
|

|

|
|
 |
Contents |
 |
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
* Residue conservation analysis
|
|
|

|
|
PDB id:
|
 |
|
 |
| Name: |
 |
Metal binding protein
|
 |
|
Title:
|
 |
The complex structure of jmjd2a and trimethylated h3k36 peptide
|
|
Structure:
|
 |
Jmjc domain-containing histone demethylation protein 3a. Chain: a, b. Fragment: catalytic core. Synonym: jumonji domain-containing protein 2a. Engineered: yes. Histone h3. Chain: i, j. Engineered: yes
|
|
Source:
|
 |
Homo sapiens. Human. Organism_taxid: 9606. Gene: jmjd2a, jhdm3a, jmjd2, kiaa0677. Expressed in: escherichia coli. Expression_system_taxid: 562. Synthetic: yes
|
|
Resolution:
|
 |
|
1.99Å
|
R-factor:
|
0.238
|
R-free:
|
0.263
|
|
|
Authors:
|
 |
G.Zhang,Z.Chen,J.Zang,X.Hong,Y.Shi
|
Key ref:

|
 |
Z.Chen
et al.
(2007).
Structural basis of the recognition of a methylated histone tail by JMJD2A.
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A,
104,
10818-10823.
PubMed id:
DOI:

|
 |
|
Date:
|
 |
|
14-Mar-07
|
Release date:
|
12-Jun-07
|
|
|

|

|
|
PROCHECK
|

|

|
|
|
Headers
|
 |
|
|
References
|
|
|
|

|

|
|
O75164
(KDM4A_HUMAN) -
Lysine-specific demethylase 4A from Homo sapiens
|
|

|

|
Seq:
Struc:
|
 |
 |
 |
1064 a.a.
347 a.a.
|

|

|

|

|
|

|

|

|
 |
 |

|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class 2:
|
 |
Chains A, B:
E.C.1.14.11.66
- [histone H3]-trimethyl-L-lysine(9) demethylase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
N6,N6,N6-trimethyl-L-lysyl9-[histone H3] + 2 2-oxoglutarate + 2 O2 = N6-methyl-L-lysyl9-[histone H3] + 2 formaldehyde + 2 succinate + 2 CO2
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
N(6),N(6),N(6)-trimethyl-L-lysyl(9)-[histone H3]
|
+
|
 2
×
2-oxoglutarate
2
×
2-oxoglutarate
|
+
|
2
×
O2
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
corresponds exactly
|
=
|
N(6)-methyl-L-lysyl(9)-[histone H3]
|
+
|
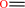 2
×
formaldehyde
2
×
formaldehyde
|
+
|
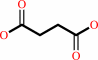 2
×
succinate
2
×
succinate
|
+
|
 2
×
CO2
2
×
CO2
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class 3:
|
 |
Chains A, B:
E.C.1.14.11.69
- [histone H3]-trimethyl-L-lysine(36) demethylase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
N6,N6,N6-trimethyl-L-lysyl36-[histone H3] + 2 2-oxoglutarate + 2 O2 = N6-methyl-L-lysyl36-[histone H3] + 2 formaldehyde + 2 succinate + 2 CO2
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
N(6),N(6),N(6)-trimethyl-L-lysyl(36)-[histone H3]
|
+
|
 2
×
2-oxoglutarate
2
×
2-oxoglutarate
|
+
|
2
×
O2
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
corresponds exactly
|
=
|
N(6)-methyl-L-lysyl(36)-[histone H3]
|
+
|
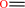 2
×
formaldehyde
2
×
formaldehyde
|
+
|
 2
×
succinate
2
×
succinate
|
+
|
 2
×
CO2
2
×
CO2
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Note, where more than one E.C. class is given (as above), each may
correspond to a different protein domain or, in the case of polyprotein
precursors, to a different mature protein.
|
|
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A
104:10818-10823
(2007)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Structural basis of the recognition of a methylated histone tail by JMJD2A.
|
|
Z.Chen,
J.Zang,
J.Kappler,
X.Hong,
F.Crawford,
Q.Wang,
F.Lan,
C.Jiang,
J.Whetstine,
S.Dai,
K.Hansen,
Y.Shi,
G.Zhang.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
The Jumonji C domain is a catalytic motif that mediates histone lysine
demethylation. The Jumonji C-containing oxygenase JMJD2A specifically
demethylates tri- and dimethylated lysine-9 and lysine-36 of histone 3 (H3K9/36
me3/2). Here we present structures of the JMJD2A catalytic core complexed with
methylated H3K36 peptide substrates in the presence of Fe(II) and
N-oxalylglycine. We found that the interaction between JMJD2A and peptides
largely involves the main chains of the enzyme and the peptide. The
peptide-binding specificity is primarily determined by the primary structure of
the peptide, which explains the specificity of JMJD2A for methylated H3K9 and
H3K36 instead of other methylated residues such as H3K27. The specificity for a
particular methyl group, however, is affected by multiple factors, such as space
and the electrostatic environment in the catalytic center of the enzyme. These
results provide insights into the mechanisms and specificity of histone
demethylation.

|

|
|
|

|
| |
Selected figure(s)
|
|

|
| |
 |
 |

|
 |

|
 |
Figure 1.
Fig. 1. The overall complex structure of c-JMJD2A with the
H3K36me3 peptide in the presence of NOG (orange), Fe(II) (pink),
and Zn (purple). (A) c-JMJD2A is shown as a ribbon model with
the Jumonji N domain (green), the long  hairpin (purple), the
mixed structural motif (gray), the Jumonji C domain (light
blue), the C-terminal domain (pink), and the methylated H3K36
peptide (yellow). Seventeen of the 22 residues (residues 27–43
from histone 3) of the methylated peptide are ordered in the
structure (molecule A). (B) A stick and ball model of the
peptide on the surface of c-JMJD2A colored according to the
electrostatic potential of the residues (red and blue represent
negatively and positively charged areas, respectively). All
structural figures were made by using the PyMOL program
(http://pymol.sourceforge.net). hairpin (purple), the
mixed structural motif (gray), the Jumonji C domain (light
blue), the C-terminal domain (pink), and the methylated H3K36
peptide (yellow). Seventeen of the 22 residues (residues 27–43
from histone 3) of the methylated peptide are ordered in the
structure (molecule A). (B) A stick and ball model of the
peptide on the surface of c-JMJD2A colored according to the
electrostatic potential of the residues (red and blue represent
negatively and positively charged areas, respectively). All
structural figures were made by using the PyMOL program
(http://pymol.sourceforge.net).
|
 |
Figure 2.
Fig. 2. The detailed interaction between c-JMJD2A and the
methylated peptides. (A) A schematic view of all of the
potential interactions between c-JMJD2A and the H3K36 peptide,
including 10 hydrogen bonds and one salt bridge. (B) Mutagenesis
data and activity assays. Residues Q86, N88, D135, and Y175 are
involved in the interaction with the peptide, whereas residues
Y177, N290, S288, and T289 are involved in methyl group binding.
K241 is proposed to recruit the O[2] molecule into the catalytic
center. (C) Characterization of the binding between the H3K36
peptide and c-JMJD2A. (D) Characterization of the binding
between of the H3K9 peptide and c-JMJD2A. Neither of the binding
curves is linear, suggesting that the peptides assume multiple
conformations.
|
 |
|
|
| |
Figures were
selected
by an automated process.
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Literature references that cite this PDB file's key reference
|
|
 |
| |
PubMed id
|
 |
Reference
|
 |
|
|
|
 |
A.K.Upadhyay,
and
X.Cheng
(2011).
Dynamics of histone lysine methylation: structures of methyl writers and erasers.
|
| |
Prog Drug Res,
67,
107-124.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
M.Ozboyaci,
A.Gursoy,
B.Erman,
and
O.Keskin
(2011).
Molecular recognition of H3/H4 histone tails by the tudor domains of JMJD2A: a comparative molecular dynamics simulations study.
|
| |
PLoS One,
6,
e14765.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
R.A.Varier,
and
H.T.Timmers
(2011).
Histone lysine methylation and demethylation pathways in cancer.
|
| |
Biochim Biophys Acta,
1815,
75-89.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
S.Krishnan,
S.Horowitz,
and
R.C.Trievel
(2011).
Structure and function of histone H3 lysine 9 methyltransferases and demethylases.
|
| |
Chembiochem,
12,
254-263.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
C.Huang,
Y.Xiang,
Y.Wang,
X.Li,
L.Xu,
Z.Zhu,
T.Zhang,
Q.Zhu,
K.Zhang,
N.Jing,
and
C.D.Chen
(2010).
Dual-specificity histone demethylase KIAA1718 (KDM7A) regulates neural differentiation through FGF4.
|
| |
Cell Res,
20,
154-165.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
J.R.Horton,
A.K.Upadhyay,
H.H.Qi,
X.Zhang,
Y.Shi,
and
X.Cheng
(2010).
Enzymatic and structural insights for substrate specificity of a family of jumonji histone lysine demethylases.
|
| |
Nat Struct Mol Biol,
17,
38-43.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
L.Yu,
Y.Wang,
S.Huang,
J.Wang,
Z.Deng,
Q.Zhang,
W.Wu,
X.Zhang,
Z.Liu,
W.Gong,
and
Z.Chen
(2010).
Structural insights into a novel histone demethylase PHF8.
|
| |
Cell Res,
20,
166-173.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
M.L.Bellows,
and
C.A.Floudas
(2010).
Computational methods for de novo protein design and its applications to the human immunodeficiency virus 1, purine nucleoside phosphorylase, ubiquitin specific protease 7, and histone demethylases.
|
| |
Curr Drug Targets,
11,
264-278.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
N.Mosammaparast,
and
Y.Shi
(2010).
Reversal of histone methylation: biochemical and molecular mechanisms of histone demethylases.
|
| |
Annu Rev Biochem,
79,
155-179.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
X.Cheng,
and
R.M.Blumenthal
(2010).
Coordinated chromatin control: structural and functional linkage of DNA and histone methylation.
|
| |
Biochemistry,
49,
2999-3008.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
X.Hong,
J.Zang,
J.White,
C.Wang,
C.H.Pan,
R.Zhao,
R.C.Murphy,
S.Dai,
P.Henson,
J.W.Kappler,
J.Hagman,
and
G.Zhang
(2010).
Interaction of JMJD6 with single-stranded RNA.
|
| |
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A,
107,
14568-14572.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
Y.Chang,
J.Wu,
X.J.Tong,
J.Q.Zhou,
and
J.Ding
(2010).
Crystal structure of the catalytic core of Saccharomyces cerevesiae histone demethylase Rph1: insights into the substrate specificity and catalytic mechanism.
|
| |
Biochem J,
433,
295-302.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
Y.Yang,
L.Hu,
P.Wang,
H.Hou,
Y.Lin,
Y.Liu,
Z.Li,
R.Gong,
X.Feng,
L.Zhou,
W.Zhang,
Y.Dong,
H.Yang,
H.Lin,
Y.Wang,
C.D.Chen,
and
Y.Xu
(2010).
Structural insights into a dual-specificity histone demethylase ceKDM7A from Caenorhabditis elegans.
|
| |
Cell Res,
20,
886-898.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
B.C.Smith,
and
J.M.Denu
(2009).
Chemical mechanisms of histone lysine and arginine modifications.
|
| |
Biochim Biophys Acta,
1789,
45-57.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
S.S.Ng,
W.W.Yue,
U.Oppermann,
and
R.J.Klose
(2009).
Dynamic protein methylation in chromatin biology.
|
| |
Cell Mol Life Sci,
66,
407-422.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
C.Loenarz,
and
C.J.Schofield
(2008).
Expanding chemical biology of 2-oxoglutarate oxygenases.
|
| |
Nat Chem Biol,
4,
152-156.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
J.Lee,
J.R.Thompson,
M.V.Botuyan,
and
G.Mer
(2008).
Distinct binding modes specify the recognition of methylated histones H3K4 and H4K20 by JMJD2A-tudor.
|
| |
Nat Struct Mol Biol,
15,
109-111.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
J.M.Simmons,
T.A.Müller,
and
R.P.Hausinger
(2008).
Fe(II)/alpha-ketoglutarate hydroxylases involved in nucleobase, nucleoside, nucleotide, and chromatin metabolism.
|
| |
Dalton Trans,
(),
5132-5142.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
M.Lloret-Llinares,
C.Carré,
A.Vaquero,
N.de Olano,
and
F.Azorín
(2008).
Characterization of Drosophila melanogaster JmjC+N histone demethylases.
|
| |
Nucleic Acids Res,
36,
2852-2863.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
P.A.Cloos,
J.Christensen,
K.Agger,
and
K.Helin
(2008).
Erasing the methyl mark: histone demethylases at the center of cellular differentiation and disease.
|
| |
Genes Dev,
22,
1115-1140.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
G.Kustatscher,
and
A.G.Ladurner
(2007).
Modular paths to 'decoding' and 'wiping' histone lysine methylation.
|
| |
Curr Opin Chem Biol,
11,
628-635.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
J.C.Culhane,
and
P.A.Cole
(2007).
LSD1 and the chemistry of histone demethylation.
|
| |
Curr Opin Chem Biol,
11,
561-568.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
J.R.Wilson
(2007).
Targeting the JMJD2A histone lysine demethylase.
|
| |
Nat Struct Mol Biol,
14,
682-684.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
S.Lall
(2007).
Primers on chromatin.
|
| |
Nat Struct Mol Biol,
14,
1110-1115.
|
 |
|
 |
 |
|
The most recent references are shown first.
Citation data come partly from CiteXplore and partly
from an automated harvesting procedure. Note that this is likely to be
only a partial list as not all journals are covered by
either method. However, we are continually building up the citation data
so more and more references will be included with time.
Where a reference describes a PDB structure, the PDB
codes are
shown on the right.
|
 |
|

