 |
PDBsum entry 1ae4

|
|
|

|
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
 |

|

|

|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
Oxidoreductase
|
PDB id
|
|

|

|
1ae4
|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
 |
Contents |
 |
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
* Residue conservation analysis
|
|
* C-alpha coords only
|
|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class 1:
|
 |
E.C.1.1.1.19
- glucuronate reductase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

Pathway:
|
 |
Mammalian Ascorbic Acid Biosynthesis
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
L-gulonate + NADP+ = aldehydo-D-glucuronate + NADPH + H+
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
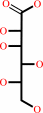 L-gulonate
L-gulonate
|
+
|
NADP(+)
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
corresponds exactly
|
=
|
aldehydo-D-glucuronate
|
+
|
 NADPH
NADPH
|
+
|
H(+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class 2:
|
 |
E.C.1.1.1.2
- alcohol dehydrogenase (NADP(+)).
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
a primary alcohol + NADP+ = an aldehyde + NADPH + H+
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
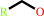 primary alcohol
primary alcohol
|
+
|
NADP(+)
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
corresponds exactly
|
=
|
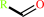 aldehyde
aldehyde
|
+
|
 NADPH
NADPH
|
+
|
H(+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Cofactor:
|
 |
Zn(2+)
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class 3:
|
 |
E.C.1.1.1.20
- glucuronolactone reductase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
L-gulono-1,4-lactone + NADP+ = D-glucurono-3,6-lactone + NADPH + H+
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
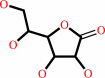 L-gulono-1,4-lactone
L-gulono-1,4-lactone
|
+
|
NADP(+)
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
corresponds exactly
|
=
|
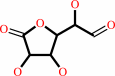 D-glucurono-3,6-lactone
D-glucurono-3,6-lactone
|
+
|
 NADPH
NADPH
|
+
|
H(+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class 4:
|
 |
E.C.1.1.1.372
- D/L-glyceraldehyde reductase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
|
1.
|
glycerol + NADP+ = L-glyceraldehyde + NADPH + H+
|
|
2.
|
glycerol + NADP+ = D-glyceraldehyde + NADPH + H+
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
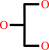 glycerol
glycerol
|
+
|
NADP(+)
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
corresponds exactly
|
=
|
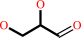 L-glyceraldehyde
L-glyceraldehyde
|
+
|
 NADPH
NADPH
|
+
|
H(+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 glycerol
glycerol
|
+
|
NADP(+)
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
corresponds exactly
|
=
|
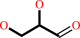 D-glyceraldehyde
D-glyceraldehyde
|
+
|
 NADPH
NADPH
|
+
|
H(+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class 5:
|
 |
E.C.1.1.1.54
- allyl-alcohol dehydrogenase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
allyl alcohol + NADP+ = acrolein + NADPH + H+
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
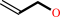 allyl alcohol
allyl alcohol
|
+
|
NADP(+)
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
corresponds exactly
|
=
|
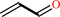 acrolein
acrolein
|
+
|
 NADPH
NADPH
|
+
|
H(+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Note, where more than one E.C. class is given (as above), each may
correspond to a different protein domain or, in the case of polyprotein
precursors, to a different mature protein.
|
|
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
|
Proteins
29:186-192
(1997)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Studies on the inhibitor-binding site of porcine aldehyde reductase: crystal structure of the holoenzyme-inhibitor ternary complex.
|
|
O.el-Kabbani,
D.A.Carper,
M.H.McGowan,
Y.Devedjiev,
K.J.Rees-Milton,
T.G.Flynn.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
Aldehyde reductase is an enzyme capable of metabolizing a wide variety of
aldehydes to their corresponding alcohols. The tertiary structures of aldehyde
reductase and aldose reductase are similar and consist of an alpha/beta-barrel
with the active site located at the carboxy terminus of the strands of the
barrel. We have determined the X-ray crystal structure of porcine aldehyde
reductase holoenzyme in complex with an aldose reductase inhibitor, tolrestat,
at 2.4 A resolution to obtain a picture of the binding conformation of
inhibitors to aldehyde reductase. Tolrestat binds in the active site pocket of
aldehyde reductase and interacts through van der Waals contacts with Arg 312 and
Asp 313. The carboxylate group of tolrestat is within hydrogen bonding distance
with His 113 and Trp 114. Mutation of Arg 312 to alanine in porcine aldehyde
reductase alters the potency of inhibition of the enzyme by aldose reductase
inhibitors. Our results indicate that the structure of the inhibitor-binding
site of aldehyde reductase differs from that of aldose reductase due to the
participation of nonconserved residues in its formation. A major difference is
the participation of Arg 312 and Asp 313 in lining the inhibitor-binding site in
aldehyde reductase but not in aldose reductase.

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Literature references that cite this PDB file's key reference
|
|
 |
| |
PubMed id
|
 |
Reference
|
 |
|
|
|
 |
E.Parisini,
P.Metrangolo,
T.Pilati,
G.Resnati,
and
G.Terraneo
(2011).
Halogen bonding in halocarbon-protein complexes: a structural survey.
|
| |
Chem Soc Rev,
40,
2267-2278.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
O.El-Kabbani,
U.Dhagat,
M.Soda,
S.Endo,
T.Matsunaga,
and
A.Hara
(2011).
Probing the inhibitor selectivity pocket of human 20α-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase (AKR1C1) with X-ray crystallography and site-directed mutagenesis.
|
| |
Bioorg Med Chem Lett,
21,
2564-2567.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
E.I.Howard,
R.Sanishvili,
R.E.Cachau,
A.Mitschler,
B.Chevrier,
P.Barth,
V.Lamour,
M.Van Zandt,
E.Sibley,
C.Bon,
D.Moras,
T.R.Schneider,
A.Joachimiak,
and
A.Podjarny
(2004).
Ultrahigh resolution drug design I: details of interactions in human aldose reductase-inhibitor complex at 0.66 A.
|
| |
Proteins,
55,
792-804.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
K.Ehrenman,
G.Yang,
W.P.Hong,
T.Gao,
W.Jang,
D.A.Brock,
R.D.Hatton,
J.D.Shoemaker,
and
R.H.Gomer
(2004).
Disruption of aldehyde reductase increases group size in dictyostelium.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
279,
837-847.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
O.El-Kabbani,
C.Darmanin,
T.R.Schneider,
I.Hazemann,
F.Ruiz,
M.Oka,
A.Joachimiak,
C.Schulze-Briese,
T.Tomizaki,
A.Mitschler,
and
A.Podjarny
(2004).
Ultrahigh resolution drug design. II. Atomic resolution structures of human aldose reductase holoenzyme complexed with Fidarestat and Minalrestat: implications for the binding of cyclic imide inhibitors.
|
| |
Proteins,
55,
805-813.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
G.Obmolova,
A.Teplyakov,
P.P.Khil,
A.J.Howard,
R.D.Camerini-Otero,
and
G.L.Gilliland
(2003).
Crystal structure of the Escherichia coli Tas protein, an NADP(H)-dependent aldo-keto reductase.
|
| |
Proteins,
53,
323-325.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
O.El-Kabbani,
P.Ramsland,
C.Darmanin,
R.P.Chung,
and
A.Podjarny
(2003).
Structure of human aldose reductase holoenzyme in complex with statil: an approach to structure-based inhibitor design of the enzyme.
|
| |
Proteins,
50,
230-238.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
Q.Ye,
D.Hyndman,
N.Green,
X.Li,
B.Korithoski,
Z.Jia,
and
T.G.Flynn
(2001).
Crystal structure of an aldehyde reductase Y50F mutant-NADP complex and its implications for substrate binding.
|
| |
Proteins,
44,
12-19.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
O.El-Kabbani,
H.Rogniaux,
P.Barth,
R.P.Chung,
E.V.Fletcher,
A.Van Dorsselaer,
and
A.Podjarny
(2000).
Aldose and aldehyde reductases: correlation of molecular modeling and mass spectrometric studies on the binding of inhibitors to the active site.
|
| |
Proteins,
41,
407-414.
|
 |
|
 |
 |
|
The most recent references are shown first.
Citation data come partly from CiteXplore and partly
from an automated harvesting procedure. Note that this is likely to be
only a partial list as not all journals are covered by
either method. However, we are continually building up the citation data
so more and more references will be included with time.
Where a reference describes a PDB structure, the PDB
code is
shown on the right.
|
 |

