 |
PDBsum entry 1ef3

|
|
|

|
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
 |

|

|

|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
Oxidoreductase
|
PDB id
|
|

|

|
1ef3
|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
 |
Contents |
 |
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
* Residue conservation analysis
|
|
|

|
|
PDB id:
|
 |
|
 |
| Name: |
 |
Oxidoreductase
|
 |
|
Title:
|
 |
Fidarestat bound to human aldose reductase
|
|
Structure:
|
 |
Aldose reductase. Chain: a, b. Engineered: yes
|
|
Source:
|
 |
Homo sapiens. Human. Organism_taxid: 9606. Tissue: muscle. Expressed in: unidentified baculovirus. Expression_system_taxid: 10469
|
|
Resolution:
|
 |
|
2.80Å
|
R-factor:
|
0.186
|
R-free:
|
0.278
|
|
|
Authors:
|
 |
M.Oka,Y.Matsumoto,S.Sugiyama,N.Tsuruta,M.Matsushima
|
|
Key ref:
|
 |
M.Oka
et al.
(2000).
A potent aldose reductase inhibitor, (2S,4S)-6-fluoro-2', 5'-dioxospiro[chroman-4,4'-imidazolidine]-2-carboxamide (Fidarestat): its absolute configuration and interactions with the aldose reductase by X-ray crystallography.
J Med Chem,
43,
2479-2483.
PubMed id:
DOI:
|
 |
|
Date:
|
 |
|
06-Feb-00
|
Release date:
|
07-Feb-01
|
|
|

|

|
|
PROCHECK
|

|

|
|
|
Headers
|
 |
|
|
References
|
|
|
|

|

|
|
P15121
(ALDR_HUMAN) -
Aldo-keto reductase family 1 member B1 from Homo sapiens
|
|

|

|
Seq:
Struc:
|
 |
 |
 |
316 a.a.
315 a.a.
|

|

|

|

|
|

|

|

|
 |
 |

|
|
Key: |
 |
PfamA domain |
 |
 |
 |
Secondary structure |
 |
 |
CATH domain |
 |
|

|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class 1:
|
 |
E.C.1.1.1.21
- aldose reductase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
|
1.
|
an alditol + NAD+ = an aldose + NADH + H+
|
|
2.
|
an alditol + NADP+ = an aldose + NADPH + H+
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
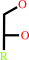 alditol
alditol
|
+
|
NAD(+)
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
matches with 91.67% similarity
|
=
|
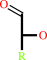 aldose
aldose
|
+
|
 NADH
NADH
|
+
|
H(+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 alditol
alditol
|
+
|
NADP(+)
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
corresponds exactly
|
=
|
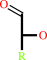 aldose
aldose
|
+
|
 NADPH
NADPH
|
+
|
H(+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class 2:
|
 |
E.C.1.1.1.300
- NADP-retinol dehydrogenase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
all-trans-retinol + NADP+ = all-trans-retinal + NADPH + H+
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
all-trans-retinol
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
matches with 41.38% similarity
|
+
|
NADP(+)
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
corresponds exactly
|
=
|
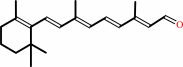 all-trans-retinal
all-trans-retinal
|
+
|
 NADPH
NADPH
|
+
|
H(+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class 3:
|
 |
E.C.1.1.1.372
- D/L-glyceraldehyde reductase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
|
1.
|
glycerol + NADP+ = L-glyceraldehyde + NADPH + H+
|
|
2.
|
glycerol + NADP+ = D-glyceraldehyde + NADPH + H+
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
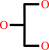 glycerol
glycerol
|
+
|
NADP(+)
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
corresponds exactly
|
=
|
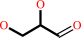 L-glyceraldehyde
L-glyceraldehyde
|
+
|
 NADPH
NADPH
|
+
|
H(+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 glycerol
glycerol
|
+
|
NADP(+)
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
corresponds exactly
|
=
|
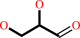 D-glyceraldehyde
D-glyceraldehyde
|
+
|
 NADPH
NADPH
|
+
|
H(+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class 4:
|
 |
E.C.1.1.1.54
- allyl-alcohol dehydrogenase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
allyl alcohol + NADP+ = acrolein + NADPH + H+
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
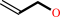 allyl alcohol
allyl alcohol
|
+
|
NADP(+)
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
corresponds exactly
|
=
|
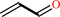 acrolein
acrolein
|
+
|
 NADPH
NADPH
|
+
|
H(+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Note, where more than one E.C. class is given (as above), each may
correspond to a different protein domain or, in the case of polyprotein
precursors, to a different mature protein.
|
|
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
J Med Chem
43:2479-2483
(2000)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
A potent aldose reductase inhibitor, (2S,4S)-6-fluoro-2', 5'-dioxospiro[chroman-4,4'-imidazolidine]-2-carboxamide (Fidarestat): its absolute configuration and interactions with the aldose reductase by X-ray crystallography.
|
|
M.Oka,
Y.Matsumoto,
S.Sugiyama,
N.Tsuruta,
M.Matsushima.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
The absolute configuration of the aldose reductase (AR) inhibitor,
(+)-(2S,4S)-6-fluoro-2',5'-dioxospiro¿chroman-4, 4'-imidazolidine-2-carboxamide
(fidarestat), was established indirectly by single-crystal X-ray analysis of
(+)-(2S, 4S)-8-bromo-6-fluoro-2',5'-dioxospiro¿chroman-4,
4'-imidazolidine-2-carboxylic acid (1). The crystal structure of human AR
complexed with fidarestat was determined, and the specific inhibition activity
was discussed on the basis of the three-dimensional interactions between them.
The structure clarified that fidarestat was located in the active site by
hydrophilic and hydrophobic interactions and that the carbamoyl group of
fidarestat was a very effective substituent for affinity to AR and for
selectivity between AR and aldehyde reductase (AHR). Explanations for the
differences between the observed activities of fidarestat and its stereoisomer 2
were suggested by computer modeling.

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Literature references that cite this PDB file's key reference
|
|
 |
| |
PubMed id
|
 |
Reference
|
 |
|
|
|
 |
P.Chen,
S.Qian,
Z.Q.Shi,
and
Y.Wu
(2010).
6-Fluoro-4-oxochroman-2-carboxylic acid.
|
| |
Acta Crystallogr Sect E Struct Rep Online,
66,
o274.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
J.C.Patra,
and
O.Singh
(2009).
Artificial neural networks-based approach to design ARIs using QSAR for diabetes mellitus.
|
| |
J Comput Chem,
30,
2494-2508.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
M.Eisenmann,
H.Steuber,
M.Zentgraf,
M.Altenkämper,
R.Ortmann,
J.Perruchon,
G.Klebe,
and
M.Schlitzer
(2009).
Structure-based optimization of aldose reductase inhibitors originating from virtual screening.
|
| |
ChemMedChem,
4,
809-819.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
D.E.Danley
(2006).
Crystallization to obtain protein-ligand complexes for structure-aided drug design.
|
| |
Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr,
62,
569-575.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
E.K.Bomati,
M.B.Austin,
M.E.Bowman,
R.A.Dixon,
and
J.P.Noel
(2005).
Structural elucidation of chalcone reductase and implications for deoxychalcone biosynthesis.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
280,
30496-30503.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
F.Ruiz,
I.Hazemann,
A.Mitschler,
A.Joachimiak,
T.Schneider,
M.Karplus,
and
A.Podjarny
(2004).
The crystallographic structure of the aldose reductase-IDD552 complex shows direct proton donation from tyrosine 48.
|
| |
Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr,
60,
1347-1354.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
O.El-Kabbani,
C.Darmanin,
T.R.Schneider,
I.Hazemann,
F.Ruiz,
M.Oka,
A.Joachimiak,
C.Schulze-Briese,
T.Tomizaki,
A.Mitschler,
and
A.Podjarny
(2004).
Ultrahigh resolution drug design. II. Atomic resolution structures of human aldose reductase holoenzyme complexed with Fidarestat and Minalrestat: implications for the binding of cyclic imide inhibitors.
|
| |
Proteins,
55,
805-813.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
O.Kraemer,
I.Hazemann,
A.D.Podjarny,
and
G.Klebe
(2004).
Virtual screening for inhibitors of human aldose reductase.
|
| |
Proteins,
55,
814-823.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
M.Goto,
Y.Yamauchi,
E.Kurosaki,
and
H.Azuma
(2003).
Possible involvement of facilitated polyol pathway in augmentation of intimal hyperplasia in rabbits with alloxan-induced hyperglycemia.
|
| |
J Cardiovasc Pharmacol,
41,
265-275.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
O.El-Kabbani,
P.Ramsland,
C.Darmanin,
R.P.Chung,
and
A.Podjarny
(2003).
Structure of human aldose reductase holoenzyme in complex with statil: an approach to structure-based inhibitor design of the enzyme.
|
| |
Proteins,
50,
230-238.
|
 |
|
 |
 |
|
The most recent references are shown first.
Citation data come partly from CiteXplore and partly
from an automated harvesting procedure. Note that this is likely to be
only a partial list as not all journals are covered by
either method. However, we are continually building up the citation data
so more and more references will be included with time.
Where a reference describes a PDB structure, the PDB
code is
shown on the right.
|
 |

