 |
PDBsum entry 5x1v
|
|

|
|
PDB id:
|
 |
|
 |
| Name: |
 |
Transferase
|
 |
|
Title:
|
 |
Pkm2 in complex with compound 2
|
|
Structure:
|
 |
Pyruvate kinase pkm. Chain: a, b, c, d. Synonym: cytosolic thyroid hormone-binding protein,cthbp,opa- interacting protein 3,oip-3,pyruvate kinase 2/3,pyruvate kinase muscle isozyme,thyroid hormone-binding protein 1,thbp1,tumor m2-pk, p58. Engineered: yes
|
|
Source:
|
 |
Homo sapiens. Human. Organism_taxid: 9606. Gene: pkm, oip3, pk2, pk3, pkm2. Expressed in: escherichia coli. Expression_system_taxid: 562.
|
|
Resolution:
|
 |
|
2.10Å
|
R-factor:
|
0.238
|
R-free:
|
0.274
|
|
|
Authors:
|
 |
Y.Matsui,H.Hanzawa
|
|
Key ref:
|
 |
Y.Matsui
et al.
(2017).
Discovery and structure-guided fragment-linking of 4-(2,3-dichlorobenzoyl)-1-methyl-pyrrole-2-carboxamide as a pyruvate kinase M2 activator.
Bioorg Med Chem,
25,
3540-3546.
PubMed id:
DOI:
|
 |
|
Date:
|
 |
|
27-Jan-17
|
Release date:
|
31-May-17
|
|
|

|

|
|
PROCHECK
|

|

|
|
|
Headers
|
 |
|
|
References
|
|
|
|

|

|
|
P14618
(KPYM_HUMAN) -
Pyruvate kinase PKM from Homo sapiens
|
|

|

|
Seq:
Struc:
|
 |
 |
 |
531 a.a.
512 a.a.
|

|

|

|

|
|

|

|

|
 |
 |

|
|
Key: |
 |
PfamA domain |
 |
 |
 |
Secondary structure |
 |
|

|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class 2:
|
 |
E.C.2.7.1.40
- pyruvate kinase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
pyruvate + ATP = phosphoenolpyruvate + ADP + H+
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 pyruvate
pyruvate
|
+
|
 ATP
ATP
|
=
|
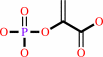 phosphoenolpyruvate
phosphoenolpyruvate
|
+
|
 ADP
ADP
|
+
|
H(+)
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
matches with 42.86% similarity
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class 3:
|
 |
E.C.2.7.10.2
- non-specific protein-tyrosine kinase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
L-tyrosyl-[protein] + ATP = O-phospho-L-tyrosyl-[protein] + ADP + H+
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
L-tyrosyl-[protein]
|
+
|
 ATP
ATP
|
=
|
O-phospho-L-tyrosyl-[protein]
|
+
|
 ADP
ADP
|
+
|
H(+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class 4:
|
 |
E.C.2.7.11.1
- non-specific serine/threonine protein kinase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
|
1.
|
L-seryl-[protein] + ATP = O-phospho-L-seryl-[protein] + ADP + H+
|
|
2.
|
L-threonyl-[protein] + ATP = O-phospho-L-threonyl-[protein] + ADP + H+
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
L-seryl-[protein]
|
+
|
 ATP
ATP
|
=
|
O-phospho-L-seryl-[protein]
|
+
|
 ADP
ADP
|
+
|
H(+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
L-threonyl-[protein]
|
+
|
 ATP
ATP
|
=
|
O-phospho-L-threonyl-[protein]
|
+
|
 ADP
ADP
|
+
|
H(+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Note, where more than one E.C. class is given (as above), each may
correspond to a different protein domain or, in the case of polyprotein
precursors, to a different mature protein.
|
|
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
Bioorg Med Chem
25:3540-3546
(2017)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Discovery and structure-guided fragment-linking of 4-(2,3-dichlorobenzoyl)-1-methyl-pyrrole-2-carboxamide as a pyruvate kinase M2 activator.
|
|
Y.Matsui,
I.Yasumatsu,
T.Asahi,
T.Kitamura,
K.Kanai,
O.Ubukata,
H.Hayasaka,
S.Takaishi,
H.Hanzawa,
S.Katakura.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
Tumor cells switch glucose metabolism to aerobic glycolysis by expressing the
pyruvate kinase M2 isoform (PKM2) in a low active form, providing glycolytic
intermediates as building blocks for biosynthetic processes, and thereby
supporting cell proliferation. Activation of PKM2 should invert aerobic
glycolysis to an oxidative metabolism and prevent cancer growth. Thus, PKM2 has
gained attention as a promising cancer therapy target. To obtain novel PKM2
activators, we conducted a high-throughput screening (HTS). Among several hit
compounds, a fragment-like hit compound with low potency but high ligand
efficiency was identified. Two molecules of the hit compound bound at one
activator binding site, and the molecules were linked based on the crystal
structure. Since this linkage succeeded in maintaining the original position of
the hit compound, the obtained compound exhibited highly improved potency in an
in vitro assay. The linked compound also showed PKM2 activating activity in a
cell based assay, and cellular growth inhibition of the A549 cancer cell line.
Discovery of this novel scaffold and binding mode of the linked compound
provides a valuable platform for the structure-guided design of PKM2 activators.

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

