Tetrahydroxynaphthalene reductase
Catalyzes the NADPH-dependent reduction of 1,3,6,8- tetrahydroxynaphthalene (T4HN) into (+)-scytalone and 1,3,8- trihydroxynaphthalene into (-)-vermelone. This enzyme is the biochemical target of several commercially important fungicides which are used to prevent blast disease in rice plants.
Reference Protein and Structure
- Sequence
-
Q12634
 (1.1.1.252)
(1.1.1.252)
 (Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
(Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
- Biological species
-
Magnaporthe oryzae 70-15 (Fungus)

- PDB
-
1ybv
- STRUCTURE OF TRIHYDROXYNAPHTHALENE REDUCTASE IN COMPLEX WITH NADPH AND AN ACTIVE SITE INHIBITOR
(2.8 Å)



- Catalytic CATH Domains
-
3.40.50.720
 (see all for 1ybv)
(see all for 1ybv)
- Cofactors
- Water (1)
Enzyme Mechanism
Introduction
The invariant tyrosine residue polarises the carbonyl oxygen of the substrate, thereby increasing the electrophilicity of the carbonyl carbon atom and facilitating hydride transfer from NADPH. After hydride transfer has occurred, the tyrosine residue donates its phenolic proton to the substrate hydroxyl group. The resulting negative charge of the side chain of the tyrosine residue is stabilised by the lysine and serine residues of the catalytic triad, either through a hydrogen bond, or through electrostatic interactions.
Catalytic Residues Roles
| UniProt | PDB* (1ybv) | ||
| Tyr223 | Tyr223A | Helps stabilise the transition state formed during the course of the reaction. | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Ser164 | Ser164A | Form part of the Ser-Tyr-Lys catalytic triad. Responsible for helping to stabilise the reactive intermediates and transition states formed during the course of the reaction. | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Tyr178 | Tyr178A | Acts as a general acid/base. | proton relay, proton acceptor, proton donor |
| Lys182 | Lys182A | Part of the Ser-Tyr-Lys catalytic triad. Lys182 also contacts a conserved water molecule that. Acts as a general acid/base, ultimately being reprotonated from the solvent via the conserved water molecule. | proton acceptor, proton relay, electrostatic stabiliser, proton donor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, hydride transfer, overall product formed, overall reactant used, native state of enzyme regenerated, native state of cofactor regeneratedReferences
- Liao D et al. (2001), Structure, 9, 19-27. Structures of trihydroxynaphthalene reductase-fungicide complexes: implications for structure-based design and catalysis. PMID:11342131.
- Schätzle MA et al. (2012), Angew Chem Int Ed Engl, 51, 2643-2646. Tetrahydroxynaphthalene reductase: catalytic properties of an enzyme involved in reductive asymmetric naphthol dearomatization. DOI:10.1002/anie.201107695. PMID:22308069.
- Oppermann U et al. (2003), Chem Biol Interact, 143-144, 247-253. Short-chain dehydrogenases/reductases (SDR): the 2002 update. DOI:10.1016/s0009-2797(02)00164-3. PMID:12604210.
- Liao DI et al. (2001), Biochemistry, 40, 8696-8704. A structural account of substrate and inhibitor specificity differences between two naphthol reductases. PMID:11467929.
- Thompson JE et al. (1997), Biochemistry, 36, 1852-1860. Trihydroxynaphthalene reductase from Magnaporthe grisea: realization of an active center inhibitor and elucidation of the kinetic mechanism. DOI:10.1021/bi962355u. PMID:9048570.
- Andersson A et al. (1996), Structure, 4, 1161-1170. Crystal structure of the ternary complex of 1,3,8-trihydroxynaphthalene reductase from Magnaporthe grisea with NADPH and an active-site inhibitor. PMID:8939741.
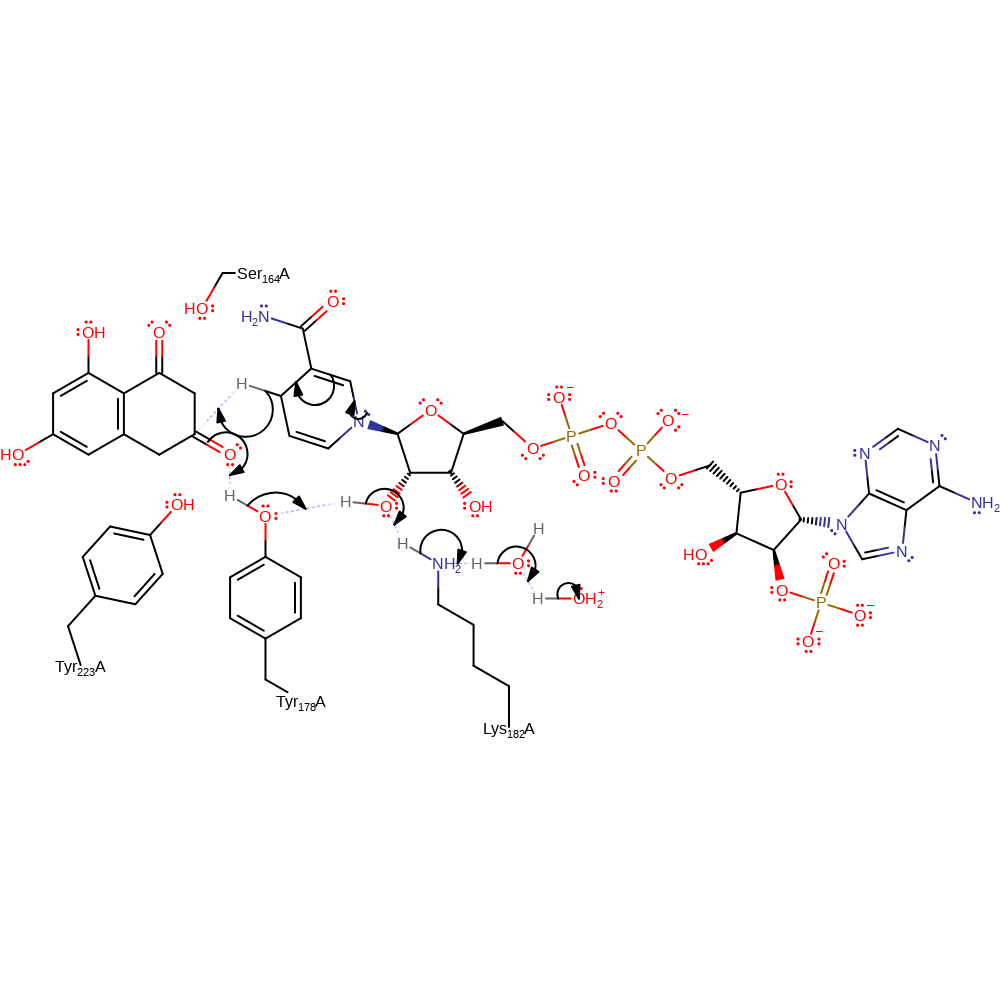
Step 1. NADPH donates a hydride to the substrate, which initiates a proton relay from the bulk solvent to the substrate via Tyr178, the ribose ring of the cosubstrate, Lys182 and the conserved active site water molecule.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Ser164A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Lys182A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Tyr223A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Tyr178A | proton donor |
| Lys182A | proton acceptor, proton donor, proton relay |
| Tyr178A | proton relay, proton acceptor |
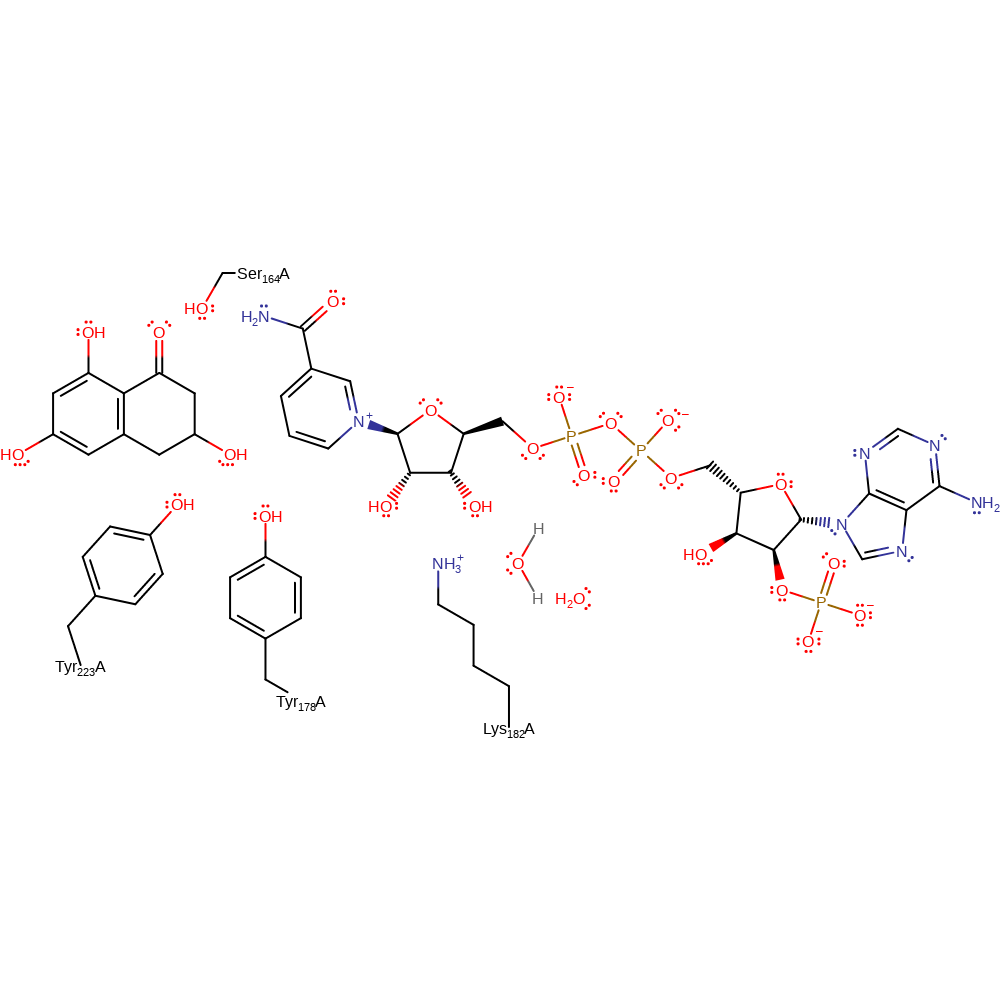




 Download:
Download: