L-fucose isomerase
L-fuctose isomerase, also known as arabinose isomerase (EC 5.3.1.3) uses both L-fucose and arabinose as substrates, converting the aldo-hexoses to ketoses to prepare them for aldol cleavage within the L-fucose metabolism pathway.
The enzyme binds the closed form of the sugar and catalyses ring opening to generate a form of open-chain conformation that facilitates the isomerisation reaction, which proceeds via an ene-diol mechanism
Reference Protein and Structure
- Sequence
-
P69922
 (5.3.1.3, 5.3.1.25)
(5.3.1.3, 5.3.1.25)
 (Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
(Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
- Biological species
-
Escherichia coli K-12 (Bacteria)

- PDB
-
1fui
- L-FUCOSE ISOMERASE FROM ESCHERICHIA COLI
(2.5 Å)



- Catalytic CATH Domains
-
3.20.14.10
 3.40.275.10
3.40.275.10  (see all for 1fui)
(see all for 1fui)
- Cofactors
- Water (1), Manganese(2+) (1) Metal MACiE
Enzyme Mechanism
Introduction
Asp361 is thought to act as a general base towards the C1-OH of the cyclic substrate, initiating ring opening. Glu337 then abstracts the alpha proton to the aldehyde group, with concomitant deprotonation of Asp361 by the developing anion, forming an enol intermediate. Asp361 is now charged and acts as a base again but this time at the C2 enol OH, leading to the formation of a ketone group with simultaneous reprotonation of the C1 from Glu337, forming an alpha hydroxyl group. The product cyclises and leaves the active site while a hydroxyl coordinated to the catalytically essential Mn divalent cation deprotonates Asp361, regenerating the active site.
Catalytic Residues Roles
| UniProt | PDB* (1fui) | ||
| Glu337 | Glu337A | Forms part of the manganese binding site. The residue acts as a general base and acid towards the substrate, facilitating the aldose-ketose interconversion. | hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donor, metal ligand, proton acceptor, proton donor |
| Asp361 | Asp361A | Forms part of the manganese bindig site. The residue acts as a general base and acid towards the substrate, initiating ring opening and facilitating the aldose-ketose interconversion | hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donor, metal ligand, proton acceptor, proton donor |
| His528 | His528A | Forms part of the manganese binding site. | metal ligand |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, bimolecular elimination, decyclisation, assisted keto-enol tautomerisation, intermediate formation, intermediate terminated, native state of enzyme regenerated, inferred reaction step, reaction occurs outside the enzyme, cyclisationReferences
- Seemann JE et al. (1997), J Mol Biol, 273, 256-268. Structure and mechanism of l-fucose isomerase from Escherichia coli. DOI:10.1006/jmbi.1997.1280. PMID:9367760.
- Prabhu P et al. (2010), Appl Environ Microbiol, 76, 1653-1660. Probing the Molecular Determinant for the Catalytic Efficiency of L-Arabinose Isomerase from Bacillus licheniformis. DOI:10.1128/aem.02254-09. PMID:20048061.
- Kim JH et al. (2010), Appl Microbiol Biotechnol, 85, 1839-1847. Characterization of an L-arabinose isomerase from Bacillus subtilis. DOI:10.1007/s00253-009-2210-6. PMID:19727704.
- Rhimi M et al. (2007), J Bacteriol, 189, 3556-3563. Probing the Essential Catalytic Residues and Substrate Affinity in the Thermoactive Bacillus stearothermophilus US100 L-Arabinose Isomerase by Site-Directed Mutagenesis. DOI:10.1128/jb.01826-06. PMID:17337581.
- Collyer CA et al. (1990), Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, 87, 1362-1366. Observations of reaction intermediates and the mechanism of aldose-ketose interconversion by D-xylose isomerase. DOI:10.1073/pnas.87.4.1362. PMID:2304904.
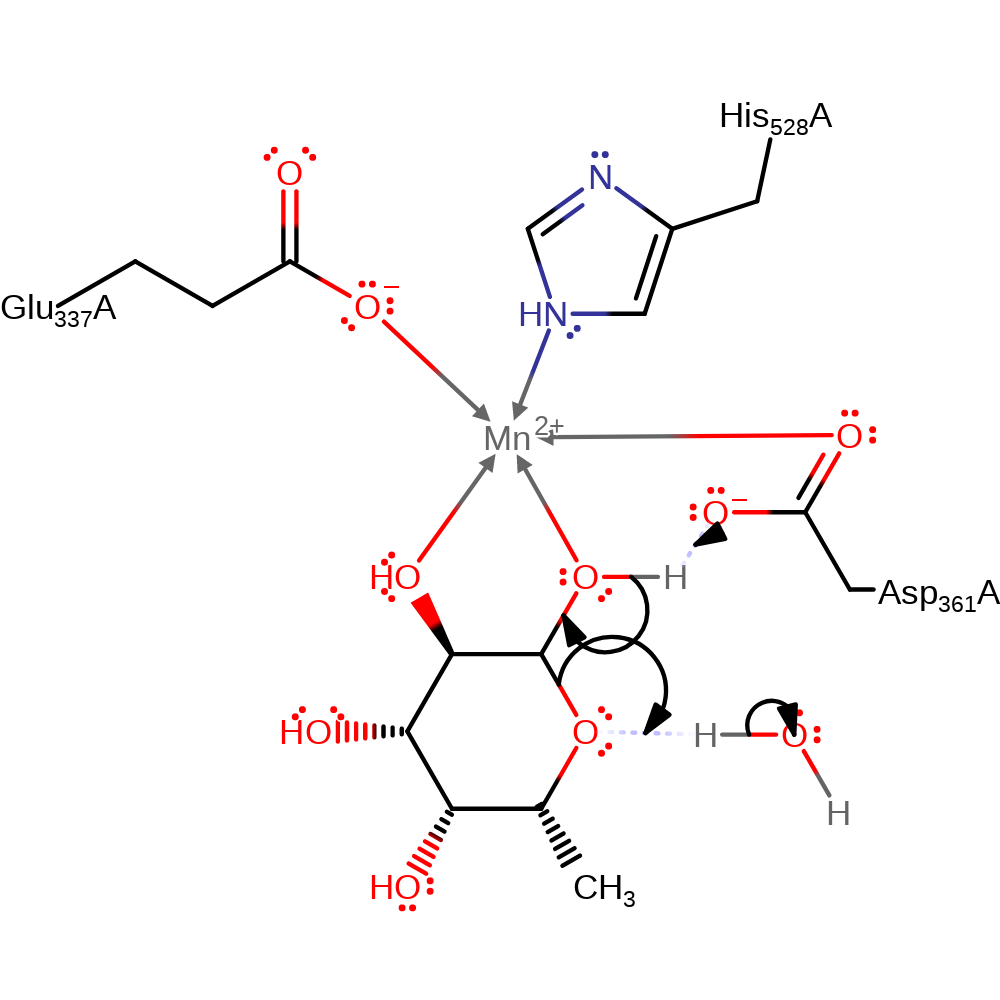
Step 1. Asp361 deprotonates the C1 alcohol of the sugar, initiating ring-opening. The C5 oxygen deprotonates water.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Asp361A | hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Asp361A | metal ligand |
| Glu337A | metal ligand |
| His528A | metal ligand |
| Asp361A | proton acceptor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, ingold: bimolecular elimination, decyclisation
Step 2. Glu337 deprotonates the C2 carbon, initiating double bond rearrangement to form the enol-form of the substrate. The newly formed oxyanion deprotonates Asp361.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Asp361A | hydrogen bond donor |
| Glu337A | hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Asp361A | metal ligand |
| Glu337A | metal ligand |
| His528A | metal ligand |
| Glu337A | proton acceptor |
| Asp361A | proton donor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, assisted keto-enol tautomerisation, intermediate formation
Step 3. Asp361 deprotonates the C2 alcohol, initiating double bond rearrangement, and the C1 atom deprotonates Glu337 to re-form the keto-form of the substrate.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Asp361A | hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Glu337A | hydrogen bond donor |
| Asp361A | metal ligand |
| Glu337A | metal ligand |
| His528A | metal ligand |
| Glu337A | proton donor |
| Asp361A | proton acceptor |
Chemical Components
assisted keto-enol tautomerisation, proton transfer, intermediate terminated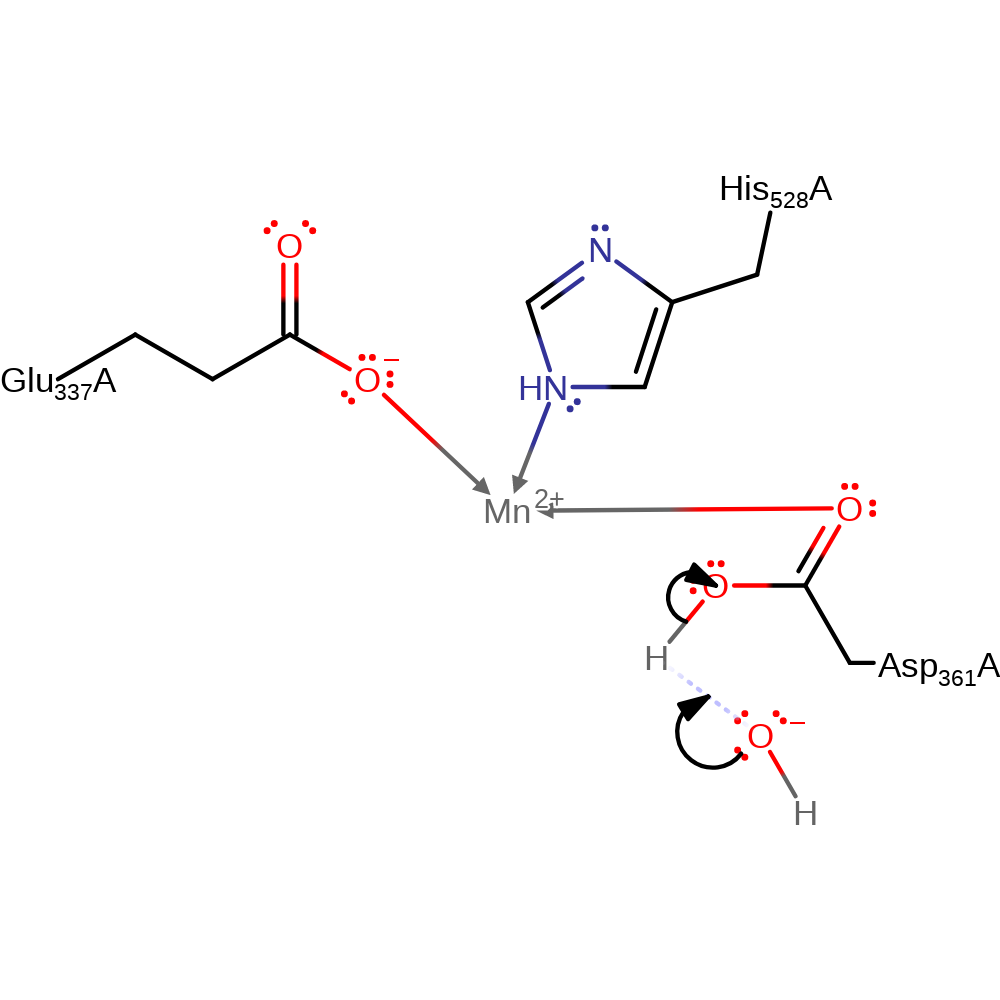
Step 4. In an inferred return step, water deprotonates Asp361 to regenerate the enzyme active site.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Asp361A | hydrogen bond donor |
| Asp361A | metal ligand |
| Glu337A | metal ligand |
| His528A | metal ligand |
| Asp361A | proton donor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, native state of enzyme regenerated, inferred reaction step
Step 5. Ring closing to form the ribulose product is assumed to occur outside of the enzyme active site.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|
Chemical Components
reaction occurs outside the enzyme, cyclisationIntroduction
The hydride-shift mechanism, in which the hydrogen atom at C2 migrates as a hydride to C1.
Catalytic Residues Roles
| UniProt | PDB* (1fui) | ||
| Glu337, Asp361, His528 | Glu337A, Asp361A, His528A | Form the manganese binding site. | metal ligand |
Chemical Components
References
- Seemann JE et al. (1997), J Mol Biol, 273, 256-268. Structure and mechanism of l-fucose isomerase from Escherichia coli. DOI:10.1006/jmbi.1997.1280. PMID:9367760.
Catalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Glu337A | metal ligand |
| Asp361A | metal ligand |
| His528A | metal ligand |


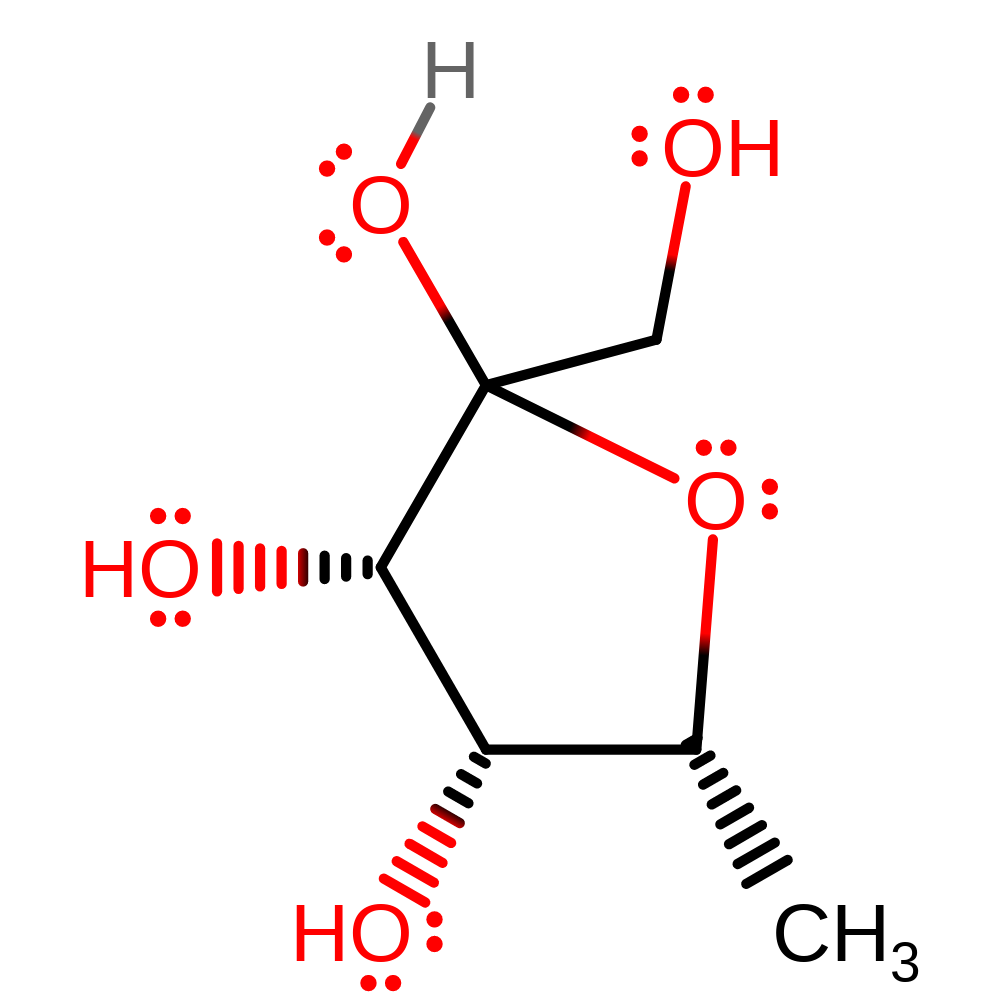 Download:
Download: 