 |
PDBsum entry 1b7b

|

|

|
|
 |
Contents |
 |
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
* Residue conservation analysis
|
|
|

|
|
PDB id:
|
 |
|
 |
| Name: |
 |
Transferase
|
 |
|
Title:
|
 |
Carbamate kinase from enterococcus faecalis
|
|
Structure:
|
 |
Carbamate kinase. Chain: a, b, c, d. Other_details: complexed with sulphate anion
|
|
Source:
|
 |
Enterococcus faecium. Organism_taxid: 1352. Strain: d10. Cellular_location: cytoplasm. Plasmid: pck41
|
|
Biol. unit:
|
 |
 Dimer (from
)
Dimer (from
)
|
|
Resolution:
|
 |
|
2.80Å
|
R-factor:
|
0.224
|
R-free:
|
0.283
|
|
|
Authors:
|
 |
A.Marina,P.M.Alzari,J.Bravo,M.Uriarte,B.Barcelona,I.Fita,V.Rubio
|
|
Key ref:
|
 |
A.Marina
et al.
(1999).
Carbamate kinase: New structural machinery for making carbamoyl phosphate, the common precursor of pyrimidines and arginine.
Protein Sci,
8,
934-940.
PubMed id:
DOI:
|
 |
|
Date:
|
 |
|
20-Jan-99
|
Release date:
|
26-Jan-00
|
|
|

|

|
|
PROCHECK
|

|

|
|
|
Headers
|
 |
|
|
References
|
|
|
|

|

|
|
P0A2X8
(ARCC1_ENTFC) -
Carbamate kinase 1 from Enterococcus faecium
|
|

|

|
Seq:
Struc:
|
 |
 |
 |
310 a.a.
307 a.a.
|

|

|

|

|
|

|

|

|
 |
 |

|
|
Key: |
 |
PfamA domain |
 |
 |
 |
Secondary structure |
 |
 |
CATH domain |
 |
|

|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
E.C.2.7.2.2
- carbamate kinase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

Pathway:
|
 |
AMP Catabolism
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
hydrogencarbonate + NH4+ + ATP = carbamoyl phosphate + ADP + H2O + H+
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 hydrogencarbonate
hydrogencarbonate
|
+
|
NH4(+)
|
+
|
 ATP
ATP
|
=
|
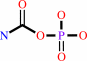 carbamoyl phosphate
carbamoyl phosphate
|
+
|
 ADP
ADP
|
+
|
H2O
|
+
|
H(+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
Protein Sci
8:934-940
(1999)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Carbamate kinase: New structural machinery for making carbamoyl phosphate, the common precursor of pyrimidines and arginine.
|
|
A.Marina,
P.M.Alzari,
J.Bravo,
M.Uriarte,
B.Barcelona,
I.Fita,
V.Rubio.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
The enzymes carbamoyl phosphate synthetase (CPS) and carbamate kinase (CK) make
carbamoyl phosphate in the same way: by ATP-phosphorylation of carbamate. The
carbamate used by CK is made chemically, whereas CPS itself synthesizes its own
carbamate in a process involving the phosphorylation of bicarbonate. Bicarbonate
and carbamate are analogs and the phosphorylations are carried out by homologous
40 kDa regions of the 120 kDa CPS polypeptide. CK can also phosphorylate
bicarbonate and is a homodimer of a 33 kDa subunit that was believed to resemble
the 40 kDa regions of CPS. Such belief is disproven now by the CK structure
reported here. The structure does not conform to the biotin carboxylase fold
found in the 40 kDa regions of CPS, and presents a new type of fold possibly
shared by homologous acylphosphate-making enzymes. A molecular 16-stranded open
beta-sheet surrounded by alpha-helices is the hallmark of the CK dimer. Each
subunit also contains two smaller sheets and a large crevice found at the
location expected for the active center. Intersubunit interactions are very
large and involve a central hydrophobic patch and more hydrophilic peripheral
contacts. The crevice holds a sulfate that may occupy the site of an ATP
phosphate, and is lined by conserved residues. Site-directed mutations tested at
two of these residues inactivate the enzyme. These findings support active site
location in the crevice. The orientation of the crevices in the dimer precludes
their physical cooperation in the catalytic process. Such cooperation is not
needed in the CK reaction but is a requirement of the mechanism of CPSs.

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Literature references that cite this PDB file's key reference
|
|
 |
| |
PubMed id
|
 |
Reference
|
 |
|
|
|
 |
A.Galkin,
L.Kulakova,
R.Wu,
T.E.Nash,
D.Dunaway-Mariano,
and
O.Herzberg
(2010).
X-ray structure and characterization of carbamate kinase from the human parasite Giardia lamblia.
|
| |
Acta Crystallogr Sect F Struct Biol Cryst Commun,
66,
386-390.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
N.Dellas,
and
J.P.Noel
(2010).
Mutation of archaeal isopentenyl phosphate kinase highlights mechanism and guides phosphorylation of additional isoprenoid monophosphates.
|
| |
ACS Chem Biol,
5,
589-601.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
S.Pakhomova,
S.G.Bartlett,
A.Augustus,
T.Kuzuyama,
and
M.E.Newcomer
(2008).
Crystal structure of fosfomycin resistance kinase FomA from Streptomyces wedmorensis.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
283,
28518-28526.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
J.L.Llácer,
L.M.Polo,
S.Tavárez,
B.Alarcón,
R.Hilario,
and
V.Rubio
(2007).
The gene cluster for agmatine catabolism of Enterococcus faecalis: study of recombinant putrescine transcarbamylase and agmatine deiminase and a snapshot of agmatine deiminase catalyzing its reaction.
|
| |
J Bacteriol,
189,
1254-1265.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
I.Pérez-Arellano,
F.Gil-Ortiz,
J.Cervera,
and
V.Rubio
(2004).
Glutamate-5-kinase from Escherichia coli: gene cloning, overexpression, purification and crystallization of the recombinant enzyme and preliminary X-ray studies.
|
| |
Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr,
60,
2091-2094.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
C.Gagyi,
N.Bucurenci,
O.Sîrbu,
G.Labesse,
M.Ionescu,
A.Ofiteru,
L.Assairi,
S.Landais,
A.Danchin,
O.Bârzu,
and
A.M.Gilles
(2003).
UMP kinase from the Gram-positive bacterium Bacillus subtilis is strongly dependent on GTP for optimal activity.
|
| |
Eur J Biochem,
270,
3196-3204.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
B.Barcelona-Andrés,
A.Marina,
and
V.Rubio
(2002).
Gene structure, organization, expression, and potential regulatory mechanisms of arginine catabolism in Enterococcus faecalis.
|
| |
J Bacteriol,
184,
6289-6300.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
S.Ramón-Maiques,
H.G.Britton,
and
V.Rubio
(2002).
Molecular physiology of phosphoryl group transfer from carbamoyl phosphate by a hyperthermophilic enzyme at low temperature.
|
| |
Biochemistry,
41,
3916-3924.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
F.Gil,
S.Ramón-Maiques,
A.Marina,
I.Fita,
and
V.Rubio
(1999).
N-Acetyl-L-glutamate kinase from Escherichia coli: cloning of the gene, purification and crystallization of the recombinant enzyme and preliminary X-ray analysis of the free and ligand-bound forms.
|
| |
Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr,
55,
1350-1352.
|
 |
|
 |
 |
|
The most recent references are shown first.
Citation data come partly from CiteXplore and partly
from an automated harvesting procedure. Note that this is likely to be
only a partial list as not all journals are covered by
either method. However, we are continually building up the citation data
so more and more references will be included with time.
Where a reference describes a PDB structure, the PDB
code is
shown on the right.
|
 |

