2'-hydroxybiphenyl-2-sulfinate desulfinase
Part of a bacerial 4S pathway that removes covalently bound sulfur from dibenzothiophene (DBT) without breaking carbon-carbon bonds. This enzymatic system employs four different enzymes (DszA, DszB, DszC, and DszD) to work sequentially in order to oxidize the C−S bond and remove the oxidized sulfur as HSO3-. Bacteria use the oxidized sulfur for their anabolic needs such as producing sulfur-containing amino acids. DszB naturally metabolizes 2′-hydroxybiphenyl-2-sulfinate (HBPS) into biphenyl-2-ol without using cofactors. This reaction might be useful in the future for the processing of crude oil in a more environmentally friendly and lucrative way.
Reference Protein and Structure
- Sequence
-
P54997
 (3.13.1.3)
(Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
(3.13.1.3)
(Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
- Biological species
-
Rhodococcus sp. IGTS8 (Bacteria)

- PDB
-
2de2
- Crystal structure of desulfurization enzyme DSZB
(1.8 Å)



- Catalytic CATH Domains
-
3.40.190.10
 (see all for 2de2)
(see all for 2de2)
Enzyme Reaction (EC:3.13.1.3)
Enzyme Mechanism
Introduction
In this mechanism the Cys27 performs a electrophilic aromatic substitution of the SO2 group. The reaction is starts by the hydrogen bond network consisting of Arg70, His60, Ser25 and Gly73(main-C) anchoring the sulfinate group. This allows Cys27 to donate a proton and cleave the bond between the SO2 and the rest of the substrate. he resulting SO2 is also protected by the hydrogen bond network from reacting with Cys27. A water molecule is then deprotonated by Cys27 and the remaining hydroxide bonds with sulfur dioxide. This forms the final hydrogen sulfite product and returns Cys27 to its native state.
Catalytic Residues Roles
| UniProt | PDB* (2de2) | ||
| His60, Gly73 (main) | His60A, Gly73A (main) | His60 and Gly73 create a stabilising structure for Cys27 after it donates a proton to the substrate. | hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Arg70, His60, Gly73 (main), Ser25 | Arg70A, His60A, Gly73A (main), Ser25A | Ser25, His60, Arg70 and Gly73 form a hydrogen bond network that anchors the substrate and protects the leaving sulfur dioxide from Cys27. The hydrogen atoms from the η-amino group of Arg70 and the ε-amino group of His60 directly interface the substrate’s sulfinate group. The His60 δ amino group is hydrogen-bonded to Ser25 and both of the η-amino groups of Arg70 are hydrogen bonded to the main chain oxygen of Gly73. | hydrogen bond donor |
| Cys27 | Cys27A | Cys27 donates a proton to the electrophilic carbon of the substrate and displaces the sulfinate group. Cys27 then deprotonates a water molecule, regenerating its native state and creating a hydroxide that binds to the sulfur dioxide in the last step of the reaction. | proton acceptor, proton donor |
Chemical Components
rate-determining step, proton transfer, bimolecular electrophilic substitution, overall reactant used, bimolecular nucleophilic addition, overall product formedReferences
- Sousa JPM et al. (2020), ACS Catal, 10, 9545-9554. Reaction Mechanism and Determinants for Efficient Catalysis by DszB, a Key Enzyme for Crude Oil Bio-desulfurization. DOI:https://doi.org/10.1021/acscatal.0c03122.
- Lee WC et al. (2006), J Biol Chem, 281, 32534-32539. Crystal Structure and Desulfurization Mechanism of 2′-Hydroxybiphenyl-2-sulfinic Acid Desulfinase. DOI:https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M602974200.
- Nakayama N et al. (2002), Biochim Biophys Acta Proteins Proteomics, 1598, 122-130. A novel enzyme, 2′-hydroxybiphenyl-2-sulfinate desulfinase (DszB), from a dibenzothiophene-desulfurizing bacterium Rhodococcus erythropolis KA2-5-1: gene overexpression and enzyme characterization. DOI:10.1016/s0167-4838(02)00365-5.
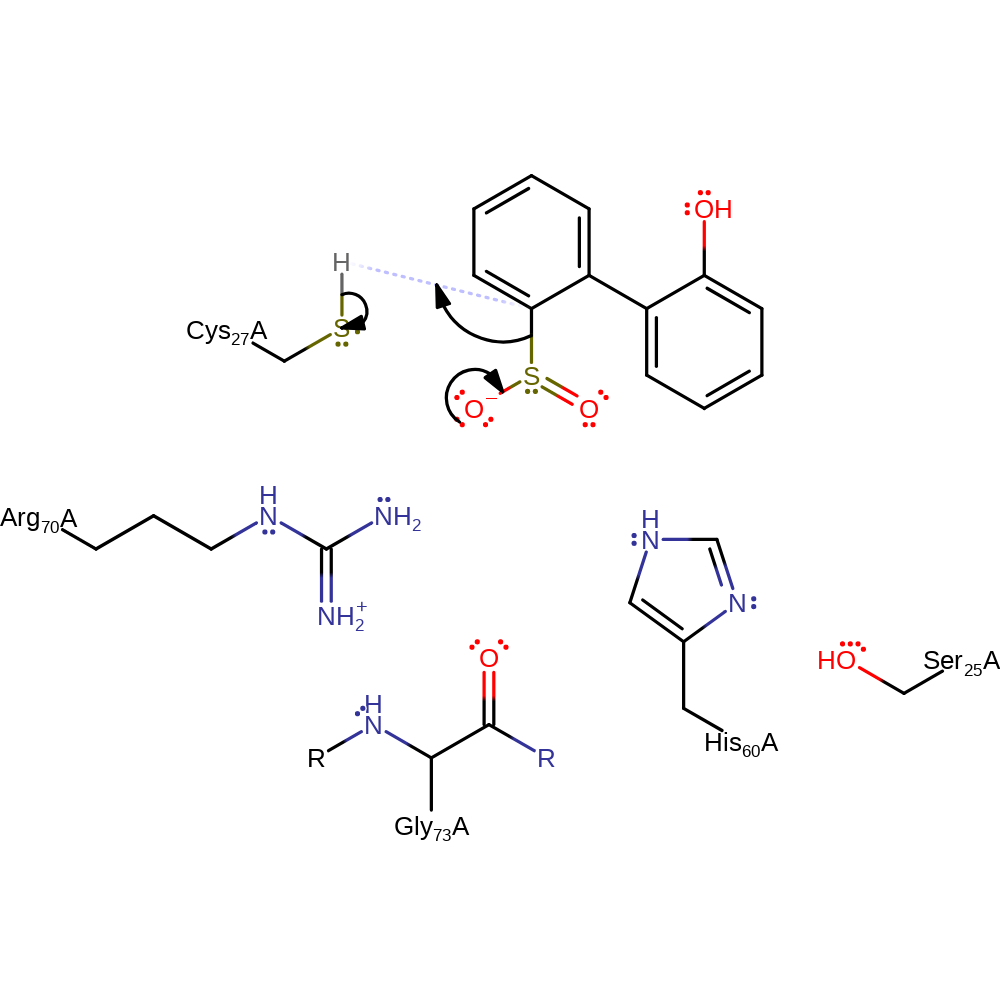
Step 1. The Cys27 proton moves toward the electrophilic carbon of HBPS and displaces the sulfinate group, leaving Cys27 deprotonated. Arg70, His60, Ser25 and Gly73(main chain oxygen) create a hydrogen bond network that allows the sulfinate to be displaced by anchoring it to the active site.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Cys27A | proton donor |
| Arg70A | hydrogen bond donor |
| His60A | hydrogen bond donor |
| Ser25A | hydrogen bond donor |
| Gly73A (main) | hydrogen bond acceptor |
| His60A | hydrogen bond acceptor |
Chemical Components
rate-determining step, proton transfer, ingold: bimolecular electrophilic substitution, overall reactant used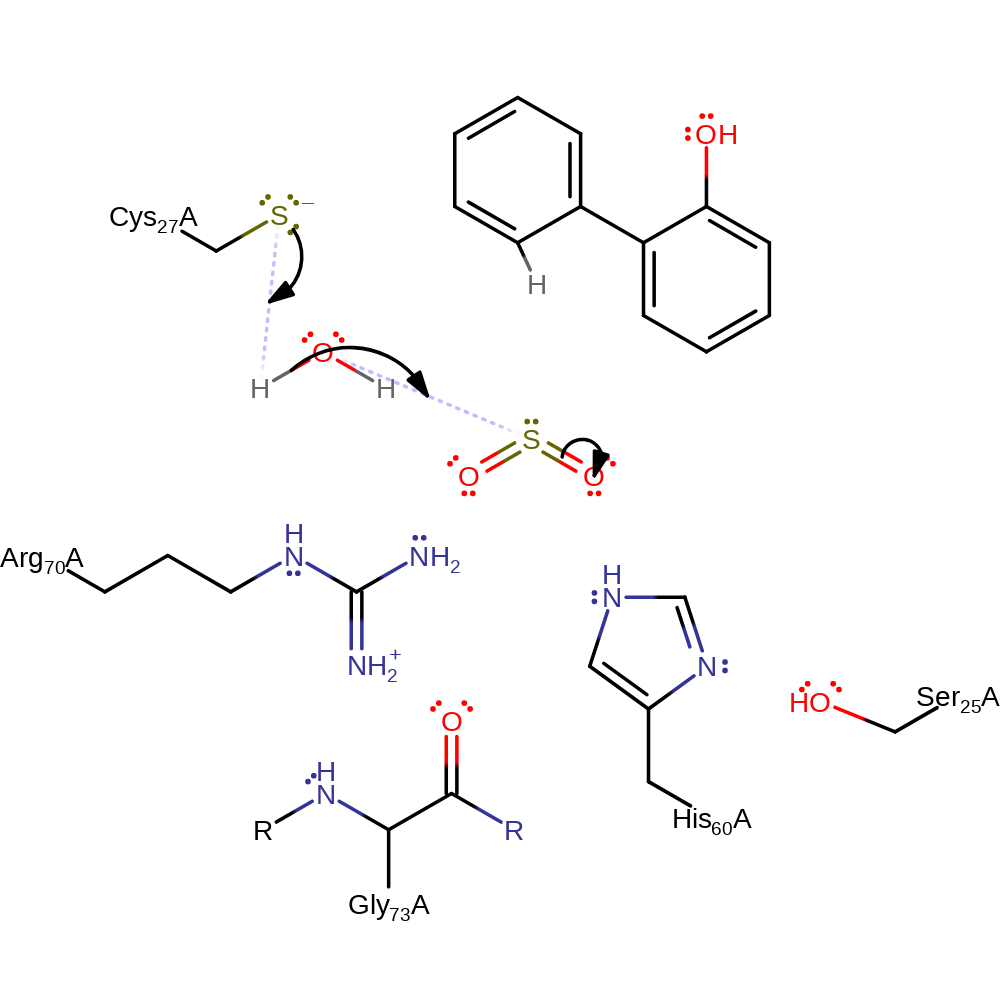
Step 2. A water molecule is deprotonated by the negatively charged Cys27. His60 and Gly73(main-C) form a stabilising structure for the negatively charged Cys27. The hydroxide molecule attacks the sulfur dioxide, creating the second product of the catalysis.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Cys27A | proton acceptor |
| His60A | hydrogen bond donor, hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Gly73A (main) | hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Arg70A | hydrogen bond donor |
| Ser25A | hydrogen bond donor |
| His60A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Gly73A (main) | electrostatic stabiliser |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, ingold: bimolecular nucleophilic addition, overall product formedIntroduction
This reaction is a nucleophilic substitution of the SO2 group through formation of a thiosulfonate-like intermediate. A proton from Cys27 is added to the sulfinate group and the nucleophilic sulfur of the Cys27 creates a covalent bond to the substrate by binding to the sulfinate sulfur. The sulfinate group is anchored by several residues which together form a hydrogen bond network; residues Arg70, Gly73, His60 and Ser25. The next step a water molecule bonds with the sulfinate after leaving a proton to Cys27, regenerating the active site and releasing the sulfinate group from the rest of the substrate. This mechanism was found unfavourable because of the six times larger energy barrier needed for it to happen.
Catalytic Residues Roles
| UniProt | PDB* (2de2) | ||
| Arg70, His60, Gly73 (main), Ser25 | Arg70A, His60A, Gly73A (main), Ser25A | Ser25, His60, Arg70 and Gly73 form a hydrogen bond network that anchors the substrate and protects the leaving sulfur dioxide from Cys27. The hydrogen atoms from the η-amino group of Arg70 and the ε-amino group of His60 directly interface the substrate’s sulfinate group. The His60 δ amino group is hydrogen-bonded to Ser25 and both of the η-amino groups of Arg70 are hydrogen bonded to the main chain oxygen of Gly73 | hydrogen bond donor |
| Cys27 | Cys27A | Cys27 donates a proton to the oxygen on the sulfinate group and attacks the sulfur creating a S-S bond. Cys27 also deprotonates a water molecule which attacks the sulfinate group, removing it from the rest of the substrate. | nucleophile, proton acceptor, proton donor |
Chemical Components
overall reactant used, bimolecular electrophilic substitution, proton transfer, overall product formed, bimolecular nucleophilic additionReferences
- Sousa JPM et al. (2020), ACS Catal, 10, 9545-9554. Reaction Mechanism and Determinants for Efficient Catalysis by DszB, a Key Enzyme for Crude Oil Bio-desulfurization. DOI:https://doi.org/10.1021/acscatal.0c03122.
- Lee WC et al. (2006), J Biol Chem, 281, 32534-32539. Crystal Structure and Desulfurization Mechanism of 2′-Hydroxybiphenyl-2-sulfinic Acid Desulfinase. DOI:https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M602974200.
- Nakayama N et al. (2002), Biochim Biophys Acta Proteins Proteomics, 1598, 122-130. A novel enzyme, 2′-hydroxybiphenyl-2-sulfinate desulfinase (DszB), from a dibenzothiophene-desulfurizing bacterium Rhodococcus erythropolis KA2-5-1: gene overexpression and enzyme characterization. DOI:10.1016/s0167-4838(02)00365-5.

Step 1. Cys27 donates a proton to the oxygen on the sulfinate group and attacks the sulfur creating a S-S bond. The sulfinate is anchored by a hydrogen bond network consisting og His60, Arg70, Ser25 and Gly73.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| His60A | hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Gly73A (main) | hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Ser25A | hydrogen bond donor |
| His60A | hydrogen bond donor |
| Arg70A | hydrogen bond donor |
| Cys27A | proton donor, nucleophile |
Chemical Components
overall reactant used, ingold: bimolecular electrophilic substitution, proton transfer
Step 2. A water molecule is deprotonated by Cys27 and in the same time the resulting hydroxide molecule attacks the sulfinate group, removing it from the rest of the substrate.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Gly73A (main) | electrostatic stabiliser |
| His60A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Ser25A | hydrogen bond donor |
| Arg70A | hydrogen bond donor |
| Gly73A (main) | hydrogen bond acceptor |
| His60A | hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donor |
| Cys27A | proton acceptor |





 Download:
Download:  Download:
Download: