 |
PDBsum entry 1mgo

|
|
|

|
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
 |

|

|

|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
Oxidoreductase
|
PDB id
|
|

|

|
1mgo
|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
 |
Contents |
 |
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
* Residue conservation analysis
|
|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
E.C.1.1.1.1
- alcohol dehydrogenase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
|
1.
|
a primary alcohol + NAD+ = an aldehyde + NADH + H+
|
|
2.
|
a secondary alcohol + NAD+ = a ketone + NADH + H+
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
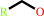 primary alcohol
primary alcohol
|
+
|
NAD(+)
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
corresponds exactly
|
=
|
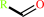 aldehyde
aldehyde
|
+
|
 NADH
NADH
|
+
|
H(+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
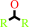 secondary alcohol
secondary alcohol
|
+
|
NAD(+)
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
corresponds exactly
|
=
|
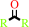 ketone
ketone
|
+
|
 NADH
NADH
|
+
|
H(+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Cofactor:
|
 |
Zn(2+) or Fe cation
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
Biochemistry
41:15770-15779
(2002)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Mobility of fluorobenzyl alcohols bound to liver alcohol dehydrogenases as determined by NMR and X-ray crystallographic studies.
|
|
J.K.Rubach,
B.V.Plapp.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
The relationship between substrate mobility and catalysis was studied with
wild-type and Phe93Ala (F93A) horse liver alcohol dehydrogenase (ADH). Wild-type
ADH binds 2,3,4,5,6-pentafluorobenzyl alcohol in one position as shown by X-ray
results, and (19)F NMR shows five resonances for the fluorines of the bound
alcohol. The two meta-fluorines exchange positions with a rate constant of about
4 s(-1), indicating that mobility (ring flipping) of the benzyl alcohol is
relatively restricted. The wild-type enzyme binds 2,3-difluorobenzyl alcohol in
two alternative conformations that are related by a ring flip and a small
translation of the fluorinated benzene ring, and the (19)F NMR spectrum shows
three resonances for the two bound fluorines, consistent with the two
orientations. Phe-93 interacts with the bound benzyl alcohols, and the F93A
substitution decreases the rate constants for hydride transfer for benzyl
alcohol oxidation and benzaldehyde reduction by 7.4- and 130-fold, respectively.
The structure of F93A ADH crystallized with NAD(+) and
2,3,4,5,6-pentafluorobenzyl alcohol is similar to the structure of the wild-type
enzyme complex except that the pentafluorobenzyl alcohol is not found in one
position. The (19)F NMR spectrum of the F93A ADH-NAD(+)-pentafluorobenzyl
alcohol complex shows three resonances for the bound fluorines. Line shape
analysis of the spectrum suggests the bound pentafluorobenzyl ring undergoes
rapid ring-flipping at about 20 000 s(-1). The F93A substitution greatly
increases the mobility of the benzyl alcohol but modestly and differentially
decreases the probability that the substrate is preorganized for hydride
transfer.

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Literature references that cite this PDB file's key reference
|
|
 |
| |
PubMed id
|
 |
Reference
|
 |
|
|
|
 |
C.Dalvit,
and
A.Vulpetti
(2011).
Fluorine-protein interactions and ¹⁹F NMR isotropic chemical shifts: An empirical correlation with implications for drug design.
|
| |
ChemMedChem,
6,
104-114.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
E.J.Dodson,
and
M.M.Woolfson
(2009).
ACORN2: new developments of the ACORN concept.
|
| |
Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr,
65,
881-891.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
S.Hammes-Schiffer,
and
S.J.Benkovic
(2006).
Relating protein motion to catalysis.
|
| |
Annu Rev Biochem,
75,
519-541.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
L.Esposito,
I.Bruno,
F.Sica,
C.A.Raia,
A.Giordano,
M.Rossi,
L.Mazzarella,
and
A.Zagari
(2003).
Crystal structure of a ternary complex of the alcohol dehydrogenase from Sulfolobus solfataricus.
|
| |
Biochemistry,
42,
14397-14407.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
|
The most recent references are shown first.
Citation data come partly from CiteXplore and partly
from an automated harvesting procedure. Note that this is likely to be
only a partial list as not all journals are covered by
either method. However, we are continually building up the citation data
so more and more references will be included with time.
Where a reference describes a PDB structure, the PDB
code is
shown on the right.
|
 |

