5843-5863.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
S.C.Trewick,
P.J.McLaughlin,
and
R.C.Allshire
(2005).
Methylation: lost in hydroxylation?
|
| |
EMBO Rep,
6,
315-320.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
S.Rohrbach,
A.Simm,
R.Pregla,
C.Franke,
and
D.M.Katschinski
(2005).
Age-dependent increase of prolyl-4-hydroxylase domain (PHD) 3 expression in human and mouse heart.
|
| |
Biogerontology,
6,
165-171.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
V.N.Uversky,
C.J.Oldfield,
and
A.K.Dunker
(2005).
Showing your ID: intrinsic disorder as an ID for recognition, regulation and cell signaling.
|
| |
J Mol Recognit,
18,
343-384.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
W.G.Kaelin
(2005).
Proline hydroxylation and gene expression.
|
| |
Annu Rev Biochem,
74,
115-128.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
C.J.Schofield,
and
P.J.Ratcliffe
(2004).
Oxygen sensing by HIF hydroxylases.
|
| |
Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol,
5,
343-354.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
E.Metzen,
and
P.J.Ratcliffe
(2004).
HIF hydroxylation and cellular oxygen sensing.
|
| |
Biol Chem,
385,
223-230.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
F.R.Sharp,
and
M.Bernaudin
(2004).
HIF1 and oxygen sensing in the brain.
|
| |
Nat Rev Neurosci,
5,
437-448.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
F.R.Sharp,
R.Ran,
A.Lu,
Y.Tang,
K.I.Strauss,
T.Glass,
T.Ardizzone,
and
M.Bernaudin
(2004).
Hypoxic preconditioning protects against ischemic brain injury.
|
| |
NeuroRx,
1,
26-35.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
K.S.Hewitson,
and
C.J.Schofield
(2004).
The HIF pathway as a therapeutic target.
|
| |
Drug Discov Today,
9,
704-711.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
K.Valegård,
A.C.Terwisscha van Scheltinga,
A.Dubus,
G.Ranghino,
L.M.Oster,
J.Hajdu,
and
I.Andersson
(2004).
The structural basis of cephalosporin formation in a mononuclear ferrous enzyme.
|
| |
Nat Struct Mol Biol,
11,
95.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
R.Bicknell,
and
A.L.Harris
(2004).
Novel angiogenic signaling pathways and vascular targets.
|
| |
Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol,
44,
219-238.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
U.Berchner-Pfannschmidt,
C.Wotzlaw,
E.Merten,
H.Acker,
and
J.Fandrey
(2004).
Visualization of the three-dimensional organization of hypoxia-inducible factor-1 alpha and interacting cofactors in subnuclear structures.
|
| |
Biol Chem,
385,
231-237.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
Z.Zhang,
J.S.Ren,
I.J.Clifton,
and
C.J.Schofield
(2004).
Crystal structure and mechanistic implications of 1-aminocyclopropane-1-carboxylic acid oxidase--the ethylene-forming enzyme.
|
| |
Chem Biol,
11,
1383-1394.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
S.Bhattacharya,
and
P.J.Ratcliffe
(2003).
ExCITED about HIF.
|
| |
Nat Struct Biol,
10,
501-503.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
S.J.Freedman,
Z.Y.Sun,
A.L.Kung,
D.S.France,
G.Wagner,
and
M.J.Eck
(2003).
Structural basis for negative regulation of hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha by CITED2.
|
| |
Nat Struct Biol,
10,
504-512.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
|
The most recent references are shown first.
Citation data come partly from CiteXplore and partly
from an automated harvesting procedure. Note that this is likely to be
only a partial list as not all journals are covered by
either method. However, we are continually building up the citation data
so more and more references will be included with time.
Where a reference describes a PDB structure, the PDB
codes are
shown on the right.
|
 |

