 |
PDBsum entry 4rut

|
|
|

|
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
 |

|

|

|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
Oxidoreductase
|
PDB id
|
|

|

|
4rut
|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
|

|
|
PDB id:
|
 |
|
 |
| Name: |
 |
Oxidoreductase
|
 |
|
Title:
|
 |
Crystal structure of murine cyclooxygenase-2 with 13-methyl- arachidonic acid
|
|
Structure:
|
 |
Prostaglandin g/h synthase 2. Chain: a, b, c, d. Synonym: cyclooxygenase-2, cox-2, glucocorticoid-regulated inflammatory cyclooxygenase, gripghs, macrophage activation- associated marker protein p71/73, pes-2, phs ii, prostaglandin h2 synthase 2, pgh synthase 2, pghs-2, prostaglandin-endoperoxide synthase 2, tis10 protein. Engineered: yes
|
|
Source:
|
 |
Mus musculus. Mouse. Organism_taxid: 10090. Gene: ptgs2, cox-2, cox2, pghs-b, tis10. Expressed in: spodoptera frugiperda. Expression_system_taxid: 7108.
|
|
Resolution:
|
 |
|
2.16Å
|
R-factor:
|
0.178
|
R-free:
|
0.224
|
|
|
Authors:
|
 |
S.Xu,S.N.Kudalkar,S.Banerjee,A.Makriyannis,S.P.Nikas,L.J.Marnett
|
|
Key ref:
|
 |
S.N.Kudalkar
et al.
(2015).
13-Methylarachidonic acid is a positive allosteric modulator of endocannabinoid oxygenation by cyclooxygenase.
J Biol Chem,
290,
7897-7909.
PubMed id:
DOI:
|
 |
|
Date:
|
 |
|
21-Nov-14
|
Release date:
|
11-Feb-15
|
|
|

|

|
|
PROCHECK
|

|

|
|
|
Headers
|
 |
|
|
References
|
|
|
|

|

|
|
Q05769
(PGH2_MOUSE) -
Prostaglandin G/H synthase 2 from Mus musculus
|
|

|

|
Seq:
Struc:
|
 |
 |
 |
604 a.a.
552 a.a.
|

|

|

|

|
|

|

|

|
 |
 |

|
|
Key: |
 |
PfamA domain |
 |
 |
 |
Secondary structure |
 |
 |
CATH domain |
 |
|

|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
E.C.1.14.99.1
- prostaglandin-endoperoxide synthase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z)-eicosatetraenoate + AH2 + 2 O2 = prostaglandin H2 + A + H2O
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z)-eicosatetraenoate
|
+
|
AH2
|
+
|
 2
×
O2
2
×
O2
|
=
|
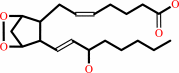 prostaglandin H2
prostaglandin H2
|
+
|
|
+
|
H2O
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
matches with 51.11% similarity
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
J Biol Chem
290:7897-7909
(2015)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
13-Methylarachidonic acid is a positive allosteric modulator of endocannabinoid oxygenation by cyclooxygenase.
|
|
S.N.Kudalkar,
S.P.Nikas,
P.J.Kingsley,
S.Xu,
J.J.Galligan,
C.A.Rouzer,
S.Banerjee,
L.Ji,
M.R.Eno,
A.Makriyannis,
L.J.Marnett.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
Cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) oxygenates arachidonic acid (AA) and the
endocannabinoids 2-arachidonoylglycerol (2-AG) and arachidonylethanolamide to
prostaglandins, prostaglandin glyceryl esters, and prostaglandin ethanolamides,
respectively. A structural homodimer, COX-2 acts as a conformational heterodimer
with a catalytic and an allosteric monomer. Prior studies have demonstrated
substrate-selective negative allosteric regulation of 2-AG oxygenation. Here we
describe AM-8138 (13(S)-methylarachidonic acid), a substrate-selective
allosteric potentiator that augments 2-AG oxygenation by up to 3.5-fold with no
effect on AA oxygenation. In the crystal structure of an AM-8138·COX-2 complex,
AM-8138 adopts a conformation similar to the unproductive conformation of AA in
the substrate binding site. Kinetic analysis suggests that binding of AM-8138 to
the allosteric monomer of COX-2 increases 2-AG oxygenation by increasing kcat
and preventing inhibitory binding of 2-AG. AM-8138 restored the activity of
COX-2 mutants that exhibited very poor 2-AG oxygenating activity and increased
the activity of COX-1 toward 2-AG. Competition of AM-8138 for the allosteric
site prevented the inhibition of COX-2-dependent 2-AG oxygenation by
substrate-selective inhibitors and blocked the inhibition of AA or 2-AG
oxygenation by nonselective time-dependent inhibitors. AM-8138 selectively
enhanced 2-AG oxygenation in intact RAW264.7 macrophage-like cells. Thus,
AM-8138 is an important new tool compound for the exploration of allosteric
modulation of COX enzymes and their role in endocannabinoid metabolism.

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

