 |
PDBsum entry 1l1l

|
|
|

|
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
 |

|

|

|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
Oxidoreductase
|
PDB id
|
|

|

|
1l1l
|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
 |
Contents |
 |
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
* Residue conservation analysis
|
|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
E.C.1.17.4.2
- ribonucleoside-triphosphate reductase (thioredoxin).
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
a 2'-deoxyribonucleoside 5'-triphosphate + [thioredoxin]-disulfide + H2O = a ribonucleoside 5'-triphosphate + [thioredoxin]-dithiol
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
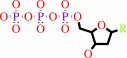 2'-deoxyribonucleoside triphosphate
2'-deoxyribonucleoside triphosphate
|
+
|
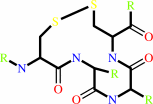 thioredoxin disulfide
thioredoxin disulfide
|
+
|
H(2)O
|
=
|
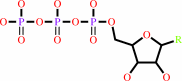 ribonucleoside triphosphate
ribonucleoside triphosphate
|
+
|
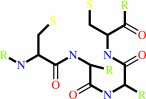 thioredoxin
thioredoxin
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Cofactor:
|
 |
Adenosylcob(III)alamin
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
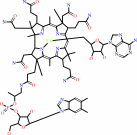 Adenosylcob(III)alamin
Adenosylcob(III)alamin
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
Nat Struct Biol
9:293-300
(2002)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
The crystal structure of class II ribonucleotide reductase reveals how an allosterically regulated monomer mimics a dimer.
|
|
M.D.Sintchak,
G.Arjara,
B.A.Kellogg,
J.Stubbe,
C.L.Drennan.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
Ribonucleotide reductases (RNRs) catalyze the conversion of ribonucleotides to
deoxyribonucleotides, an essential step in DNA biosynthesis and repair. Here we
present the crystal structure of class II (coenzyme B12-dependent)
ribonucleoside triphosphate reductase (RTPR) from Lactobacillus leichmannii in
the apo enzyme form and in complex with the B12 analog adeninylpentylcobalamin
at 1.75 and 2.0 A resolution, respectively. This monomeric, allosterically
regulated class II RNR retains all the key structural features associated with
the catalytic and regulatory machinery of oligomeric RNRs. Surprisingly, the
dimer interface responsible for effector binding in class I RNR is preserved
through a single 130-residue insertion in the class II structure. Thus, L.
leichmannii RNR is a paradigm for the simplest structural entity capable of
ribonucleotide reduction, a reaction linking the RNA and DNA worlds.

|

|
|
|

|
| |
Selected figure(s)
|
|

|
| |
 |
 |

|
 |

|
 |
Figure 1.
Figure 1. General reaction catalyzed by ribonucleotide
reductases. Each of the three well-characterized RNR classes
uses a different metallocofactor to generate the thiyl radical
(S  ).
For class II RNRs, the S ).
For class II RNRs, the S  (Cys
408 in L. leichmannii) is generated by AdoCbl carbon-cobalt (C
-Co) bond homolysis. Hydrogen atom (red) abstraction from the
substrate by the thiyl radical and the subsequent multiple step
radical rearrangements result in the loss of the 2' hydroxyl
group in the form of water. In class I and II RNRs, reducing
equivalents for the reaction are provided by the oxidation of
two Cys residues to a disulfide (Cys 119 -Cys 419 in L.
leichmannii)35. In contrast, class III RNR obtains reducing
equivalents by the oxidation of formate^36. (Cys
408 in L. leichmannii) is generated by AdoCbl carbon-cobalt (C
-Co) bond homolysis. Hydrogen atom (red) abstraction from the
substrate by the thiyl radical and the subsequent multiple step
radical rearrangements result in the loss of the 2' hydroxyl
group in the form of water. In class I and II RNRs, reducing
equivalents for the reaction are provided by the oxidation of
two Cys residues to a disulfide (Cys 119 -Cys 419 in L.
leichmannii)35. In contrast, class III RNR obtains reducing
equivalents by the oxidation of formate^36.
|
 |
Figure 4.
Figure 4. B[12] bound to RNR. a, Chemical structures of
adenosylcobalamin (AdoCbl, left panel) and
adeninylpentylcobalamin (AdPentCbl, right panel). b, Difference
(F[o] - F[c]) electron density at 2.0 Å resolution (2  contour)
for AdPentCbl bound to L. leichmannii RTPR, calculated before
the inclusion of any AdPentCbl atoms in the refinement. The
orientation of AdPentCbl in (b) is the same as in (a). Figure
prepared using Ribbons37. contour)
for AdPentCbl bound to L. leichmannii RTPR, calculated before
the inclusion of any AdPentCbl atoms in the refinement. The
orientation of AdPentCbl in (b) is the same as in (a). Figure
prepared using Ribbons37.
|
 |
|
|

|
| |
The above figures are
reprinted
by permission from Macmillan Publishers Ltd:
Nat Struct Biol
(2002,
9,
293-300)
copyright 2002.
|
|
| |
Figures were
selected
by an automated process.
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Literature references that cite this PDB file's key reference
|
|
 |
| |
PubMed id
|
 |
Reference
|
 |
|
|
|
 |
A.N.Volkov,
H.Barrios,
P.Mathonet,
C.Evrard,
M.Ubbink,
J.P.Declercq,
P.Soumillion,
and
J.Fastrez
(2011).
Engineering an Allosteric Binding Site for Aminoglycosides into TEM1-β-Lactamase.
|
| |
Chembiochem,
12,
904-913.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
D.T.Logan
(2011).
Closing the circle on ribonucleotide reductases.
|
| |
Nat Struct Mol Biol,
18,
251-253.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
J.W.Fairman,
S.R.Wijerathna,
M.F.Ahmad,
H.Xu,
R.Nakano,
S.Jha,
J.Prendergast,
R.M.Welin,
S.Flodin,
A.Roos,
P.Nordlund,
Z.Li,
T.Walz,
and
C.G.Dealwis
(2011).
Structural basis for allosteric regulation of human ribonucleotide reductase by nucleotide-induced oligomerization.
|
| |
Nat Struct Mol Biol,
18,
316-322.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
M.Högbom
(2011).
Metal use in ribonucleotide reductase R2, di-iron, di-manganese and heterodinuclear--an intricate bioinorganic workaround to use different metals for the same reaction.
|
| |
Metallomics,
3,
110-120.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
B.M.Sjöberg
(2010).
Biochemistry. A never-ending story.
|
| |
Science,
329,
1475-1476.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
D.Lundin,
S.Gribaldo,
E.Torrents,
B.M.Sjöberg,
and
A.M.Poole
(2010).
Ribonucleotide reduction - horizontal transfer of a required function spans all three domains.
|
| |
BMC Evol Biol,
10,
383.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
E.N.Marsh,
D.P.Patterson,
and
L.Li
(2010).
Adenosyl radical: reagent and catalyst in enzyme reactions.
|
| |
Chembiochem,
11,
604-621.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
G.J.Lohman,
G.J.Gerfen,
and
J.Stubbe
(2010).
Inactivation of Lactobacillus leichmannii ribonucleotide reductase by 2',2'-difluoro-2'-deoxycytidine 5'-triphosphate: adenosylcobalamin destruction and formation of a nucleotide-based radical.
|
| |
Biochemistry,
49,
1396-1403.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
V.Mathieu,
J.Fastrez,
and
P.Soumillion
(2010).
Engineering allosteric regulation into the hinge region of a circularly permuted TEM-1 beta-lactamase.
|
| |
Protein Eng Des Sel,
23,
699-709.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
F.Luttringer,
E.Mulliez,
B.Dublet,
D.Lemaire,
and
M.Fontecave
(2009).
The Zn center of the anaerobic ribonucleotide reductase from E. coli.
|
| |
J Biol Inorg Chem,
14,
923-933.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
S.W.Ragsdale
(2008).
Catalysis of methyl group transfers involving tetrahydrofolate and B(12).
|
| |
Vitam Horm,
79,
293-324.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
T.Toraya,
N.Tamura,
T.Watanabe,
M.Yamanishi,
N.Hieda,
and
K.Mori
(2008).
Mechanism-based inactivation of coenzyme B12-dependent diol dehydratase by 3-unsaturated 1,2-diols and thioglycerol.
|
| |
J Biochem,
144,
437-446.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
H.Seedorf,
C.H.Hagemeier,
S.Shima,
R.K.Thauer,
E.Warkentin,
and
U.Ermler
(2007).
Structure of coenzyme F420H2 oxidase (FprA), a di-iron flavoprotein from methanogenic Archaea catalyzing the reduction of O2 to H2O.
|
| |
FEBS J,
274,
1588-1599.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
Q.Meng,
Y.Zhang,
and
X.Q.Liu
(2007).
Rare group I intron with insertion sequence element in a bacterial ribonucleotide reductase gene.
|
| |
J Bacteriol,
189,
2150-2154.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
R.Bonneau,
M.T.Facciotti,
D.J.Reiss,
A.K.Schmid,
M.Pan,
A.Kaur,
V.Thorsson,
P.Shannon,
M.H.Johnson,
J.C.Bare,
W.Longabaugh,
M.Vuthoori,
K.Whitehead,
A.Madar,
L.Suzuki,
T.Mori,
D.E.Chang,
J.Diruggiero,
C.H.Johnson,
L.Hood,
and
N.S.Baliga
(2007).
A predictive model for transcriptional control of physiology in a free living cell.
|
| |
Cell,
131,
1354-1365.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
E.Torrents,
C.Trevisiol,
C.Rotte,
U.Hellman,
W.Martin,
and
P.Reichard
(2006).
Euglena gracilis ribonucleotide reductase: the eukaryote class II enzyme and the possible antiquity of eukaryote B12 dependence.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
281,
5604-5611.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
E.Torrents,
M.Westman,
M.Sahlin,
and
B.M.Sjöberg
(2006).
Ribonucleotide reductase modularity: Atypical duplication of the ATP-cone domain in Pseudomonas aeruginosa.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
281,
25287-25296.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
H.Xu,
C.Faber,
T.Uchiki,
J.Racca,
and
C.Dealwis
(2006).
Structures of eukaryotic ribonucleotide reductase I define gemcitabine diphosphate binding and subunit assembly.
|
| |
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A,
103,
4028-4033.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
H.Xu,
C.Faber,
T.Uchiki,
J.W.Fairman,
J.Racca,
and
C.Dealwis
(2006).
Structures of eukaryotic ribonucleotide reductase I provide insights into dNTP regulation.
|
| |
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A,
103,
4022-4027.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
K.L.Brown
(2006).
The enzymatic activation of coenzyme B12.
|
| |
Dalton Trans,
(),
1123-1133.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
L.Sun,
and
K.Warncke
(2006).
Comparative model of EutB from coenzyme B12-dependent ethanolamine ammonia-lyase reveals a beta8alpha8, TIM-barrel fold and radical catalytic site structural features.
|
| |
Proteins,
64,
308-319.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
M.Galander,
M.Uppsten,
U.Uhlin,
and
F.Lendzian
(2006).
Orientation of the tyrosyl radical in Salmonella typhimurium class Ib ribonucleotide reductase determined by high field EPR of R2F single crystals.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
281,
31743-31752.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
M.Kawata,
K.Kinoshita,
S.Takahashi,
K.Ogura,
N.Komoto,
M.Yamanishi,
T.Tobimatsu,
and
T.Toraya
(2006).
Survey of catalytic residues and essential roles of glutamate-alpha170 and aspartate-alpha335 in coenzyme B12-dependent diol dehydratase.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
281,
18327-18334.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
P.Nordlund,
and
P.Reichard
(2006).
Ribonucleotide reductases.
|
| |
Annu Rev Biochem,
75,
681-706.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
W.Buckel,
and
B.T.Golding
(2006).
Radical enzymes in anaerobes.
|
| |
Annu Rev Microbiol,
60,
27-49.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
E.Torrents,
A.Poplawski,
and
B.M.Sjöberg
(2005).
Two proteins mediate class II ribonucleotide reductase activity in Pseudomonas aeruginosa: expression and transcriptional analysis of the aerobic enzymes.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
280,
16571-16578.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
G.Guntas,
T.J.Mansell,
J.R.Kim,
and
M.Ostermeier
(2005).
Directed evolution of protein switches and their application to the creation of ligand-binding proteins.
|
| |
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A,
102,
11224-11229.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
J.He,
B.Roy,
C.Périgaud,
O.B.Kashlan,
and
B.S.Cooperman
(2005).
The enantioselectivities of the active and allosteric sites of mammalian ribonucleotide reductase.
|
| |
FEBS J,
272,
1236-1242.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
M.Fukuoka,
Y.Nakanishi,
R.B.Hannak,
B.Kräutler,
and
T.Toraya
(2005).
Homoadenosylcobalamins as probes for exploring the active sites of coenzyme B12-dependent diol dehydratase and ethanolamine ammonia-lyase.
|
| |
FEBS J,
272,
4787-4796.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
M.S.Hamza,
X.Zou,
R.Banka,
K.L.Brown,
and
R.van Eldik
(2005).
Kinetic and thermodynamic studies on ligand substitution reactions and base-on/base-off equilibria of cyanoimidazolylcobamide, a vitamin B12 analog with an imidazole axial nucleoside.
|
| |
Dalton Trans,
(),
782-787.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
I.Borovok,
B.Gorovitz,
M.Yanku,
R.Schreiber,
B.Gust,
K.Chater,
Y.Aharonowitz,
and
G.Cohen
(2004).
Alternative oxygen-dependent and oxygen-independent ribonucleotide reductases in Streptomyces: cross-regulation and physiological role in response to oxygen limitation.
|
| |
Mol Microbiol,
54,
1022-1035.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
K.M.Larsson,
A.Jordan,
R.Eliasson,
P.Reichard,
D.T.Logan,
and
P.Nordlund
(2004).
Structural mechanism of allosteric substrate specificity regulation in a ribonucleotide reductase.
|
| |
Nat Struct Mol Biol,
11,
1142-1149.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
M.C.Chang,
C.S.Yee,
J.Stubbe,
and
D.G.Nocera
(2004).
Turning on ribonucleotide reductase by light-initiated amino acid radical generation.
|
| |
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A,
101,
6882-6887.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
T.M.Anderson,
W.A.Neiwert,
M.L.Kirk,
P.M.Piccoli,
A.J.Schultz,
T.F.Koetzle,
D.G.Musaev,
K.Morokuma,
R.Cao,
and
C.L.Hill
(2004).
A late-transition metal oxo complex: K7Na9[O=PtIV(H2O)L2], L = [PW9O34]9-.
|
| |
Science,
306,
2074-2077.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
H.A.Lindner,
V.V.Lunin,
A.Alary,
R.Hecker,
M.Cygler,
and
R.Ménard
(2003).
Essential roles of zinc ligation and enzyme dimerization for catalysis in the aminoacylase-1/M20 family.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
278,
44496-44504.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
I.M.Nooren,
and
J.M.Thornton
(2003).
Diversity of protein-protein interactions.
|
| |
EMBO J,
22,
3486-3492.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
K.R.Strand,
Y.S.Yang,
K.K.Andersson,
and
E.I.Solomon
(2003).
Circular dichroism and magnetic circular dichroism studies of the biferrous form of the R2 subunit of ribonucleotide reductase from mouse: comparison to the R2 from Escherichia coli and other binuclear ferrous enzymes.
|
| |
Biochemistry,
42,
12223-12234.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
N.Shibata,
Y.Nakanishi,
M.Fukuoka,
M.Yamanishi,
N.Yasuoka,
and
T.Toraya
(2003).
Structural rationalization for the lack of stereospecificity in coenzyme B12-dependent diol dehydratase.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
278,
22717-22725.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
R.Banerjee,
and
S.W.Ragsdale
(2003).
The many faces of vitamin B12: catalysis by cobalamin-dependent enzymes.
|
| |
Annu Rev Biochem,
72,
209-247.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
X.Q.Liu,
J.Yang,
and
Q.Meng
(2003).
Four inteins and three group II introns encoded in a bacterial ribonucleotide reductase gene.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
278,
46826-46831.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
E.L.Borths,
K.P.Locher,
A.T.Lee,
and
D.C.Rees
(2002).
The structure of Escherichia coli BtuF and binding to its cognate ATP binding cassette transporter.
|
| |
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A,
99,
16642-16647.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
F.K.Gleason,
and
N.E.Olszewski
(2002).
Isolation of the gene for the B12-dependent ribonucleotide reductase from Anabaena sp. strain PCC 7120 and expression in Escherichia coli.
|
| |
J Bacteriol,
184,
6544-6550.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
K.R.Strand,
S.Karlsen,
and
K.K.Andersson
(2002).
Cobalt substitution of mouse R2 ribonucleotide reductase as a model for the reactive diferrous state Spectroscopic and structural evidence for a ferromagnetically coupled dinuclear cobalt cluster.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
277,
34229-34238.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
M.L.Ludwig,
and
R.G.Matthews
(2002).
Effector regulation in a monomeric enzyme.
|
| |
Nat Struct Biol,
9,
236-238.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
M.Yamanishi,
M.Yunoki,
T.Tobimatsu,
H.Sato,
J.Matsui,
A.Dokiya,
Y.Iuchi,
K.Oe,
K.Suto,
N.Shibata,
Y.Morimoto,
N.Yasuoka,
and
T.Toraya
(2002).
The crystal structure of coenzyme B12-dependent glycerol dehydratase in complex with cobalamin and propane-1,2-diol.
|
| |
Eur J Biochem,
269,
4484-4494.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
|
The most recent references are shown first.
Citation data come partly from CiteXplore and partly
from an automated harvesting procedure. Note that this is likely to be
only a partial list as not all journals are covered by
either method. However, we are continually building up the citation data
so more and more references will be included with time.
Where a reference describes a PDB structure, the PDB
codes are
shown on the right.
|
 |

