Nucleoside-diphosphate kinase
Nucleoside diphosphate kinase (NDP kinase) is responsible for phosphorylating non-adenine nucleoside diphosphates. The phosphate donor is usually ATP, but the diphosphate nucleotide substrate is non-specific for either base or ribose / deoxyribose.
The mechanism of nucleotide binding is different from that of most other phoshokinases and nucleotide binding proteins which use a parallel beta-sheet, NDP using an anti-parallel beta-sheet. NDPK from Dictyostelium discoideum is used as a model because it is particularly easy to crystallise.
Reference Protein and Structure
- Sequence
-
P22887
 (2.7.4.6)
(2.7.4.6)
 (Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
(Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
- Biological species
-
Dictyostelium discoideum (Slime mould)

- PDB
-
1ndp
- ADENOSINE 5'-DIPHOSPHATE BINDING AND THE ACTIVE SITE OF NUCLEOSIDE DIPHOSPHATE KINASE
(2.2 Å)



- Catalytic CATH Domains
-
3.30.70.141
 (see all for 1ndp)
(see all for 1ndp)
- Cofactors
- Magnesium(2+) (1) Metal MACiE
Enzyme Reaction (EC:2.7.4.6)
Enzyme Mechanism
Introduction
NDPK operates using a 'ping-pong' mechanism. The gamma-phosphate of ATP is transferred to the delta-N atom of the doubly protonated His 122 of NDPK, with the delta-N proton concomitantly transferred to the gamma-phosphate. A nucleoside diphosphate binds in the active site. The phosphate group is transferred from His 122-P to the 5' hydroxyl of the ribose. Both phosphoryl transfers are dissociative SN2-like reactions, similar to the uncatalysed reaction.
The 3' ribose / deoxyribose hydroxyl group is more catalytically important than Tyr 56 or Lys 16; in the first transfer to His 122, it hydrogen bonds to the gamma-phosphate group, forcing the substrate into a reactive conformation and stabilising the negative charge by hydrogen bonding. The enzymatic reaction can therefore be described as substrate-assisted.
Catalytic Residues Roles
| UniProt | PDB* (1ndp) | ||
| Asn119 | Asn119B | Ensures that the substrates are bound in the correct position. | hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donor, steric role, electrostatic stabiliser |
| His122 | His122B | Acts as a general acid/base and the catalytic nucleophile. It is phosphrylated during the course of the reaction. | hydrogen bond donor, nucleophile, proton acceptor, proton donor, nucleofuge |
| Glu133 | Glu133B | Activates the catalytic histidine as part of a Glu-His dyad. | increase nucleophilicity, hydrogen bond acceptor, steric role |
| Lys16 | Lys16B | Lys 16 stabilises the negative charge on the phosphoryl group, lowering the transition state energy. Lys 16 also plays a role in keeping Tyr 56 protonated. | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Tyr56 | Tyr56B | Tyr 56 stabilises the phosphohistidine intermediate by hydrogen bonding to phosphohistidine. | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, bimolecular nucleophilic substitution, overall reactant used, enzyme-substrate complex formation, overall product formed, intermediate formation, enzyme-substrate complex cleavage, intermediate collapse, intermediate terminated, native state of enzyme regeneratedReferences
- Schneider B et al. (2001), Eur J Biochem, 268, 1964-1971. Mechanism of phosphoryl transfer by nucleoside diphosphate kinase pH dependence and role of the active site Lys16 and Tyr56 residues. PMID:11277918.
- Pédelacq JD et al. (2005), Protein Sci, 14, 2562-2573. Structural and functional features of an NDP kinase from the hyperthermophile crenarchaeon Pyrobaculum aerophilum. DOI:10.1110/ps.051664205. PMID:16195547.
- Gallois-Montbrun S et al. (2003), Mol Pharmacol, 63, 538-546. Structural Analysis of the Activation of Ribavirin Analogs by NDP Kinase: Comparison with Other Ribavirin Targets. DOI:10.1124/mol.63.3.538. PMID:12606760.
- Hutter MC et al. (2002), Chembiochem, 3, 643-651. The Mechanism of Phosphorylation of Natural Nucleosides and Anti-HIV Analogues by Nucleoside Diphosphate Kinase Is Independent of Their Sugar Substituents. DOI:10.1002/1439-7633(20020703)3:7<643::aid-cbic643>3.0.co;2-l. PMID:12324998.
- Gonin P et al. (1999), Biochemistry, 38, 7265-7272. Catalytic Mechanism of Nucleoside Diphosphate Kinase Investigated Using Nucleotide Analogues, Viscosity Effects, and X-ray Crystallography†,‡. DOI:10.1021/bi982990v. PMID:10353838.
- Admiraal SJ et al. (1999), Biochemistry, 38, 4701-4711. Nucleophilic Activation by Positioning in Phosphoryl Transfer Catalyzed by Nucleoside Diphosphate Kinase†,‡. DOI:10.1021/bi9827565. PMID:10200157.
- Moréra S et al. (1995), Biochemistry, 34, 11062-11070. Mechanism of phosphate transfer by nucleoside diphosphate kinase: X-ray structures of the phosphohistidine intermediate of the enzymes from Drosophila and Dictyostelium. DOI:10.2210/pdb1nsp/pdb. PMID:7669763.
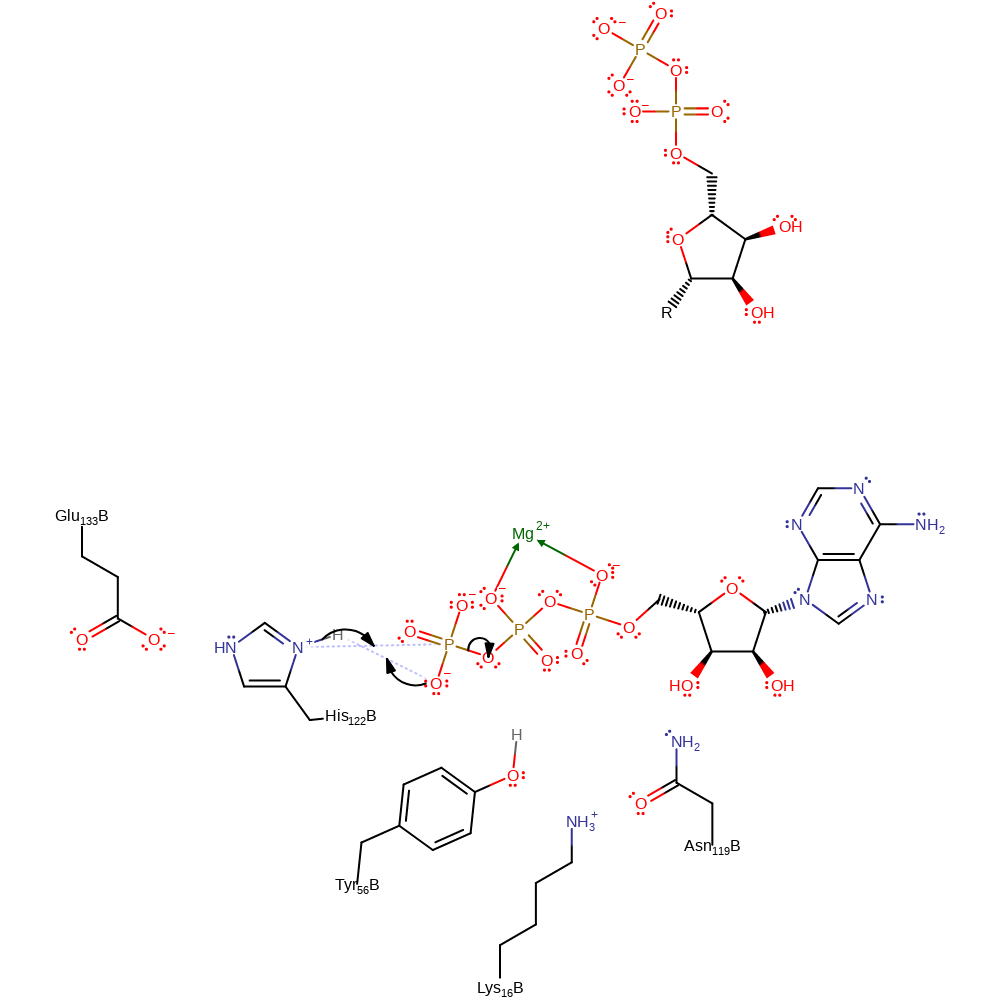
Step 1. The gamma phosphate of ATP deprotonates His122. His122 then attacks the gamma phosphate of ATP in a nucleophilic substitution, releasing the ADP product.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| His122B | hydrogen bond donor |
| Lys16B | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Tyr56B | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asn119B | hydrogen bond donor, steric role, hydrogen bond acceptor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Glu133B | hydrogen bond acceptor, increase nucleophilicity, steric role |
| His122B | nucleophile, proton donor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, ingold: bimolecular nucleophilic substitution, overall reactant used, enzyme-substrate complex formation, overall product formed, intermediate formation
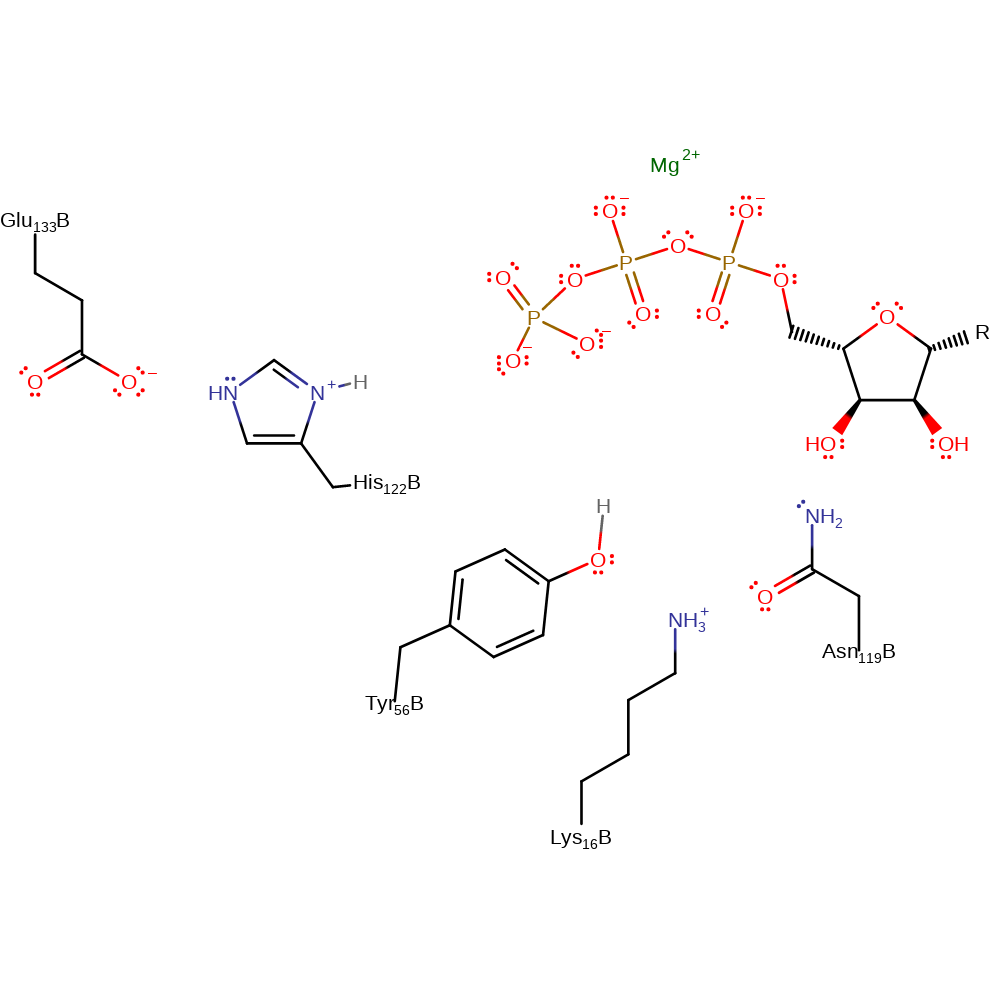
Step 2. The nucleoside diphosphate substrate attacks the phosphate of the phosphorylated His122 in a nucleophilic substitution. The released His122 then deprotonates the triphosphate giving the nucleoside triphosphate product.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Lys16B | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Tyr56B | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asn119B | hydrogen bond donor, steric role, hydrogen bond acceptor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Glu133B | hydrogen bond acceptor, steric role |
| His122B | proton acceptor, nucleofuge |




 Download:
Download: