Phosphonate dehydrogenase
Phosphonate dehydrogenase, originally isolated from the Gram-negative bacterium Pseudomonas stutzeri (strain WM88), was the first protein known to catalyze redox chemistry on inorganic phosphorus compounds. Phosphonate dehydrogenase catalyzes the oxidation of phosphonate to phosphate with the concurrent reduction of NAD+ to NADH. Due to the strong exergonic nature of the reaction, phosphonate dehydrogenase has gained a particularly high interest for use as a cofactor regeneration enzyme.
Reference Protein and Structure
- Sequence
-
O69054
 (1.20.1.1)
(1.20.1.1)
 (Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
(Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
- Biological species
-
Pseudomonas stutzeri (Bacteria)

- PDB
-
4e5k
- Thermostable phosphite dehydrogenase in complex with NAD and sulfite
(1.95 Å)



- Catalytic CATH Domains
-
3.40.50.720
 (see all for 4e5k)
(see all for 4e5k)
Enzyme Reaction (EC:1.20.1.1)
Enzyme Mechanism
Introduction
The catalytic mechanism of phosphonate dehydrogenase includes deprotonation of a water molecule by His292, followed by nucleophilic attack of resulting hydroxide on phosphonate together with the direct transfer of a hydride leaving group to NAD+, forming NADH and phosphate product. Met53 plays a catalytic role through transient stabilization of a positively charged His292 side chain.
Catalytic Residues Roles
| UniProt | PDB* (4e5k) | ||
| Met53 | Met53B | His53 plays a catalytic role through transient stabilization of a positively charged histidine side chain. | electrostatic stabiliser |
| His292 | His292B | His292 acts as a general acid/base and abstracts proton from a water molecule for subsequent nucleophilic addition steps | proton acceptor, proton donor |
| Arg237 | Arg237B | Arg237 is important for substrate binding and stabilization of the negative charges on the phosphonate and phosphate. | electrostatic stabiliser |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, bimolecular nucleophilic addition, aromatic bimolecular nucleophilic addition, overall product formed, overall reactant usedReferences
- Ranaghan KE et al. (2014), Chem Sci, 5, 2191-2199. A catalytic role for methionine revealed by a combination of computation and experiments on phosphite dehydrogenase. DOI:10.1039/c3sc53009d.
- Vrtis JM et al. (2001), J Am Chem Soc, 123, 2672-2673. Phosphite dehydrogenase: an unusual phosphoryl transfer reaction. DOI:10.1021/ja004301k. PMID:11456941.
- Costas AM et al. (2001), J Biol Chem, 276, 17429-17436. Purification and characterization of a novel phosphorus-oxidizing enzyme from Pseudomonas stutzeri WM88. DOI:10.1074/jbc.M011764200. PMID:11278981.

Step 1. Deprotonation of water molecule by His292, followed by nucleophilic attack of resulting hydroxide on phosphonate.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| His292B | proton acceptor |
| Arg237B | electrostatic stabiliser |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, ingold: bimolecular nucleophilic addition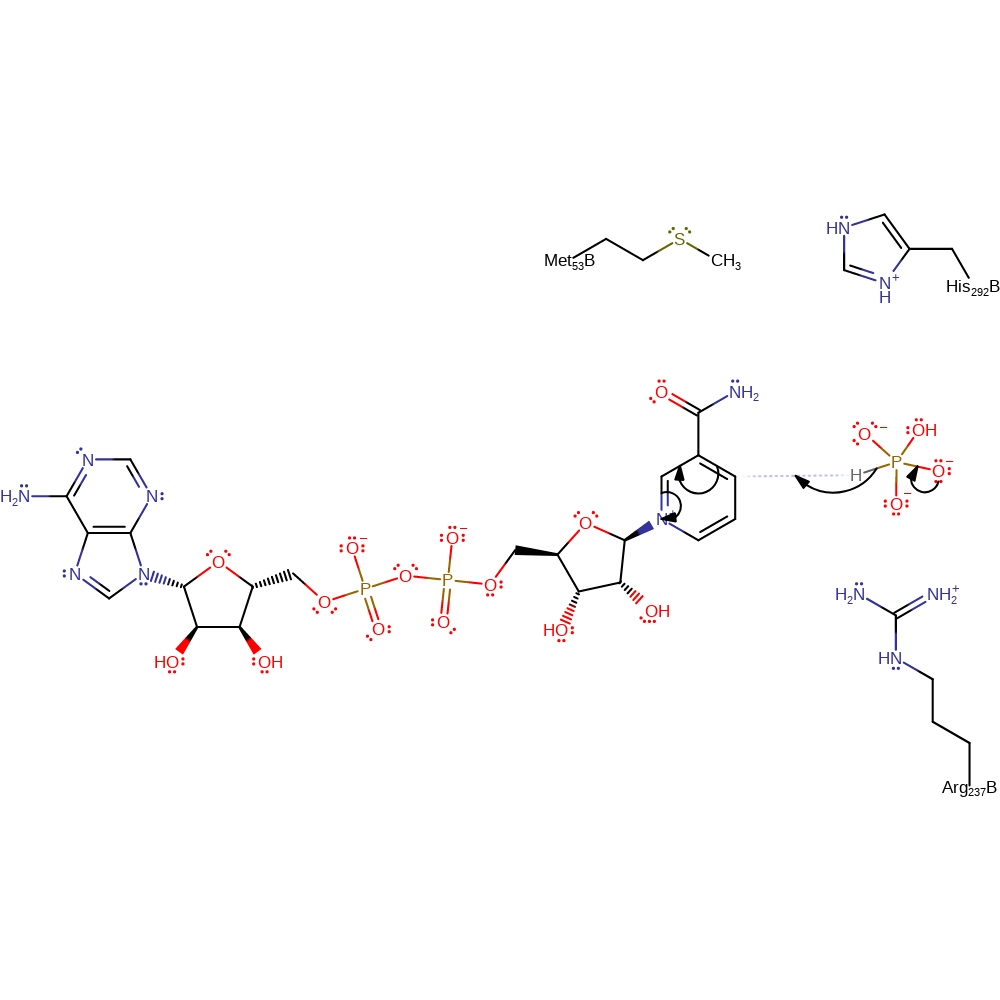
Step 2. Nucleophilic addition of hydride leaving group to NAD+, forming NADH and phosphate product. Met53 plays a catalytic role through transient stabilization of a positively charged His292 side chain.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Met53B | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Arg237B | electrostatic stabiliser |
Chemical Components
ingold: aromatic bimolecular nucleophilic addition, overall product formed, overall reactant used
Step 3. In an inferred reaction step His292 is deprotonated to regenerate the native state of the enzyme.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| His292B | proton donor |
| Arg237B | electrostatic stabiliser |






 Download:
Download: