Alpha-D-ribose 1-methylphosphonate 5-phosphate C-P-lyase
This radical SAM (AdoMet) enzyme is part of the C-P lyase complex, which is responsible for processing phophonates into usable phosphate. The enzyme from the bacterium Escherichia coli can act on additional alpha-D-ribose phosphonate substrates with different substituents attached to the phosphonate phosphorus (e.g. alpha-D-ribose-1- (N-(phosphonomethyl)glycine)-5-phosphate and alpha-D-ribose-1-(2-N- acetamidomethylphosphonate)-5-phosphate).
Reference Protein and Structure
- Sequence
-
P16688
 (4.7.1.1)
(4.7.1.1)
 (Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
(Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
- Biological species
-
Escherichia coli K-12 (Bacteria)

- PDB
-
4xb6
- Structure of the E. coli C-P lyase core complex
(1.7 Å)



- Catalytic CATH Domains
- (see all for 4xb6)
- Cofactors
- Tetra-mu3-sulfido-tetrairon (1)
Enzyme Mechanism
Introduction
The reaction cascade is initiated by formation of a 5'-deoxyadenosyl radical. This intermediate abstracts the pro-R hydrogen from Gly 32 to form a glycyl radical. Hydrogen atom transfer from Cys 272 to the Gly 32 radical generates a thiyl radical on the side chain of Cys 272. This radical attacks the phosphonate moiety of the substrate to create a thiophosphonate radical intermediate. Homolytic C–P bond cleavage and hydrogen atom transfer from the original pro-S hydrogen of Gly 32 produces a thiophosphate intermediate, methane, and regenerates the radical intermediate at Gly 32. The ultimate product, PRcP, is formed by nucleophilic attack of the C2 hydroxyl on the covalent thiophosphate intermediate.
Catalytic Residues Roles
| UniProt | PDB* (4xb6) | ||
| Gly32 | Gly32D | Acts as a radical hydrogen atom proton/donor. | hydrogen radical acceptor, hydrogen radical donor |
| Cys266, Cys244, Cys241 | Cys266D, Cys244D, Cys241D | Forms the iron-sulfur cluster binding site. | metal ligand |
| Cys272 | Cys272D | Acts as a hydrogen atom acceptor/donor and also as a radical combinant and nucleofuge. | hydrogen radical donor, covalently attached, nucleofuge, proton acceptor, radical combinant |
Chemical Components
inferred reaction step, homolysis, electron transfer, overall reactant used, overall product formed, hydrogen transfer, bimolecular homolytic addition, unimolecular homolytic elimination, proton transfer, native state of enzyme regenerated, bimolecular nucleophilic substitutionReferences
- Kamat SS et al. (2013), Nature, 497, 132-136. The catalytic mechanism for aerobic formation of methane by bacteria. DOI:10.1038/nature12061. PMID:23615610.
- Seweryn P et al. (2015), Nature, 525, 68-72. Structural insights into the bacterial carbon-phosphorus lyase machinery. DOI:10.1038/nature14683. PMID:26280334.
- Kamat SS et al. (2011), Nature, 480, 570-573. Intermediates in the transformation of phosphonates to phosphate by bacteria. DOI:10.1038/nature10622. PMID:22089136.

Step 1. Initial formation of the 5'-deoxyadenosyl radical. The mechanism is assumed to be identical to other Radical SAM type proteins.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Cys241D | metal ligand |
| Cys266D | metal ligand |
| Cys244D | metal ligand |
Chemical Components
inferred reaction step, homolysis, electron transfer, overall reactant used, overall product formed
Step 2. The adenosyl radical abstracts a hydrogen atom from the catalytic glycine residue. The products of this activation step represent the ground state of this enzyme.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Cys241D | metal ligand |
| Cys266D | metal ligand |
| Cys244D | metal ligand |
| Gly32D | hydrogen radical donor |
Chemical Components
hydrogen transfer, overall product formed
Step 3. The glycyl radical abstracts a hydrogen atom from the catalytic cysteine residue.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Cys241D | metal ligand |
| Cys266D | metal ligand |
| Cys244D | metal ligand |
| Cys272D | hydrogen radical donor |
| Gly32D | hydrogen radical acceptor |
Chemical Components
hydrogen transfer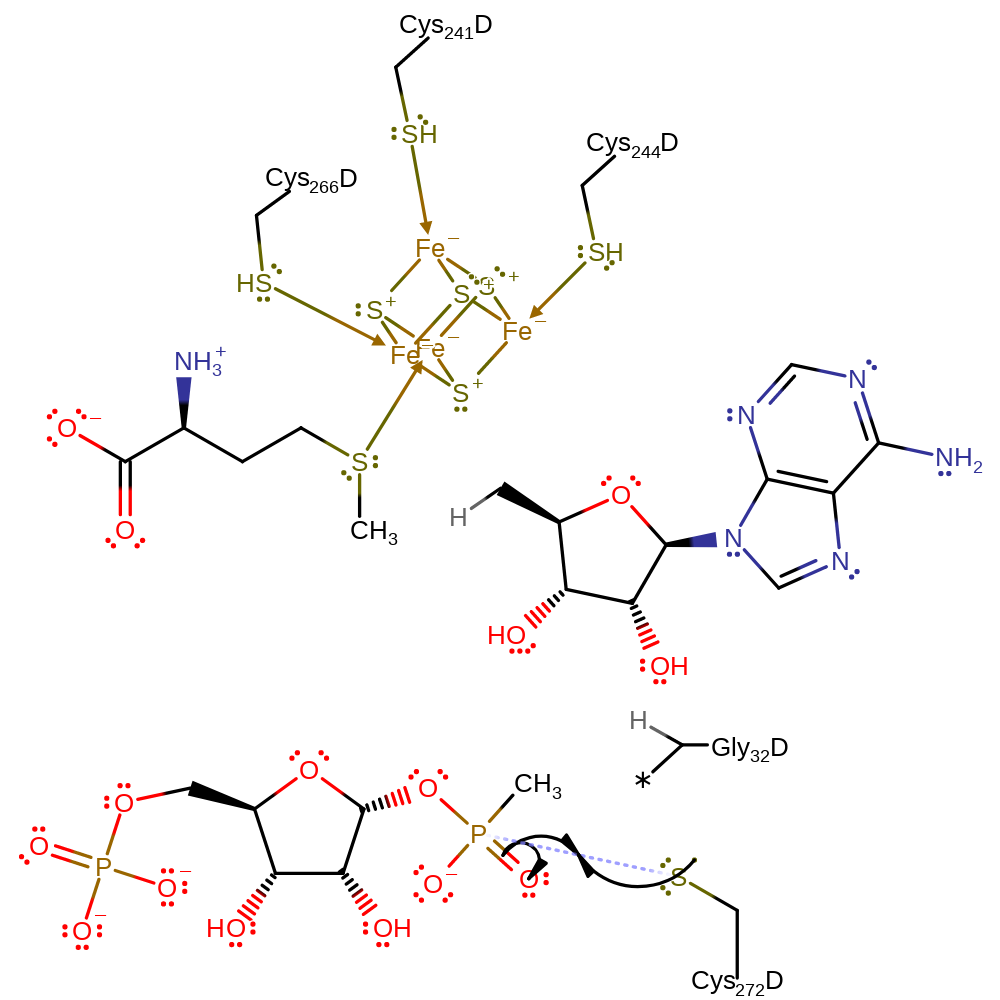
Step 4. The cysteinyl residue attacks the phosphate group, forming a pentavalent intermediate.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Cys241D | metal ligand |
| Cys266D | metal ligand |
| Cys244D | metal ligand |
| Cys272D | radical combinant |
Chemical Components
ingold: bimolecular homolytic addition, overall reactant used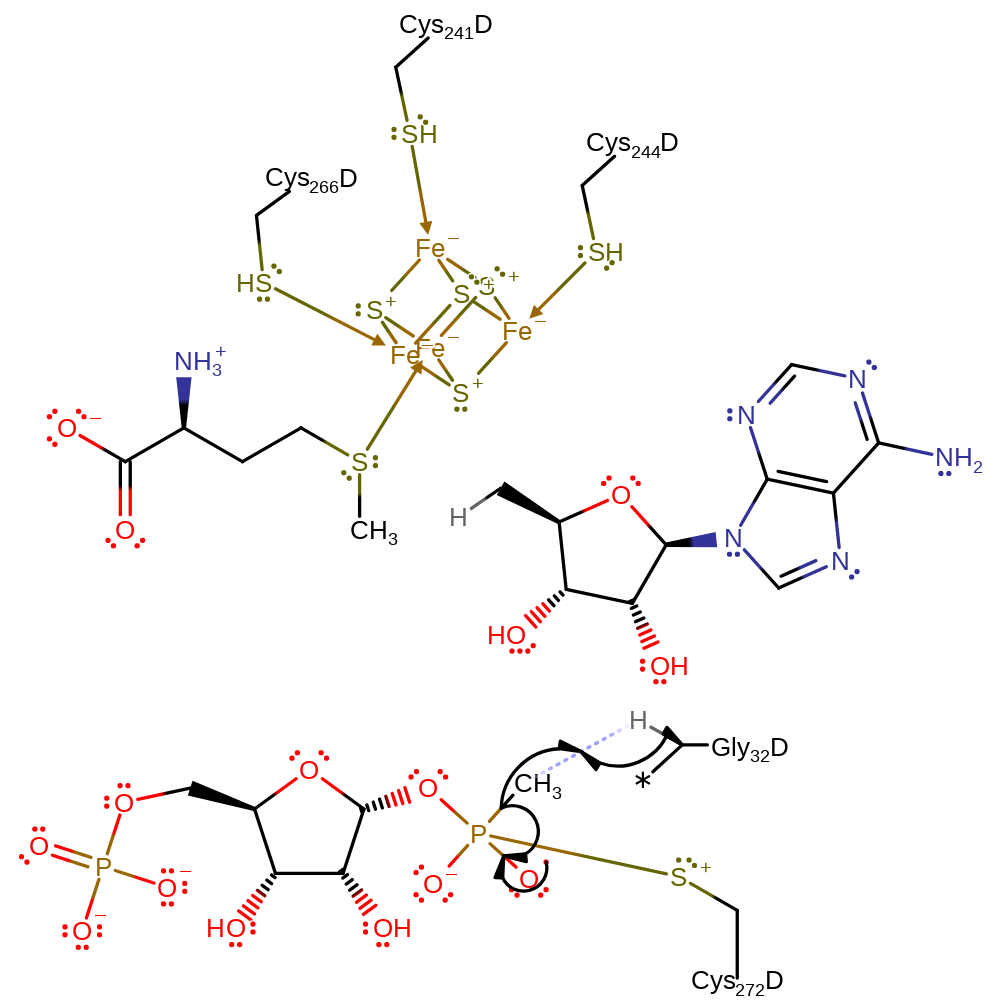
Step 5. The pentavalent intermediate collapses, eliminating a methyl radical with concomitant abstraction of a hydrogen atom from the glycine residue.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Cys241D | metal ligand |
| Cys266D | metal ligand |
| Cys244D | metal ligand |
| Cys272D | covalently attached |
| Gly32D | hydrogen radical donor |
Chemical Components
ingold: unimolecular homolytic elimination, hydrogen transfer, overall product formed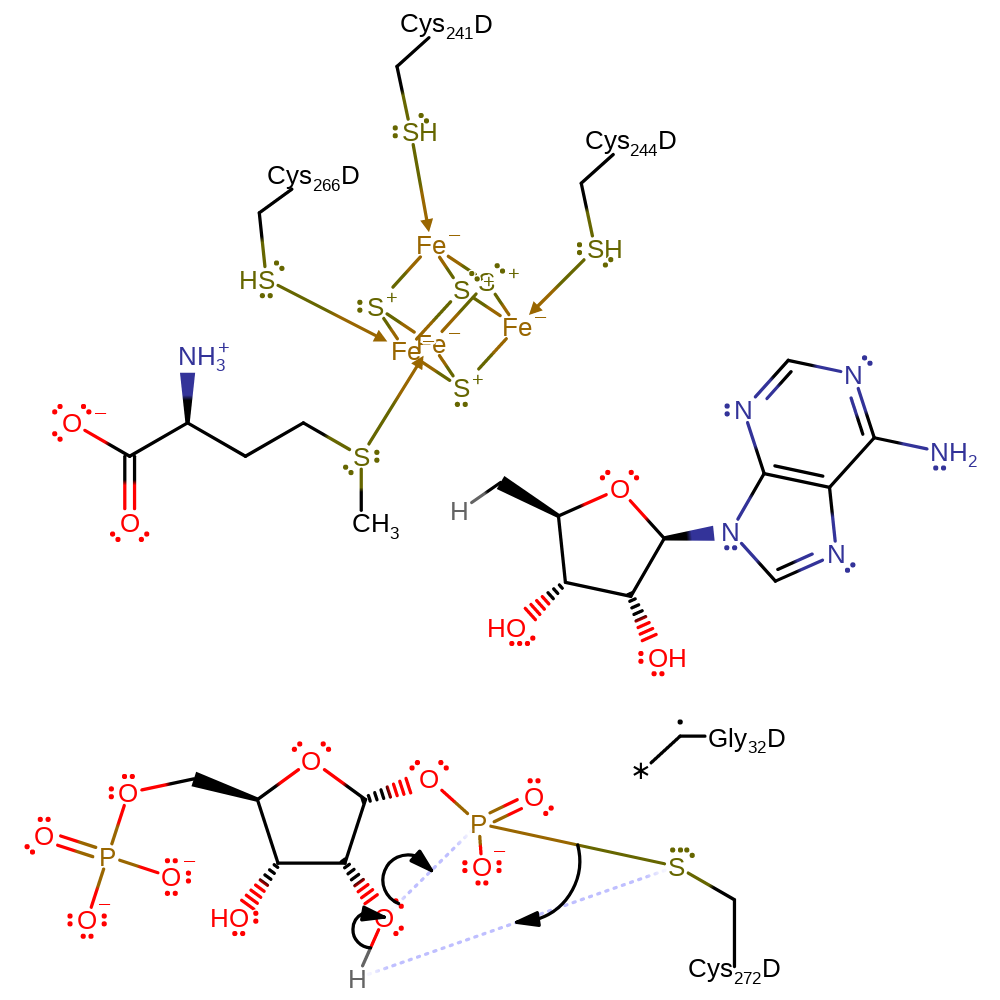
Step 6. One of the hydroxyl groups of the ribose intermediate initiates a nucleophilic attack on the covalently bound phosphate to regenerate the cysteine residue and final product. The enzyme is now in a state that it can perform another round of catalysis.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Cys241D | metal ligand |
| Cys266D | metal ligand |
| Cys244D | metal ligand |
| Cys272D | proton acceptor, nucleofuge |







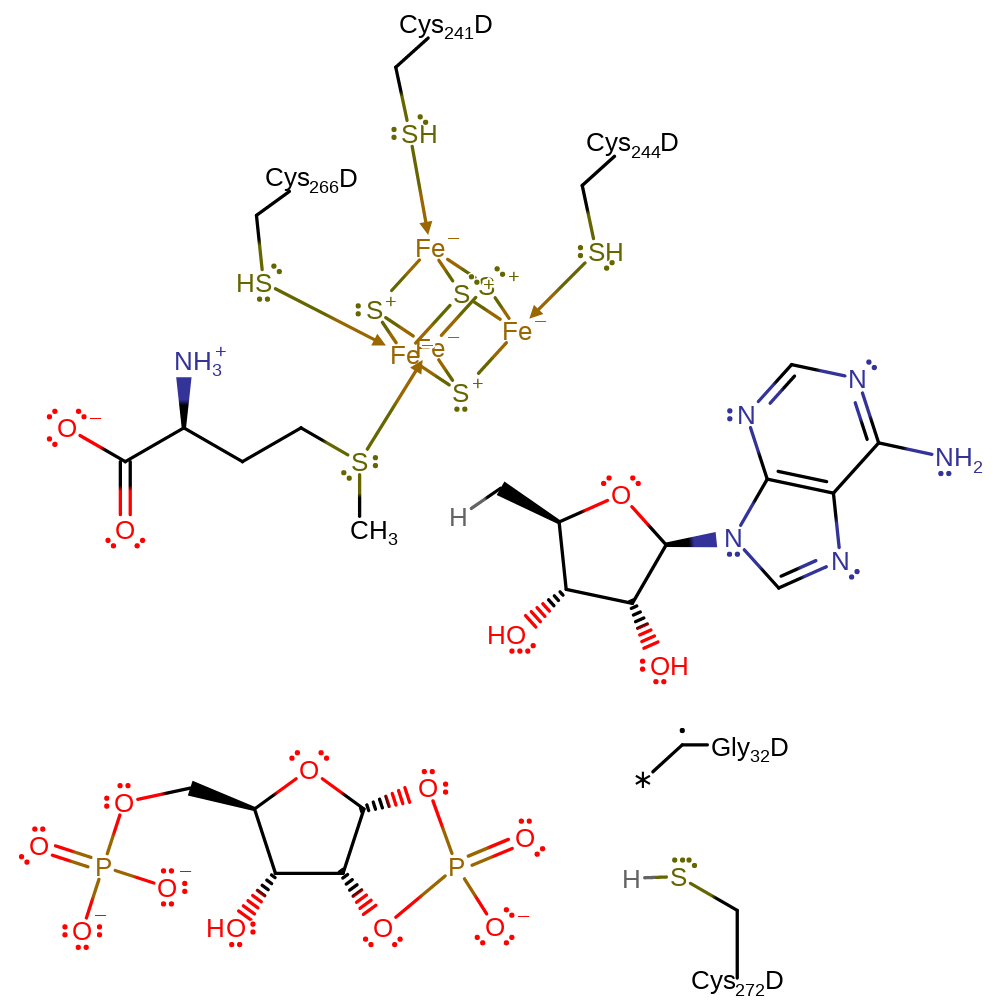 Download:
Download: