 |
PDBsum entry 1f3b

|

|

|
|
 |
Contents |
 |
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
* Residue conservation analysis
|
|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class 2:
|
 |
E.C.1.11.1.-
- ?????
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class 3:
|
 |
E.C.2.5.1.18
- glutathione transferase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
RX + glutathione = an S-substituted glutathione + a halide anion + H+
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
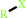 RX
RX
|
+
|
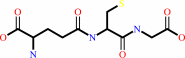 glutathione
glutathione
|
=
|
S-substituted glutathione
|
+
|
halide anion
|
+
|
H(+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class 4:
|
 |
E.C.5.3.3.-
- ?????
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Note, where more than one E.C. class is given (as above), each may
correspond to a different protein domain or, in the case of polyprotein
precursors, to a different mature protein.
|
|
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
Biochemistry
39:12552-12557
(2000)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Residue R216 and catalytic efficiency of a murine class alpha glutathione S-transferase toward benzo[a]pyrene 7(R),8(S)-diol 9(S), 10(R)-epoxide.
|
|
Y.Gu,
S.V.Singh,
X.Ji.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
Murine class alpha glutathione S-transferase A1-1 (mGSTA1-1), unlike mammalian
class alpha GSTs, is the most efficient in the glutathione (GSH) conjugation of
the ultimate carcinogenic metabolite of benzo[a]pyrene,
(+)-anti-7,8-dihydroxy-9,10-oxy-7,8,9, 10-tetrahydrobenzo[a]pyrene
[(+)-anti-BPDE] [Hu, X., Srivastava, S. K., Xia, H., Awasthi, Y. C., and Singh,
S. V. (1996) J. Biol. Chem. 271, 32684-32688]. Here, we report the crystal
structures of mGSTA1-1 in complex with GSH and with the GSH conjugate of
(+)-anti-BPDE (GSBpd) at 1.9 and 2.0 A resolution, respectively. Both crystals
belong to monoclinic space group C2 with one dimer in the asymmetric unit. The
structures reveal that, within one subunit, the GSH moiety interacts with
residues Y8, R14, K44, Q53, V54, Q66, and T67, whereas the hydrophobic moiety of
GSBpd interacts with the side chains of F9, R14, M207, A215, R216, F219, and
I221. In addition, the GSH moiety interacts with D100 and R130 from the other
subunit across the dimer interface. The structural comparison between
mGSTA1-1.GSH and mGSTA1-1.GSBpd reveals significant conformational differences.
The movement of helix alpha9 brings the residues on the helix into direct
interaction with the product. Most noticeable are the positional displacement
and conformational change of R216, one of the residues located in helix alpha9.
The side chain of R216, which points away from the H-site in the mGSTA1-1.GSH
complex, probes into the active site and becomes parallel with the aromatic ring
system of GSBpd. Moreover, the guanidinium group of R216 shifts approximately 8
A and forms a strong hydrogen bond with the C8 hydroxyl group of GSBpd,
suggesting that the electrostatic assistance provided by the guanidinium group
facilitates the ring-opening reaction of (+)-anti-BPDE. The structure of
mGSTA1-1. GSBpd is also compared with those of hGSTP1-1[V104,A113].GSBpd,
hGSPA1-1.S-benzylglutathione, and mGSTA4-4.
4-S-glutathionyl-5-pentyltetrahydrofuran-2-ol. The comparison provides further
evidence that supports the functional roles of R216 and helix alpha9. The lack
of mobility of helix alpha9 and/or the lack of electrostatic assistance from
R216 may be responsible for the relatively lower activity of hGSTA1-1, mGSTA4-4,
and hGSTP1-1 toward (+)-anti-BPDE.

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Literature references that cite this PDB file's key reference
|
|
 |
| |
PubMed id
|
 |
Reference
|
 |
|
|
|
 |
A.Oakley
(2011).
Glutathione transferases: a structural perspective.
|
| |
Drug Metab Rev,
43,
138-151.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
E.Grahn,
M.Novotny,
E.Jakobsson,
A.Gustafsson,
L.Grehn,
B.Olin,
D.Madsen,
M.Wahlberg,
B.Mannervik,
and
G.J.Kleywegt
(2006).
New crystal structures of human glutathione transferase A1-1 shed light on glutathione binding and the conformation of the C-terminal helix.
|
| |
Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr,
62,
197-207.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
Y.M.Koen,
W.Yue,
N.A.Galeva,
T.D.Williams,
and
R.P.Hanzlik
(2006).
Site-specific arylation of rat glutathione s-transferase A1 and A2 by bromobenzene metabolites in vivo.
|
| |
Chem Res Toxicol,
19,
1426-1434.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
S.Mosebi,
Y.Sayed,
J.Burke,
and
H.W.Dirr
(2003).
Residue 219 impacts on the dynamics of the C-terminal region in glutathione transferase A1-1: implications for stability and catalytic and ligandin functions.
|
| |
Biochemistry,
42,
15326-15332.
|
 |
|
 |
 |
|
The most recent references are shown first.
Citation data come partly from CiteXplore and partly
from an automated harvesting procedure. Note that this is likely to be
only a partial list as not all journals are covered by
either method. However, we are continually building up the citation data
so more and more references will be included with time.
Where a reference describes a PDB structure, the PDB
codes are
shown on the right.
|
 |

