 |
PDBsum entry 1kpm

|

|

|
|
 |
Contents |
 |
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
* Residue conservation analysis
|
|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
E.C.3.1.1.4
- phospholipase A2.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
a 1,2-diacyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine + H2O = a 1-acyl-sn-glycero-3- phosphocholine + a fatty acid + H+
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 1,2-diacyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine
1,2-diacyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine
|
+
|
H2O
|
=
|
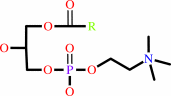 1-acyl-sn-glycero-3- phosphocholine
1-acyl-sn-glycero-3- phosphocholine
|
+
|
fatty acid
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
matches with 60.00% similarity
|
+
|
H(+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Cofactor:
|
 |
Ca(2+)
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
J Mol Biol
320:215-222
(2002)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
First structural evidence of a specific inhibition of phospholipase A2 by alpha-tocopherol (vitamin E) and its implications in inflammation: crystal structure of the complex formed between phospholipase A2 and alpha-tocopherol at 1.8 A resolution.
|
|
V.Chandra,
J.Jasti,
P.Kaur,
C.h.Betzel,
A.Srinivasan,
T.P.Singh.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
This is the first structural evidence of alpha-tocopherol (alpha-TP) as a
possible candidate against inflammation, as it inhibits phospholipase A2
specifically and effectively. The crystal structure of the complex formed
between Vipera russelli phospholipase A2 and alpha-tocopherol has been
determined and refined to a resolution of 1.8 A. The structure contains two
molecules, A and B, of phospholipase A2 in the asymmetric unit, together with
one alpha-tocopherol molecule, which is bound specifically to one of them. The
phospholipase A2 molecules interact extensively with each other in the
crystalline state. The two molecules were found in a stable association in the
solution state as well, thus indicating their inherent tendency to remain
together as a structural unit, leading to significant functional implications.
In the crystal structure, the most important difference between the
conformations of two molecules as a result of their association pertains to the
orientation of Trp31. It may be noted that Trp31 is located at the mouth of the
hydrophobic channel that forms the binding domain of the enzyme. The values of
torsion angles (phi, psi, chi(1) and chi(2)) for both the backbone as well as
for the side-chain of Trp31 in molecules A and B are -94 degrees, -30 degrees,
-66 degrees, 116 degrees and -128 degrees, 170 degrees, -63 degrees, -81
degrees, respectively. The conformation of Trp31 in molecule A is suitable for
binding, while that in B hinders the passage of the ligand to the binding site.
Consequently, alpha-tocopherol is able to bind to molecule A only, while the
binding site of molecule B contains three water molecules. In the complex, the
aromatic moiety of alpha-tocopherol is placed in the large space at the active
site of the enzyme, while the long hydrophobic channel in the enzyme is filled
by hydrocarbon chain of alpha-tocopherol. The critical interactions between the
enzyme and alpha-tocopherol are generated between the hydroxyl group of the
six-membered ring of alpha-tocopherol and His48 N(delta1) and Asp49 O(delta1) as
characteristic hydrogen bonds. The remaining part of alpha-tocopherol interacts
extensively with the residues of the hydrophobic channel of the enzyme, giving
rise to a number of hydrophobic interactions, resulting in the formation of a
stable complex.

|

|
|
|

|
| |
Selected figure(s)
|
|

|
| |
 |
 |

|
 |

|
 |
Figure 4.
Figure 4. (F[o] -F[c]) electron density map contoured at
2.5s showing water molecules in the binding region of molecule
B. The Figure was drawn with BOBSCRIPT21 and rendered by
Raster3D.22
|
 |
Figure 6.
Figure 6. The binding of a-tocopherol in molecule A. The OH
group of the aromatic moiety in a-tocopherol plays a key role by
interacting simultaneously with both Asp49 and His48. The
hydrocarbon chain of a-tocopherol fills the hydrophobic channel
in the protein. The Figure was drawn with MOLSCRIPT23 and
rendered by Raster3D.22
|
 |
|
|

|
| |
The above figures are
reprinted
by permission from Elsevier:
J Mol Biol
(2002,
320,
215-222)
copyright 2002.
|
|
| |
Figures were
selected
by an automated process.
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Literature references that cite this PDB file's key reference
|
|
 |
| |
PubMed id
|
 |
Reference
|
 |
|
|
|
 |
B.Gray,
J.Swick,
and
A.G.Ronnenberg
(2011).
Vitamin E and adiponectin: proposed mechanism for vitamin E-induced improvement in insulin sensitivity.
|
| |
Nutr Rev,
69,
155-161.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
C.E.Cassidy,
and
W.N.Setzer
(2010).
Cancer-relevant biochemical targets of cytotoxic Lonchocarpus flavonoids: a molecular docking analysis.
|
| |
J Mol Model,
16,
311-326.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
G.Leonarduzzi,
B.Sottero,
and
G.Poli
(2010).
Targeting tissue oxidative damage by means of cell signaling modulators: the antioxidant concept revisited.
|
| |
Pharmacol Ther,
128,
336-374.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
K.K.Dharmappa,
R.Mohamed,
H.V.Shivaprasad,
and
B.S.Vishwanath
(2010).
Genistein, a potent inhibitor of secretory phospholipase A2: a new insight in down regulation of inflammation.
|
| |
Inflammopharmacology,
18,
25-31.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
D.P.Marchi-Salvador,
L.C.Corrêa,
A.J.Magro,
C.Z.Oliveira,
A.M.Soares,
and
M.R.Fontes
(2008).
Insights into the role of oligomeric state on the biological activities of crotoxin: crystal structure of a tetrameric phospholipase A2 formed by two isoforms of crotoxin B from Crotalus durissus terrificus venom.
|
| |
Proteins,
72,
883-891.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
J.Atkinson,
R.F.Epand,
and
R.M.Epand
(2008).
Tocopherols and tocotrienols in membranes: a critical review.
|
| |
Free Radic Biol Med,
44,
739-764.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
H.Maeda,
and
D.DellaPenna
(2007).
Tocopherol functions in photosynthetic organisms.
|
| |
Curr Opin Plant Biol,
10,
260-265.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
R.Mohamed,
J.Fernández,
M.Pineda,
and
M.Aguilar
(2007).
Roselle (Hibiscus sabdariffa) seed oil is a rich source of gamma-tocopherol.
|
| |
J Food Sci,
72,
S207-S211.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
V.M.Vecchio,
M.Benedetti,
D.Migoni,
S.A.De Pascali,
A.Ciccarese,
S.Marsigliante,
F.Capitelli,
and
F.P.Fanizzi
(2007).
Highly selective metal mediated ortho-alkylation of phenol. First platinum containing organometallic chromane analogues.
|
| |
Dalton Trans,
(),
5720-5725.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
K.Sekar,
D.Gayathri,
D.Velmurugan,
J.Jeyakanthan,
T.Yamane,
M.J.Poi,
and
M.D.Tsai
(2006).
Third calcium ion found in an inhibitor-bound phospholipase A2.
|
| |
Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr,
62,
392-397.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
N.Singh,
T.Jabeen,
A.Pal,
S.Sharma,
M.Perbandt,
C.Betzel,
and
T.P.Singh
(2006).
Crystal structures of the complexes of a group IIA phospholipase A2 with two natural anti-inflammatory agents, anisic acid, and atropine reveal a similar mode of binding.
|
| |
Proteins,
64,
89.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
N.Singh,
T.Jabeen,
S.Sharma,
R.K.Somvanshi,
S.Dey,
A.Srinivasan,
and
T.P.Singh
(2006).
Specific binding of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) to phospholipase A2: structure of the complex formed between phospholipase A2 and diclofenac at 2.7 A resolution.
|
| |
Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr,
62,
410-416.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
G.Singh,
J.Jasti,
K.Saravanan,
S.Sharma,
P.Kaur,
A.Srinivasan,
and
T.P.Singh
(2005).
Crystal structure of the complex formed between a group I phospholipase A2 and a naturally occurring fatty acid at 2.7 A resolution.
|
| |
Protein Sci,
14,
395-400.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
T.Jabeen,
S.Sharma,
N.Singh,
R.K.Singh,
A.K.Verma,
M.Paramasivam,
A.Srinivasan,
and
T.P.Singh
(2005).
Structure of the zinc-induced heterodimer of two calcium-free isoforms of phospholipase A2 from Naja naja sagittifera at 2.7 angstroms resolution.
|
| |
Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr,
61,
302-308.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
A.Azzi,
R.Gysin,
P.Kempná,
A.Munteanu,
Y.Negis,
L.Villacorta,
T.Visarius,
and
J.M.Zingg
(2004).
Vitamin E mediates cell signaling and regulation of gene expression.
|
| |
Ann N Y Acad Sci,
1031,
86-95.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
C.Kusmic,
G.Basta,
G.Lazzerini,
N.Vesentini,
and
R.Barsacchi
(2004).
The effect of Ginkgo biloba in isolated ischemic/reperfused rat heart: a link between vitamin E preservation and prostaglandin biosynthesis.
|
| |
J Cardiovasc Pharmacol,
44,
356-362.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
P.Kempná,
E.Reiter,
M.Arock,
A.Azzi,
and
J.M.Zingg
(2004).
Inhibition of HMC-1 mast cell proliferation by vitamin E: involvement of the protein kinase B pathway.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
279,
50700-50709.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
S.L.Cuddihy,
E.S.Musiek,
J.D.Morrow,
and
L.L.Dugan
(2004).
Long-term vitamin E deficiency in mice decreases superoxide radical production in brain.
|
| |
Ann N Y Acad Sci,
1031,
428-431.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
R.K.Singh,
P.Vikram,
J.Makker,
T.Jabeen,
S.Sharma,
S.Dey,
P.Kaur,
A.Srinivasan,
and
T.P.Singh
(2003).
Design of specific peptide inhibitors for group I phospholipase A2: structure of a complex formed between phospholipase A2 from Naja naja sagittifera (group I) and a designed peptide inhibitor Val-Ala-Phe-Arg-Ser (VAFRS) at 1.9 A resolution reveals unique features.
|
| |
Biochemistry,
42,
11701-11706.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
V.Chandra,
J.Jasti,
P.Kaur,
S.Dey,
A.Srinivasan,
C.h.Betzel,
and
T.P.Singh
(2002).
Design of specific peptide inhibitors of phospholipase A2: structure of a complex formed between Russell's viper phospholipase A2 and a designed peptide Leu-Ala-Ile-Tyr-Ser (LAIYS).
|
| |
Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr,
58,
1813-1819.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
V.Chandra,
J.Jasti,
P.Kaur,
S.Dey,
M.Perbandt,
A.Srinivasan,
C.h.Betzel,
and
T.P.Singh
(2002).
Crystal structure of a complex formed between a snake venom phospholipase A(2) and a potent peptide inhibitor Phe-Leu-Ser-Tyr-Lys at 1.8 A resolution.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
277,
41079-41085.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
|
The most recent references are shown first.
Citation data come partly from CiteXplore and partly
from an automated harvesting procedure. Note that this is likely to be
only a partial list as not all journals are covered by
either method. However, we are continually building up the citation data
so more and more references will be included with time.
Where a reference describes a PDB structure, the PDB
code is
shown on the right.
|
 |

