Para-nitrobenzyl esterase
Catalyses hydrolysis of several beta-lactam antibiotic PNB esters to the corresponding free acid and PNB alcohol.
Reference Protein and Structure
- Sequence
-
P37967
 (3.1.1.-)
(3.1.1.-)
 (Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
(Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
- Biological species
-
Bacillus subtilis subsp. subtilis str. 168 (Bacteria)

- PDB
-
1qe3
- PNB ESTERASE
(1.5 Å)



- Catalytic CATH Domains
-
3.40.50.1820
 (see all for 1qe3)
(see all for 1qe3)
Enzyme Mechanism
Introduction
The enzyme para-Nitrobenzyl (PNB) esterase is a classic Ser-His-Glu triad esterase from the 3.1.1 EC family of proteins. The reaction of para-nitrobenzyl esterase is a classic Ser-His-Asp/Glu triad reaction. His399 is stabilized by Glu310 while deprotonating Ser189. Ser189 then performs a nucleophilic attack on the acyl carbon of the substrate. The nucleophilic attack is followed by the dissociation of 4-nitroanliline from the substrate, leaving the butyraldehyde-protein complex. His399 deprotonates a water molecule which, as a hydroxide binds to the butyraldehyde creating butyric acid. The His399 proton gained by the water molecule in the previous step is given to Ser189, regenerating the active site.
Catalytic Residues Roles
| UniProt | PDB* (1qe3) | ||
| His399 | His399A | Part of the Ser-His-Glu catalytic triad; activates the serine by acting as a general acid/base. | hydrogen bond donor, proton acceptor, proton donor |
| Glu310 | Glu310A | Part of the Ser-His-Glu catalytic triad; activates and stabilises the histidine residue. | increase basicity, modifies pKa, hydrogen bond acceptor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Ser189 | Ser189A | Part of the Ser-His-Glu catalytic triad; acts as a general acid/base and forms an acyl-enzyme intermediate during the course of the reaction. | covalently attached, hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donor, nucleophile, nucleofuge, proton donor, proton acceptor |
| Gly106 (main-N), Ala107 (main-N), Ala190 (main-N) | Gly106A (main-N), Ala107A (main-N), Ala190A (main-N) | Gly106(main-N), Ala107(main-N) and Ala190(main-N) form a three point oxyanion hole that stabilizes the acyl intermediates formed in this reaction. This tri-point oxyanion hole is unique to EC 3.1 ester hydrolases. | electrostatic stabiliser |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, bimolecular nucleophilic addition, enzyme-substrate complex formation, overall reactant used, intermediate formation, unimolecular elimination by the conjugate base, intermediate collapse, enzyme-substrate complex cleavage, overall product formed, native state of enzyme regeneratedReferences
- Galmés MÀ et al. (2021), ACS Catal, 8635-8644. Combined Theoretical and Experimental Study to Unravel the Differences in Promiscuous Amidase Activity of Two Nonhomologous Enzymes. DOI:https://doi.org/10.1021/acscatal.1c02150.
- Galmés MÀ et al. (2021), ACS Catal, 8635-8644. Combined Theoretical and Experimental Study to Unravel the Differences in Promiscuous Amidase Activity of Two Nonhomologous Enzymes. DOI:https://doi.org/10.1021/acscatal.1c02150.
- Legler PM et al. (2014), Front Chem, 2, 46-. Development of organophosphate hydrolase activity in a bacterial homolog of human cholinesterase. DOI:10.3389/fchem.2014.00046. PMID:25077141.
- Ribitsch D et al. (2011), Biotechnol Prog, 27, 951-960. Hydrolysis of polyethyleneterephthalate by p-nitrobenzylesterase from Bacillus subtilis. DOI:10.1002/btpr.610. PMID:21574267.
- Spiller B et al. (1999), Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, 96, 12305-12310. A structural view of evolutionary divergence. PMID:10535917.

Step 1. His399 activates Ser189 to nucleophilically attack the substrate.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Glu310A | modifies pKa, electrostatic stabiliser |
| His399A | hydrogen bond donor |
| Glu310A | hydrogen bond acceptor |
| His399A | proton acceptor |
| Ser189A | proton donor |
| Gly106A (main-N) | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Ala107A (main-N) | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Ala190A (main-N) | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Ser189A | hydrogen bond donor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer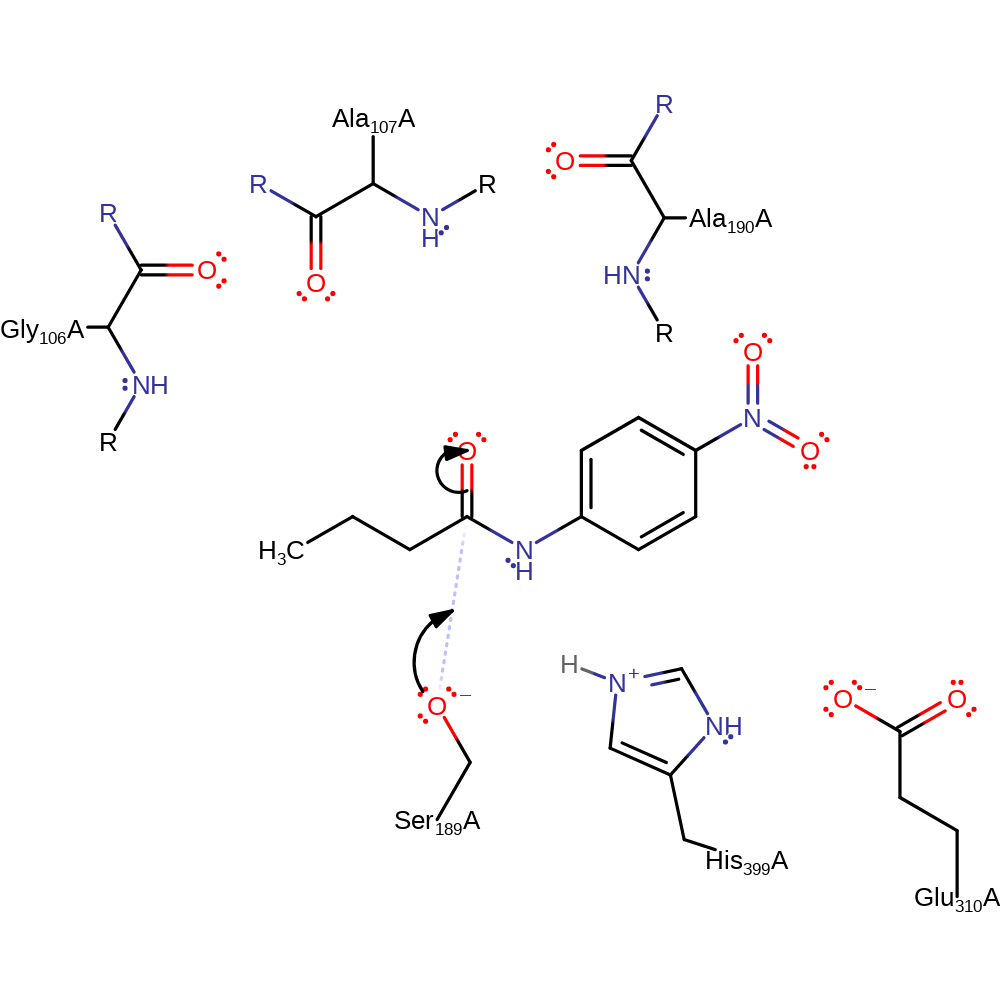
Step 2. Ser189 performs a nucleophilic attack on to the carbonyl carbon creating the acyl-enzyme intermediate.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Ser189A | nucleophile, hydrogen bond acceptor |
| His399A | hydrogen bond donor |
| Glu310A | modifies pKa, increase basicity |
| Gly106A (main-N) | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Ala107A (main-N) | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Ala190A (main-N) | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Glu310A | electrostatic stabiliser, hydrogen bond acceptor |
Chemical Components
ingold: bimolecular nucleophilic addition, enzyme-substrate complex formation, overall reactant used, intermediate formation
Step 3. The nitroaniline is cleaved off the rest of the enzyme-acyl complex by recieving a proton from His399. The double bond reforms in the carbonyl oxygen. This step was inferred from the curator.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| His399A | proton donor |
| Glu310A | increase basicity, modifies pKa, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Ser189A | covalently attached |
| Gly106A (main-N) | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Ala107A (main-N) | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Ala190A (main-N) | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Glu310A | hydrogen bond acceptor |
Chemical Components
ingold: unimolecular elimination by the conjugate base, proton transfer, intermediate collapse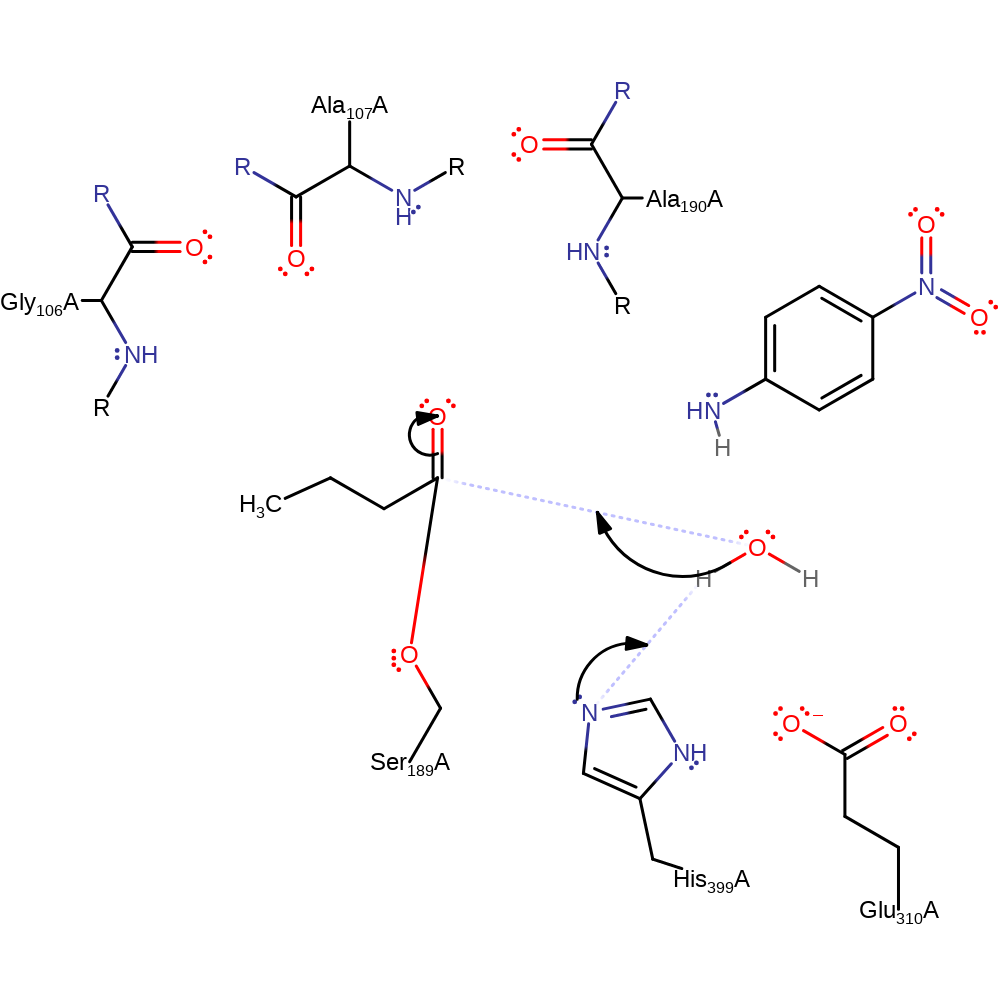
Step 4. His399 removes a proton from a water molecule creating a hydroxide that binds to the carbonyl carbon of the substrate.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Glu310A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Gly106A (main-N) | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Ala107A (main-N) | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Ala190A (main-N) | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Ser189A | covalently attached |
| His399A | hydrogen bond donor |
| Glu310A | hydrogen bond acceptor |
| His399A | proton acceptor |
Chemical Components
ingold: bimolecular nucleophilic addition, intermediate formation, overall reactant used, proton transfer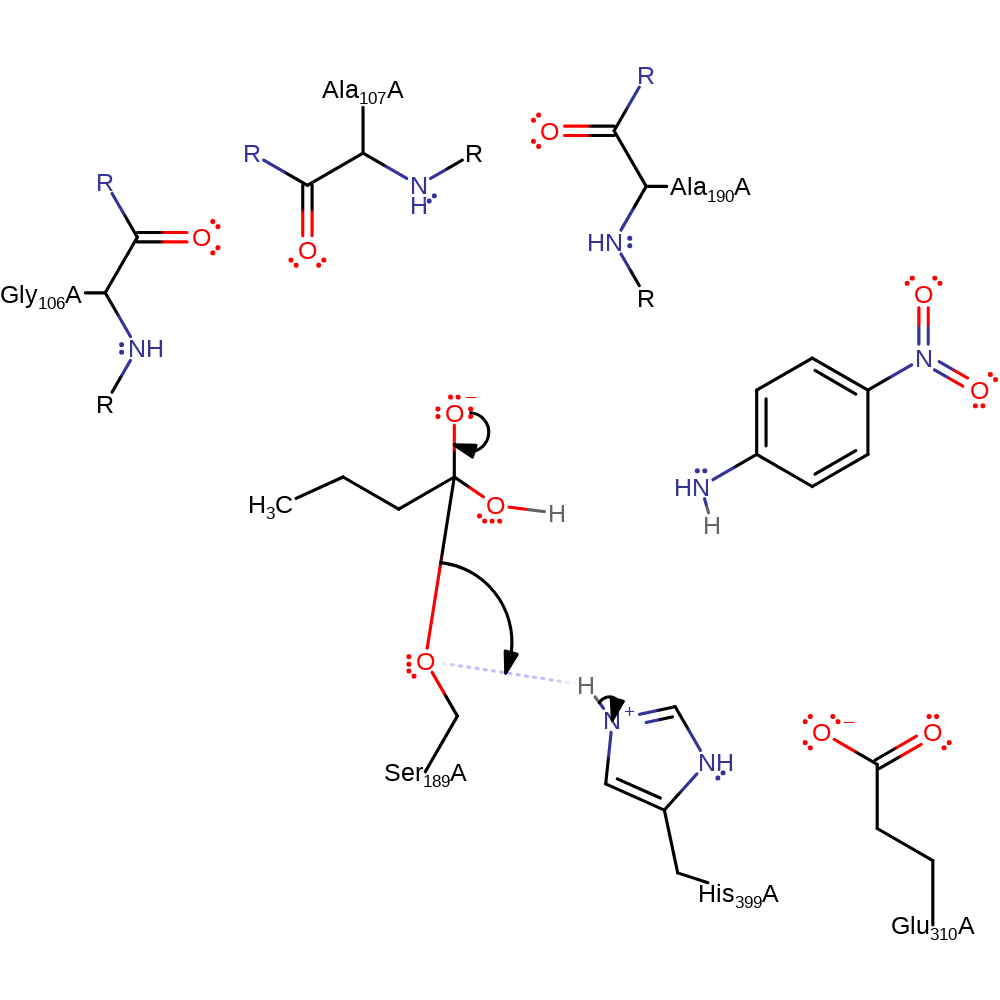
Step 5. His399 donates a proton to Ser189 collapsing the intermediate. This cleaves the substrate from the enzyme and regenerates the enzymes native state.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Glu310A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Gly106A (main-N) | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Ala107A (main-N) | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Ala190A (main-N) | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Glu310A | hydrogen bond acceptor, increase basicity, modifies pKa |
| Ser189A | nucleofuge, proton acceptor |
| His399A | proton donor |




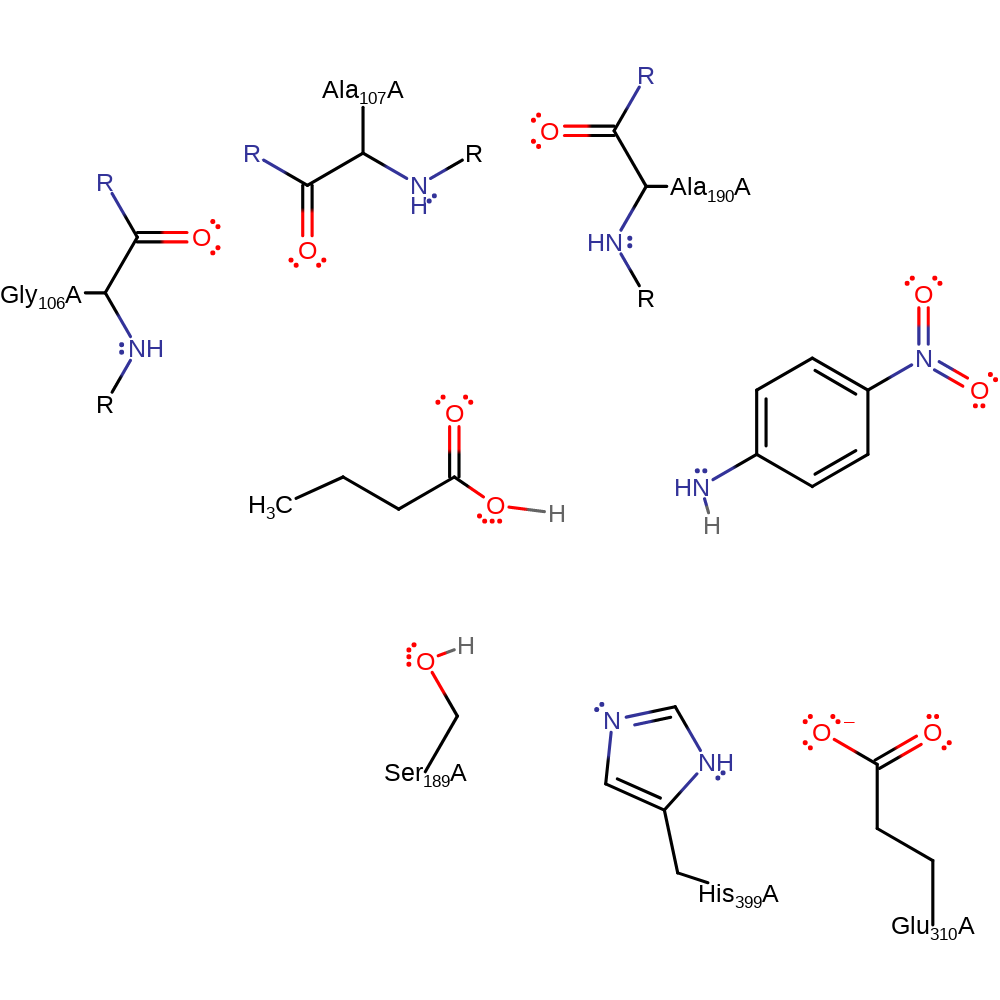 Download:
Download: