Methionyl aminopeptidase
Methionine aminopeptidase (MAP) catalyses the hydrolytic cleavage of the N-terminal methionine from newly synthesised polypeptides. These enzymes have a requirement for a divalent metal which has been shown to be feasible with multiple different metal ions including Co(II), Mn(II), Fe(II) and Zn(II) with Zinc showing to be the lowest activation energy .
Reference Protein and Structure
- Sequence
-
P56218
 (3.4.11.18)
(3.4.11.18)
 (Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
(Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
- Biological species
-
Pyrococcus furiosus DSM 3638 (Archaea)

- PDB
-
1xgm
- METHIONINE AMINOPEPTIDASE FROM HYPERTHERMOPHILE PYROCOCCUS FURIOSUS
(2.8 Å)



- Catalytic CATH Domains
-
3.90.230.10
 (see all for 1xgm)
(see all for 1xgm)
- Cofactors
- Zinc(2+) (2)
Enzyme Reaction (EC:3.4.11.18)
Enzyme Mechanism
Introduction
Water is polarised by coordinating to Zinc which is a strong Lewis acid as a result Glu 187 can more easily abstract a proton from the activated water molecule. The activated hydroxide can then nucleophilically attack the carbon of the scissille peptide bond and produce an oxyanion intermediate which is stabilised by coordination to zinc and hydrogen bonding to His 161. The oxyanion will then initiate an elimination which results in the cleavage of the peptide bond releasing the terminal Methionine. The N-terminal product then accepts a proton from Glu 187.
Catalytic Residues Roles
| UniProt | PDB* (1xgm) | ||
| His161 | His161A | Forms an oxyanion hole with Zinc to stabilise the negative charge on the oxyanion intermediate. | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asp82, His153, Asp93, Glu280, Glu187 | Asp82A, His153A, Asp93A, Glu280A, Glu187A | Forms part of the catalytic metal binding site. | metal ligand |
| Glu187 | Glu187A | Acts as a general acid/base by at first accepting a proton from Zinc activated water and then donating a proton to the N-terminal amino group. | metal ligand, proton acceptor, proton donor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, overall reactant used, bimolecular nucleophilic addition, intermediate formation, rate-determining step, unimolecular elimination by the conjugate base, intermediate collapse, overall product formed, native state of enzyme regeneratedReferences
- Copik AJ et al. (2005), Biochemistry, 44, 121-129. EPR and X-ray crystallographic characterization of the product-bound form of the MnII-loaded methionyl aminopeptidase from Pyrococcus furiosus. DOI:10.1021/bi048123+. PMID:15628852.
- Mitra S et al. (2008), FEBS J, 275, 6248-6259. Analyzing the catalytic role of Asp97 in the methionine aminopeptidase from Escherichia coli. DOI:10.1111/j.1742-4658.2008.06749.x. PMID:19019076.
- Leopoldini M et al. (2007), J Am Chem Soc, 129, 7776-7784. Which one among Zn(II), Co(II), Mn(II), and Fe(II) is the most efficient ion for the methionine aminopeptidase catalyzed reaction? DOI:10.1021/ja068168t. PMID:17523636.
- Meng L et al. (2002), Biochemistry, 41, 7199-7208. Overexpression and divalent metal binding properties of the methionyl aminopeptidase from Pyrococcus furiosus. PMID:12044150.
- Tahirov TH et al. (1998), J Mol Biol, 284, 101-124. Crystal structure of methionine aminopeptidase from hyperthermophile, Pyrococcus furiosus. DOI:10.1006/jmbi.1998.2146. PMID:9811545.
Catalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Asp93A | metal ligand |
| His153A | metal ligand |
| Glu187A | metal ligand |
| Glu280A | metal ligand |
| Asp82A | metal ligand |
| His161A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Glu187A | proton acceptor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, overall reactant used
Step 2. The activated hydroxide attacks the peptide carbonyl in a nucleophilic addition producing an oxyanion intermediate.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Asp82A | metal ligand |
| Asp93A | metal ligand |
| His153A | metal ligand |
| Glu187A | metal ligand |
| Glu280A | metal ligand |
| His161A | electrostatic stabiliser |
Chemical Components
ingold: bimolecular nucleophilic addition, intermediate formation, overall reactant used, rate-determining step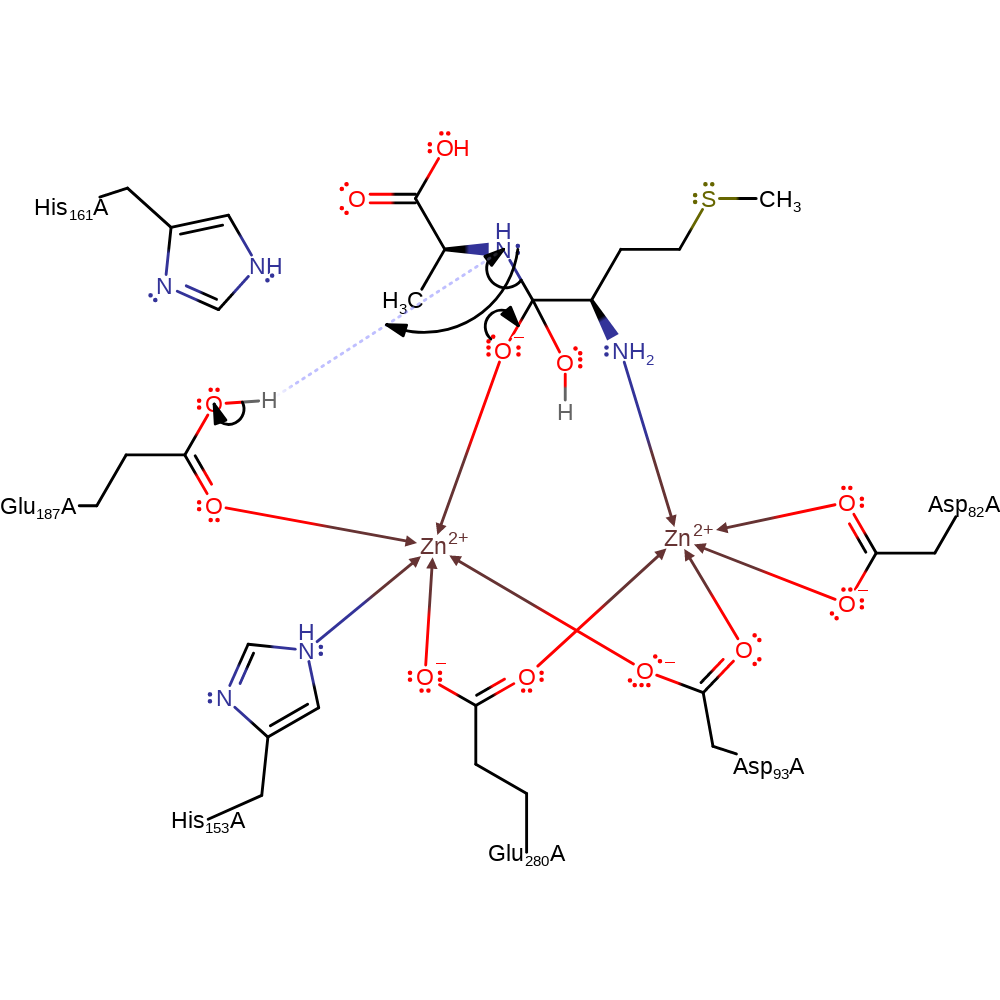
Step 3. The oxyanion initiates an elimination which results in the cleavage of the peptide bond. The N-terminal amino group accepts a proton from Glu187.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Asp82A | metal ligand |
| Asp93A | metal ligand |
| His153A | metal ligand |
| Glu187A | metal ligand |
| Glu280A | metal ligand |
| His161A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Glu187A | proton donor |





 Download:
Download: