Isotuberculosinol synthase
This enzyme is responsible for the conversion of tuberculosinyl diphosphate to tuberculosinol and the R and S iso-tuberculosinols. Tuberculosinols are one class of virulence factor in Mycobacterium tuberculosis. The active site for both of these functions is the same, but the R- and S-iso-tuberculosinol formation involves the addition of water at the C13 atom, rather than the C15, and involve an allylic rearrangement.
Reference Protein and Structure
- Sequence
-
P9WJ61
 (2.5.1.153)
(2.5.1.153)
 (Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
(Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
- Biological species
-
Mycobacterium tuberculosis H37Rv (Bacteria)

- PDB
-
3wql
- Crystal structure of Rv3378c with Mg2+ and PPi
(2.1 Å)



- Catalytic CATH Domains
-
3.40.1180.10
 (see all for 3wql)
(see all for 3wql)
- Cofactors
- Magnesium(2+) (1)
Enzyme Mechanism
Introduction
This mechanism represents formation of the 13R product. the Tyr51 abstracts a proton from the catalytic water, which attacks the C13 position. This initiates an allylic rearrangement and elimination of the phosphate group with concomitant deprotonation of Arg38.
Catalytic Residues Roles
| UniProt | PDB* (3wql) | ||
| Asp34 | Asp34B | Forms part of the magnesium binding site. | metal ligand |
| Tyr90 | Tyr90B | No direct function in this mechanism proposal, although may help to activate the Arg38 to act as a general acid/base. | activator |
| Arg38, Tyr51 | Arg38B, Tyr51B | Acts as a general acid/base. | proton acceptor, proton donor |
Chemical Components
bimolecular nucleophilic substitution with allylic rearrangement, proton transfer, overall reactant used, overall product formed, hydrolysis, inferred reaction step, native state of enzyme regeneratedReferences
- Chan HC et al. (2014), J Am Chem Soc, 136, 2892-2896. Structure and inhibition of tuberculosinol synthase and decaprenyl diphosphate synthase from Mycobacterium tuberculosis. DOI:10.1021/ja413127v. PMID:24475925.
- Nakano C et al. (2011), Biosci Biotechnol Biochem, 75, 75-81. Characterization of the Rv3378c gene product, a new diterpene synthase for producing tuberculosinol and (13R, S)-isotuberculosinol (nosyberkol), from the Mycobacterium tuberculosis H37Rv genome. DOI:10.1271/bbb.100570. PMID:21228491.

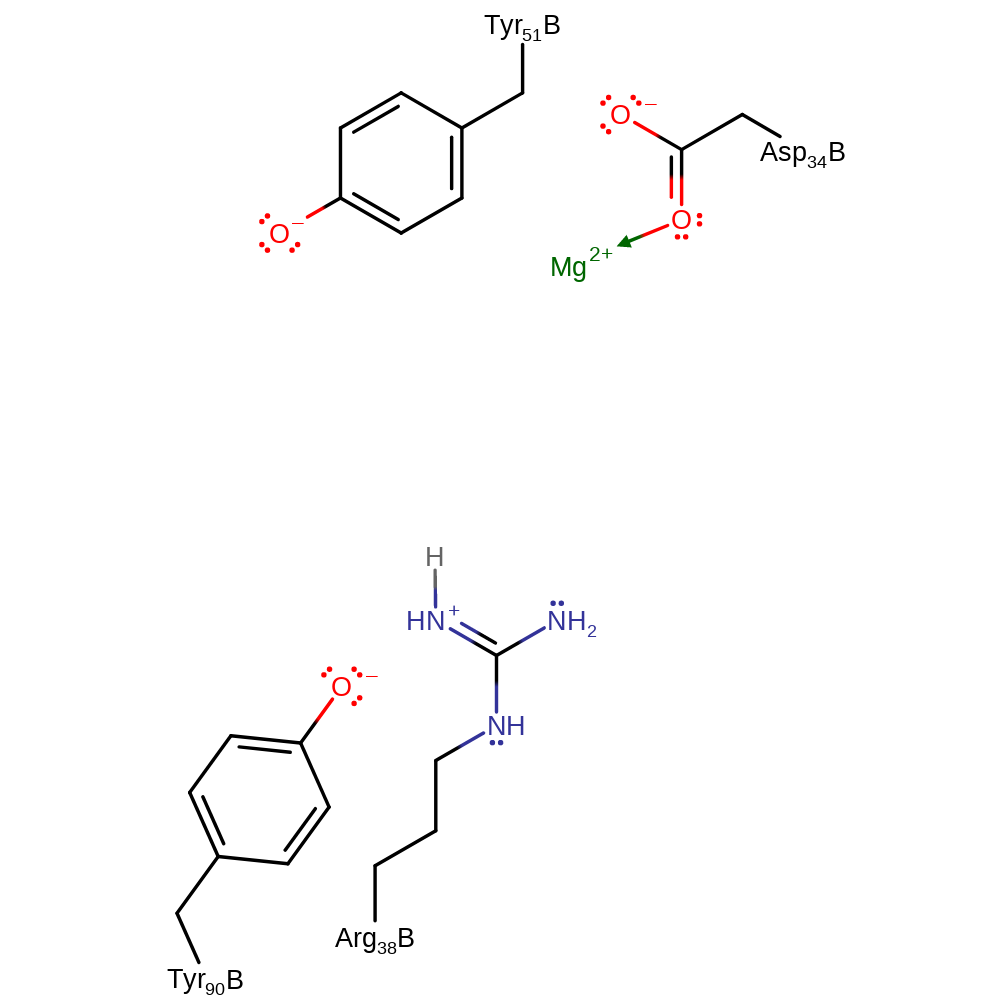
Step 1. Tyr51 abstracts a proton from the catalytic water, which attacks the C13 position. This initiates an allylic rearrangement and elimination of the phosphate group with concomitant deprotonation of Arg38.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Asp34B | metal ligand |
| Tyr51B | proton acceptor |
| Arg38B | proton donor |
Chemical Components
ingold: bimolecular nucleophilic substitution with allylic rearrangement, proton transfer, overall reactant used, overall product formed, hydrolysis
Step 2. Inferred return step. It is unknown if the transfer of a proton from Tyr51 to Arg38 is direct or mediated through one or more water molecules.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Asp34B | metal ligand |
| Tyr90B | activator |
| Tyr51B | proton donor |
| Arg38B | proton acceptor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, inferred reaction step, native state of enzyme regeneratedIntroduction
This mechanism represents formation of the 13S product. Tyr80 abstracts a proton from the catalytic water, which attacks the C13 position. This initiates an allylic rearrangement and elimination of the phosphate group with concomitant deprotonation of Arg38.
Catalytic Residues Roles
| UniProt | PDB* (3wql) | ||
| Asp34 | Asp34B | Forms part of the magnesium binding site. | metal ligand |
| Arg38, Tyr90 | Arg38B, Tyr90B | Acts as a general acid/base. | proton acceptor, proton donor |
| Tyr51 | Tyr51B | No direct function in this mechanism proposal. |
Chemical Components
hydrolysis, overall product formed, overall reactant used, proton transfer, bimolecular nucleophilic substitution with allylic rearrangement, inferred reaction step, native state of enzyme regeneratedReferences
- Chan HC et al. (2014), J Am Chem Soc, 136, 2892-2896. Structure and inhibition of tuberculosinol synthase and decaprenyl diphosphate synthase from Mycobacterium tuberculosis. DOI:10.1021/ja413127v. PMID:24475925.
- Nakano C et al. (2011), Biosci Biotechnol Biochem, 75, 75-81. Characterization of the Rv3378c gene product, a new diterpene synthase for producing tuberculosinol and (13R, S)-isotuberculosinol (nosyberkol), from the Mycobacterium tuberculosis H37Rv genome. DOI:10.1271/bbb.100570. PMID:21228491.

Step 1. Tyr80 abstracts a proton from the catalytic water, which attacks the C13 position. This initiates an allylic rearrangement and elimination of the phosphate group with concomitant deprotonation of Arg38.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Asp34B | metal ligand |
| Tyr90B | proton acceptor |
| Arg38B | proton donor |
Chemical Components
hydrolysis, overall product formed, overall reactant used, proton transfer, ingold: bimolecular nucleophilic substitution with allylic rearrangement
Step 2. In an inferred return step, Arg38 abstracts a proton from Tyr90.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Asp34B | metal ligand |
| Arg38B | proton acceptor |
| Tyr90B | proton donor |




 Download:
Download: 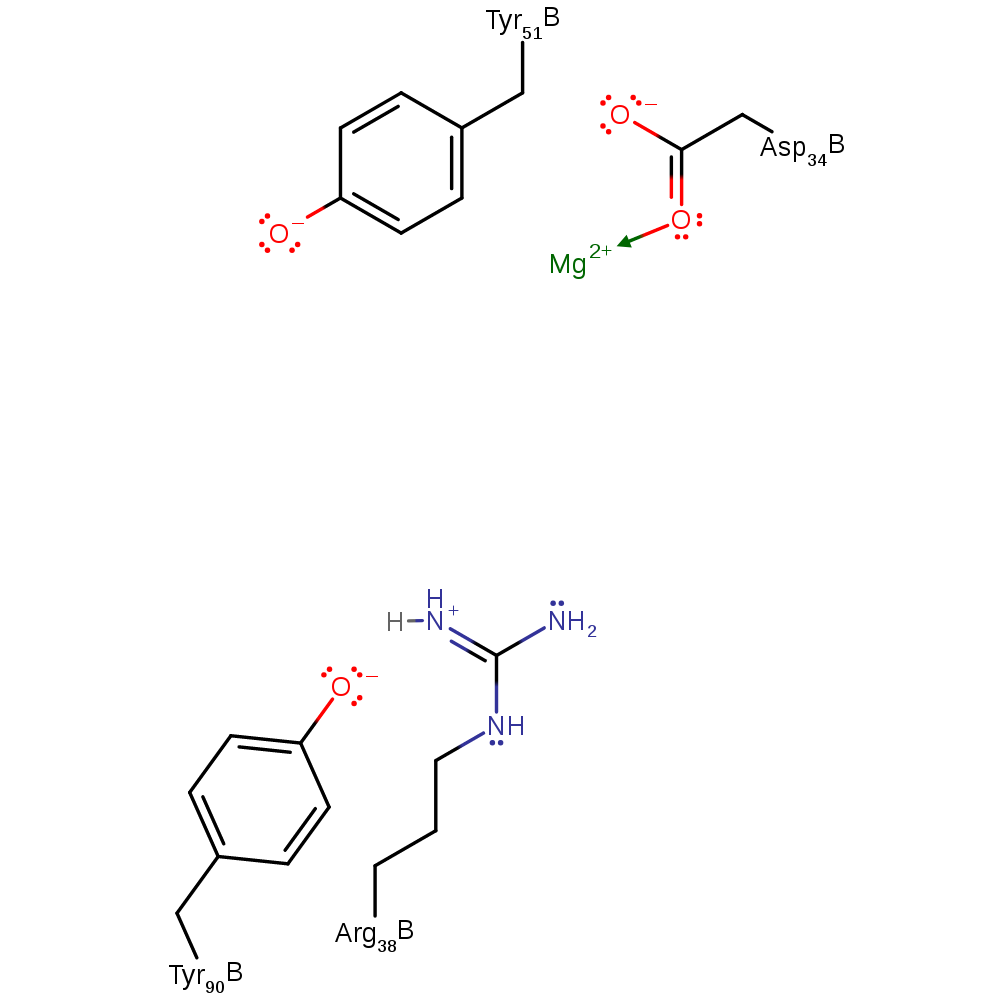 Download:
Download: