Solution 2: downloading the sequence of human IRAK2 and build the 3D model
Step 1: downloading the sequence of human IRAK2 and build the 3D model
Go to EBI Search and type IRAK2 in the search box. Find human IRAK2 and download the FASTA format sequence for it, or copy the sequence from here:
>sp|O43187|IRAK2_HUMAN Interleukin-1 receptor-associated kinase-like 2 OS=Homo sapiens GN=IRAK2 PE=1 SV=2 MACYIYQLPSWVLDDLCRNMDALSEWDWMEFASYVITDLTQLRKIKSMERVQGVSITRELLWWWGMRQAT VQQLVDLLCRLELYRAAQIILNWKPAPEIRCPIPAFPDSVKPEKPLAASVRKAEDEQEEGQPVRMATFPG PGSSPARAHQPAFLQPPEEDAPHSLRSDLPTSSDSKDFSTSIPKQEKLLSLAGDSLFWSEADVVQATDDF NQNRKISQGTFADVYRGHRHGKPFVFKKLRETACSSPGSIERFFQAELQICLRCCHPNVLPVLGFCAARQ FHSFIYPYMANGSLQDRLQGQGGSDPLPWPQRVSICSGLLCAVEYLHGLEIIHSNVKSSNVLLDQNLTPK LAHPMAHLCPVNKRSKYTMMKTHLLRTSAAYLPEDFIRVGQLTKRVDIFSCGIVLAEVLTGIPAMDNNRS PVYLKDLLLSDIPSSTASLCSRKTGVENVMAKEICQKYLEKGAGRLPEDCAEALATAACLCLRRRNTSLQ EVCGSVAAVEERLRGRETLLPWSGLSEGTGSSSNTPEETDDVDNSSLDASSSMSVAPWAGAATPLLPTEN GEGRLRVIVGREADSSSEACVGLEPPQDVTETSWQIEINEAKRKLMENILLYKEEKVDSIELFGP Now go to the SWISS-MODEL service at the Swiss Institute of Bioinformatics. Click on the ‘Start modelling’ button and paste your sequence into the box. Click on ‘Build model’. SwissModel will automatically choose templates based on the most closely aligned protein sequence that has a three-dimensional structure available for it, and model a structure based on that (Figure 18).
Model evaluation
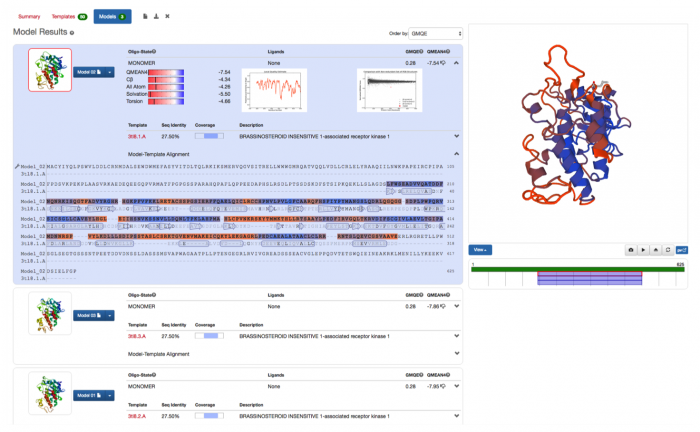
There are several approaches to assessing models. One is to check that values such as bond angles, distances etc. in the model match values that have been observed in experimentally derived structures. In SWISS-MODEL the QMEAN z-score represents an estimate of how comparable the model is to experimentally derived structures of similar size. QMEAN z-scores around zero indicate good agreement between the model structure and experimental structures of similar size. Models of low quality typically have scores of -4.0 or lower. The “thumbs-up” and “thumbs-down” symbols next to the score are used to indicate whether or not the model is of good quality (9). Another approach is to factor in observations of the quality of the alignment and template search method – this is represented in the GMQE (Global Model Quality Estimation) score. The GMQE score reflects the expected accuracy of that alignment and is expressed as a number between 0 and 1 where higher numbers indicate higher reliability (9). For more information see the SWISS-MODEL documentation pages.
Step 2: building a model based on your chosen template
You can also choose your own structural template. Click on ‘Search for templates’. SWISS-MODEL will look for structures in the PDB that have a closely related sequence (Figure 19). Be patient; it can take some time to generate your list of templates. Once you’ve done this, you can align as many of these templates as you like to your target sequence. Here we’ve chosen structures for IRAK4 (2oib.2.A), brassinosteroid insensitive 1-associated receptor kinase 1 (3tl8.2.A) and JAK2 (4bbe.1.A). These three structures align quite closely to each other. Based on this evidence, it might be worth doing some assays to find out whether any known inhibitors of these enzymes also inhibit IRAK2.
