Intracellular protease
The intracellular protease from Pyrococcus horikoshii (PH1704) and PfpI from Pyrococcus furiosus are members of a class of intracellular proteases that have no sequence homology to any other known protease family. They have significant similarity with deglycases that catalyse the deglycation of the Maillard adducts formed between amino groups of proteins and reactive carbonyl groups of glyoxals. The protein is a member of the DJ-1 family, mutations of which appear to have a significant role in the cause of recessively transmitted early-onset Parkinson disease (PD), and oxidative damage to DJ-1 has been associated with the pathogenesis of late-onset sporadic PD. However, the precise role of DJ-1 proteins have yet to be fully elucidated.
Reference Protein and Structure
- Sequence
-
O59413
 (3.4.22.-, 3.5.1.124)
(3.4.22.-, 3.5.1.124)
 (Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
(Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
- Biological species
-
Pyrococcus horikoshii OT3 (Bacteria)

- PDB
-
1g2i
- CRYSTAL STRUCTURE OF A NOVEL INTRACELLULAR PROTEASE FROM PYROCOCCUS HORIKOSHII AT 2 A RESOLUTION
(2.0 Å)



- Catalytic CATH Domains
-
3.40.50.880
 (see all for 1g2i)
(see all for 1g2i)
Enzyme Mechanism
Introduction
The nucleophillic cysteine then attacks the carbonyl group adjacent to the amine group in the same manner as other cysteine proteases, with Cys100 acting as a nucleophile and water then cleaving the enzyme-substrate adduct.
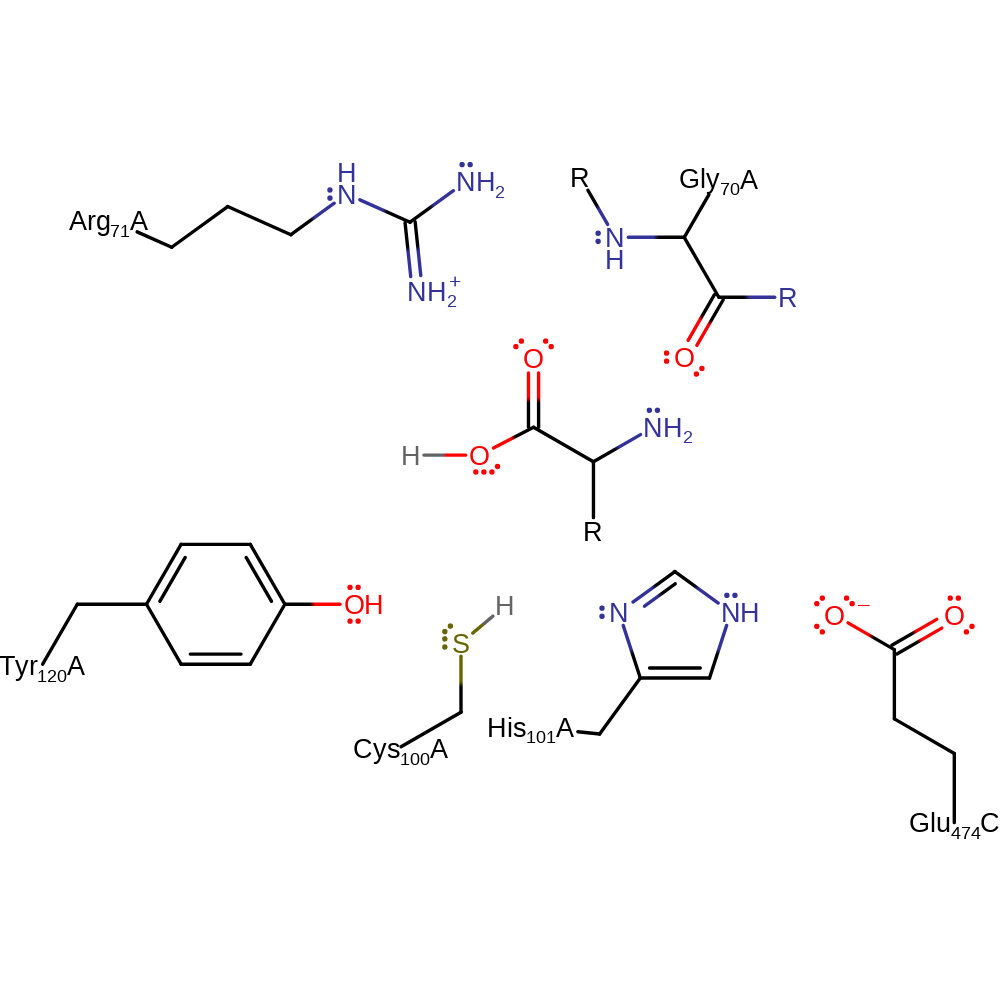
Catalytic Residues Roles
| UniProt | PDB* (1g2i) | ||
| Glu74 | Glu474(74)C | Activates the histidine as the acid/base in the catalytic triad. | modifies pKa, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Cys100 | Cys100A | Thought to be the catalytic nucleophile based on the presence of the nucleophile elbow in the crystal structure and similarity to other similar enzymes in the family. It also forms a "catalytic triad" with His101 and Glu474 (from an adjacent monomer). | covalently attached, nucleofuge, nucleophile, proton acceptor, proton donor |
| His101 | His101A | Thought to act as a general acid/base in the catalytic triad that activates cysteine to function as the nucleophile. | proton acceptor, electrostatic stabiliser, proton donor |
| Tyr120 | Tyr120A | Mutational studies suggest involvement in enzyme activity to form a hydrogen bond with Cys100, helping activate that residue. The residue also acts as an entrance gate to the active site along with Lys43. | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Arg71, Gly70 (main-N) | Arg71A, Gly70A (main-N) | Form the oxyanion hole that stabilises the reactive intermediates. | electrostatic stabiliser |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, bimolecular nucleophilic addition, overall reactant used, enzyme-substrate complex formation, unimolecular elimination by the conjugate base, overall product formed, enzyme-substrate complex cleavage, native state of enzyme regeneratedReferences
- Zhan D et al. (2014), PLoS One, 9, e103902-. Characterization of the PH1704 protease from Pyrococcus horikoshii OT3 and the critical functions of Tyr120. DOI:10.1371/journal.pone.0103902. PMID:25192005.
- Richarme G et al. (2016), Biochem Biophys Res Commun, 478, 1111-1116. DJ-1 family Maillard deglycases prevent acrylamide formation. DOI:10.1016/j.bbrc.2016.08.077. PMID:27530919.
- Du X et al. (2000), Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, 97, 14079-14084. Crystal structure of an intracellular protease from Pyrococcus horikoshii at 2-A resolution. DOI:10.1073/pnas.260503597. PMID:11114201.
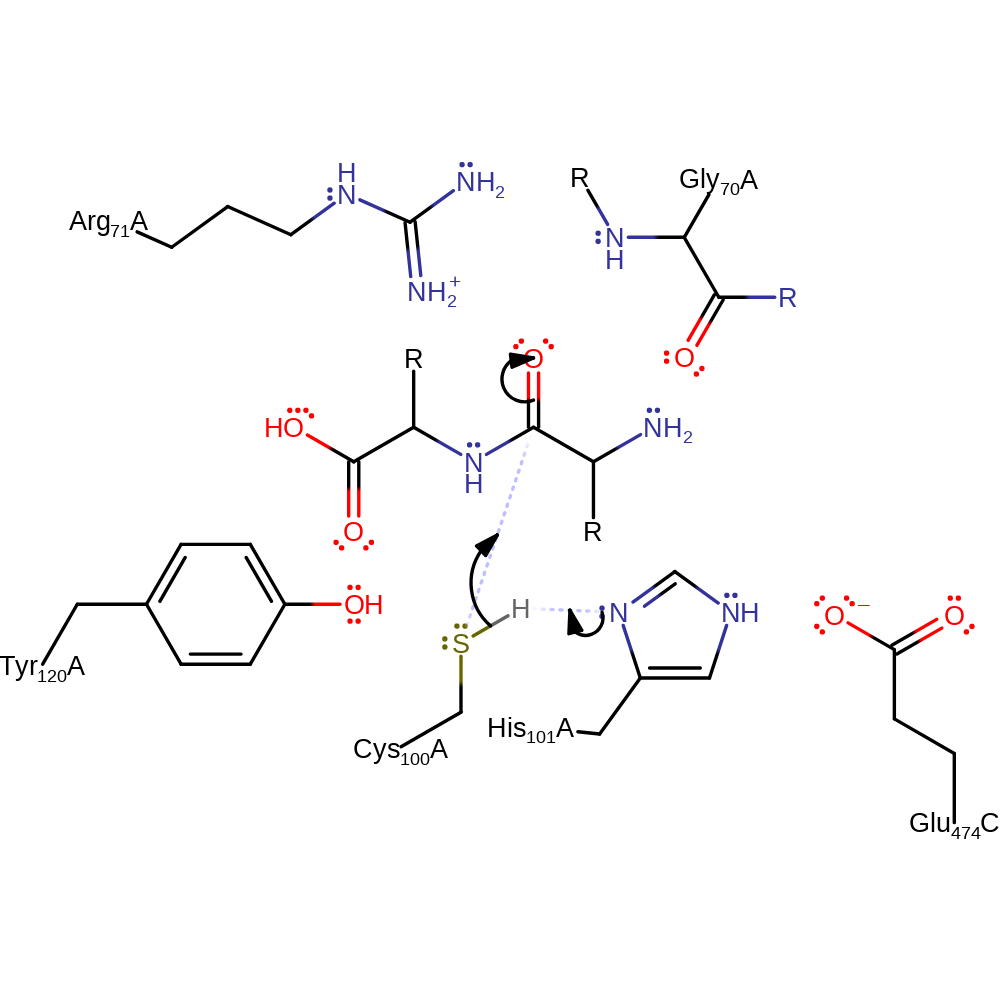
Step 1. His101 activates the catalytic cysteine to act as a nucleophile, which in turn attacks the substrate to form the enzyme-substrate adduct.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Gly70A (main-N) | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Arg71A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| His101A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Tyr120A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Glu474(74)C | electrostatic stabiliser, modifies pKa |
| Cys100A | nucleophile |
| His101A | proton acceptor |
| Cys100A | proton donor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, ingold: bimolecular nucleophilic addition, overall reactant used, enzyme-substrate complex formation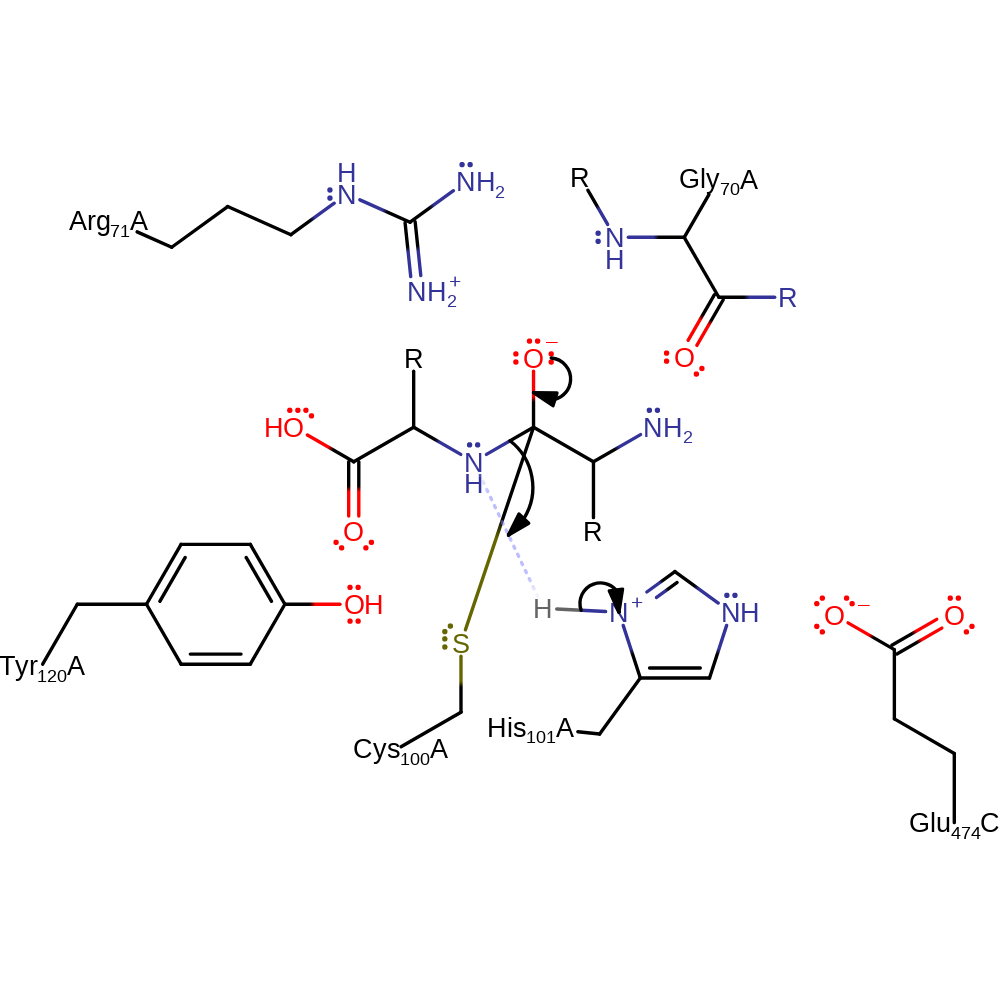
Step 2. The oxyanion collapses and eliminates the first of the products.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Cys100A | covalently attached |
| Gly70A (main-N) | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Arg71A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Tyr120A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Glu474(74)C | modifies pKa |
| His101A | proton donor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, ingold: unimolecular elimination by the conjugate base, overall product formed, enzyme-substrate complex cleavage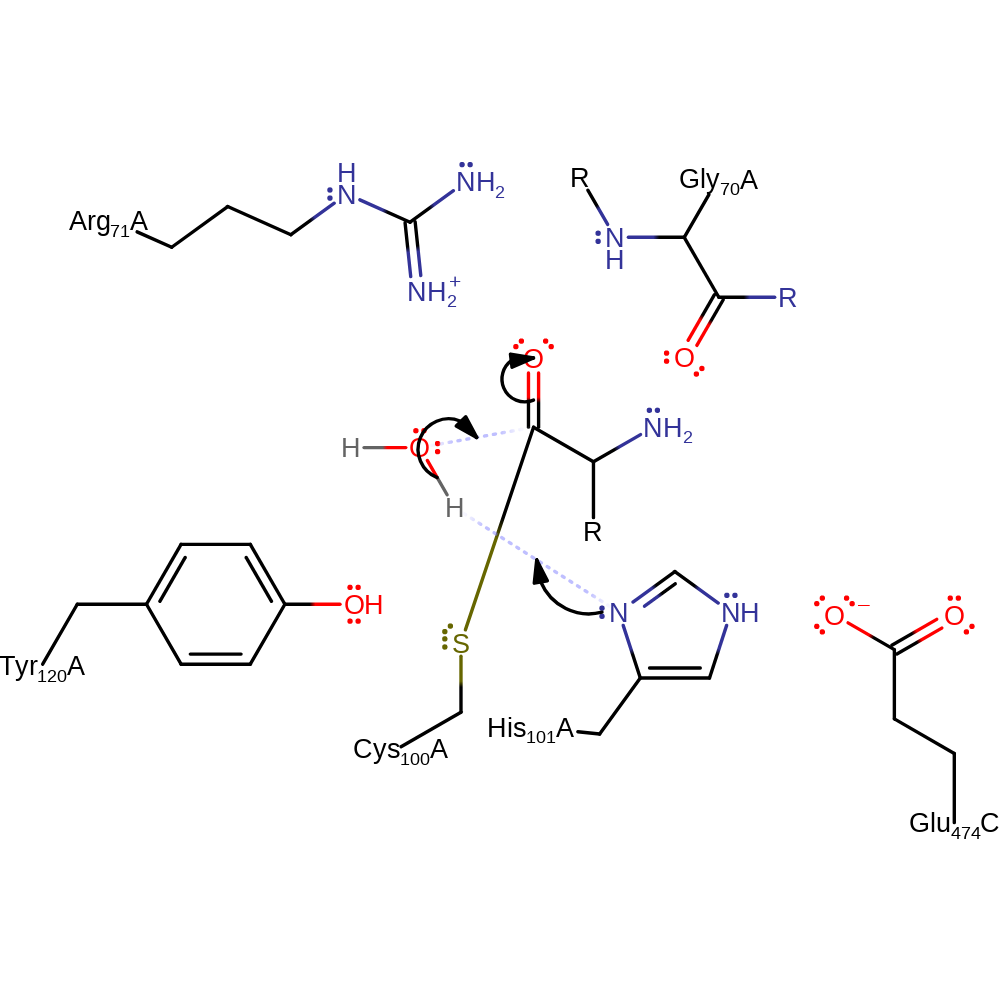
Step 3. His101 abstracts a proton from the substrate water molecule, which attacks the carbonyl group of the enzyme-intermediate adduct.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Gly70A (main-N) | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Arg71A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Tyr120A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Glu474(74)C | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Cys100A | covalently attached |
| Glu474(74)C | modifies pKa |
| His101A | proton acceptor |
Chemical Components
overall reactant used, ingold: bimolecular nucleophilic addition, proton transfer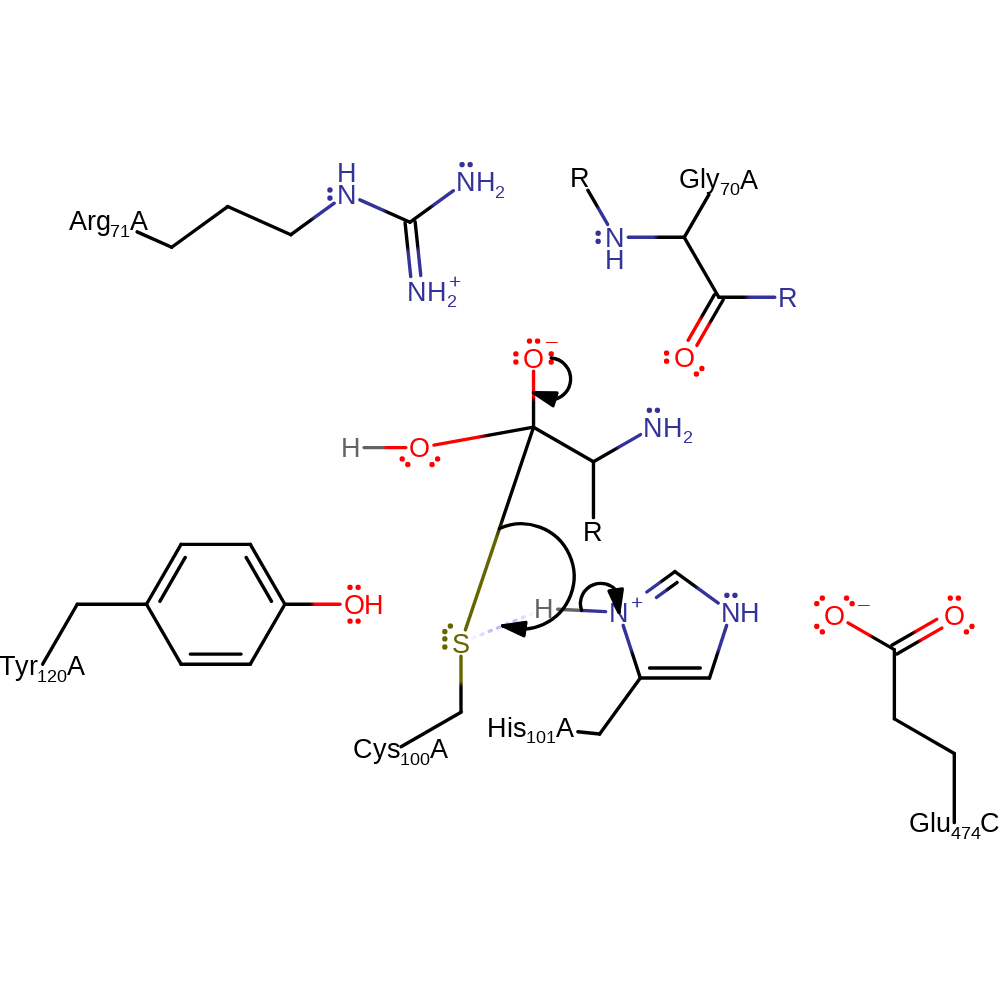
Step 4. The oxyanion collapses, eliminating the cysteine residue and forming the final product of the reaction.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Glu474(74)C | modifies pKa |
| Gly70A (main-N) | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Arg71A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| His101A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Tyr120A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Glu474(74)C | electrostatic stabiliser |
| His101A | proton donor |
| Cys100A | nucleofuge, proton acceptor |



 Download:
Download: