Cephalosporin-C deacetylase
Cephalosporin-C deacetylase is an esterase that removes acetyl groups from a number of O-acetylated small substrates, such as acetylated xylose, short xylooligosaccharides and cephalosporin C. It is known not to cleave amide bonds. It is used in the pharmaceutical industry for the chemoenzymatic deacetylation of cephalosporins and the synthesis of novel antibiotics. It is an alpha-beta hydrolase, a member of the carbohydrate esterase 7 family.
Reference Protein and Structure
- Sequence
-
P94388
 (3.1.1.41, 3.1.1.72)
(3.1.1.41, 3.1.1.72)
 (Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
(Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
- Biological species
-
Bacillus subtilis subsp. subtilis str. 168 (Bacteria)

- PDB
-
1l7a
- structural Genomics, crystal structure of Cephalosporin C deacetylase
(1.5 Å)



- Catalytic CATH Domains
-
3.40.50.1820
 (see all for 1l7a)
(see all for 1l7a)
Enzyme Reaction (EC:3.1.1.41)
Enzyme Mechanism
Introduction
Serine is activated by the histidine of the Ser-His-Asp catalytic triad. Serine then attacks the substrate in a nucleophilic addition reaction, eliminating the acetate group. Water then cleaves the enzyme-substrate bond to regenerate the active site and produce the final product.
Catalytic Residues Roles
| UniProt | PDB* (1l7a) | ||
| Ser181 | Ser181A | Forms part of the catalytic Ser-His-Asp triad. Functions as the nucleophile. | covalently attached, nucleofuge, nucleophile, proton acceptor, proton donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asp269 | Asp269A | Forms part of the catalytic Ser-His-Asp triad. Activates and stabilises the catalytic histidine. | increase basicity, electrostatic stabiliser |
| His298 | His298A | Forms part of the catalytic Ser-His-Asp triad. Acts as a general acid/base, abstracting a proton from the catalytic serine. | proton acceptor, proton donor |
| Gln182 (main-N), Tyr91 (main-N) | Gln182A (main-N), Tyr91A (main-N) | Forms part of the oxyanion hole. | electrostatic stabiliser |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, overall reactant used, intermediate formation, bimolecular nucleophilic addition, unimolecular elimination by the conjugate base, overall product formed, intermediate terminated, native state of enzyme regeneratedReferences
- Vincent F et al. (2003), J Mol Biol, 330, 593-606. Multifunctional Xylooligosaccharide/Cephalosporin C Deacetylase Revealed by the Hexameric Structure of the Bacillus subtilis Enzyme at 1.9Å Resolution. DOI:10.1016/s0022-2836(03)00632-6. PMID:12842474.
- Dodson G et al. (1998), Trends Biochem Sci, 23, 347-352. Catalytic triads and their relatives. DOI:10.1016/s0968-0004(98)01254-7. PMID:9787641.
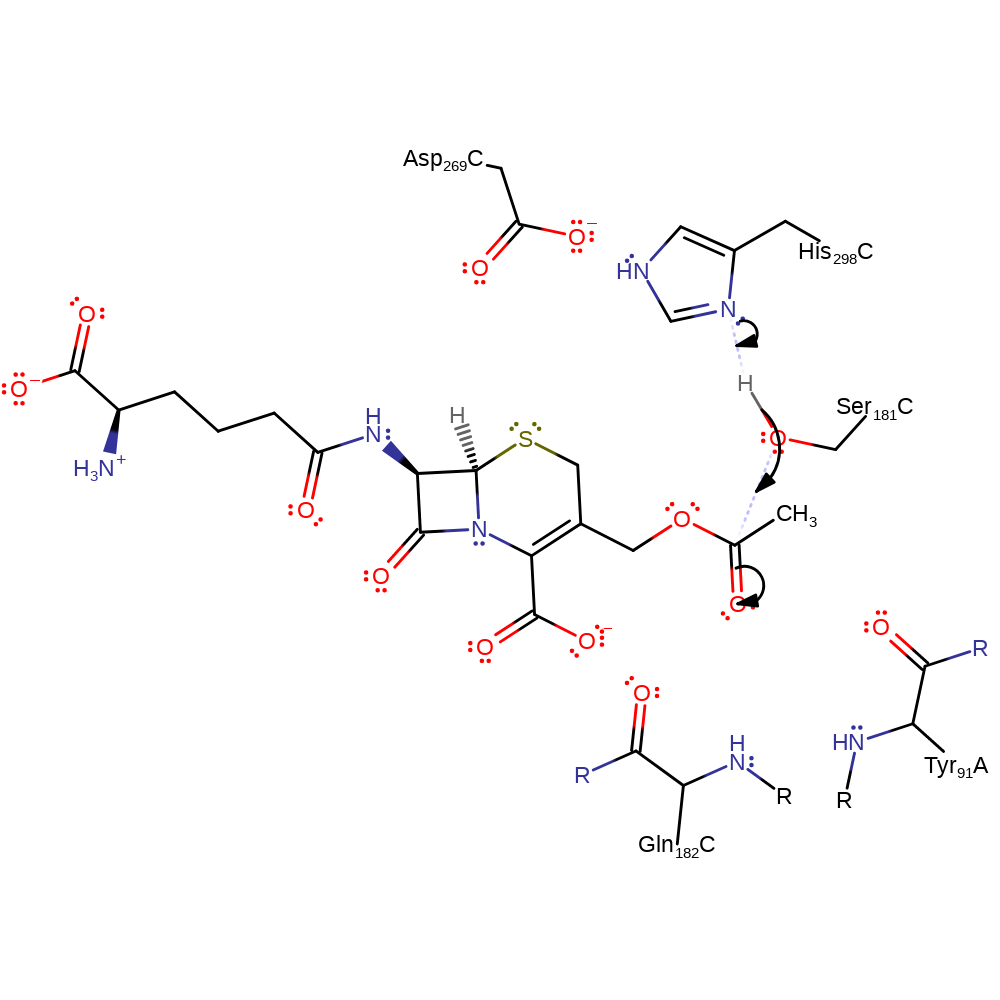
Step 1. His298 acts as a general base activating the Ser181 hydroxyl group for nucleophilic attack on the carbonyl carbon of the ester bond. The third component of this catalytic triad- Asp269 acts to increase the basicity of the histidine. The oxyanion intermediate formed is stabilized by the amide groups of Gln182 and Tyr91.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Gln182A (main-N) | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asp269A | electrostatic stabiliser, increase basicity |
| Ser181A | covalently attached |
| Tyr91A (main-N) | electrostatic stabiliser |
| His298A | proton acceptor |
| Ser181A | proton donor, nucleophile |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, overall reactant used, intermediate formation, ingold: bimolecular nucleophilic addition
Step 2. The tetrahedral intermediate collapses and deacetylcephalosporin is eliminated.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Tyr91A (main-N) | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Gln182A (main-N) | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asp269A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Ser181A | covalently attached |
| His298A | proton donor |
Chemical Components
ingold: unimolecular elimination by the conjugate base, proton transfer, overall product formed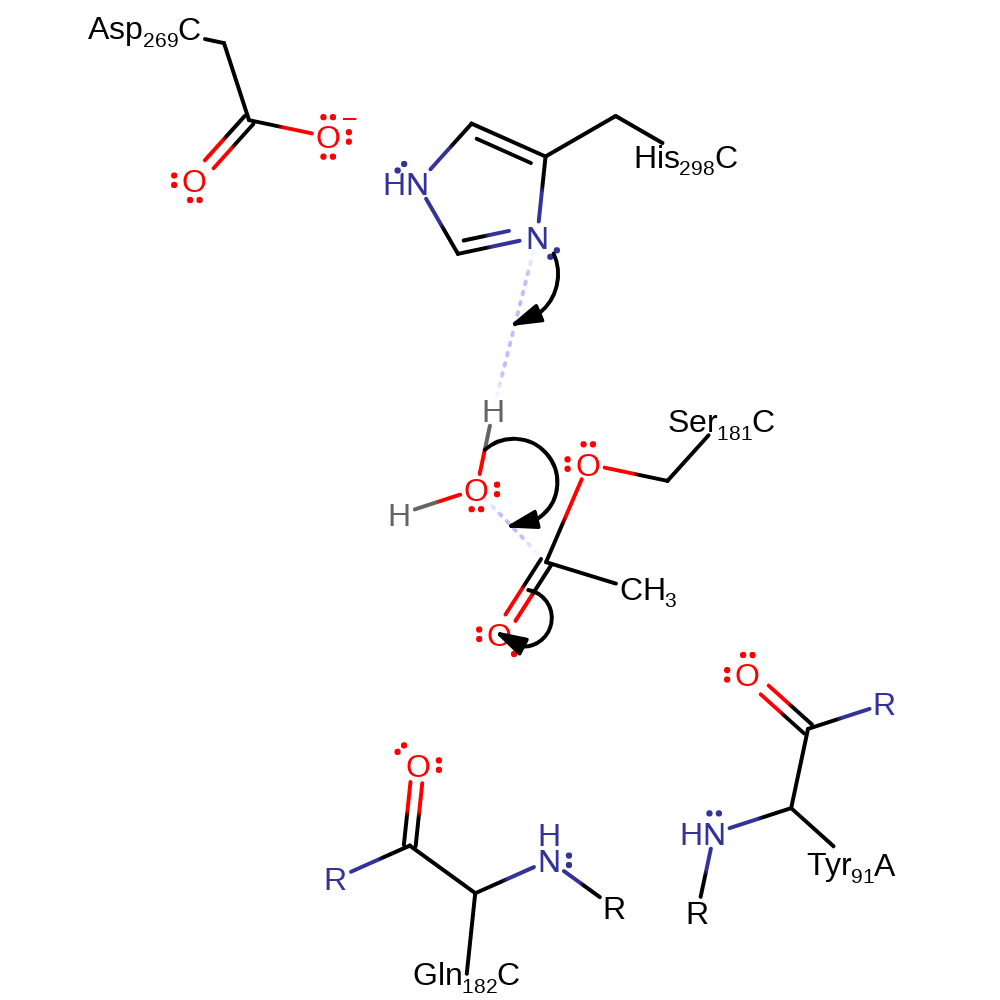
Step 3. His298 activates water for nucleophilic attack and another oxyanion intermediate is formed.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Tyr91A (main-N) | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Gln182A (main-N) | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asp269A | electrostatic stabiliser, increase basicity |
| Ser181A | covalently attached |
| His298A | proton acceptor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, ingold: bimolecular nucleophilic addition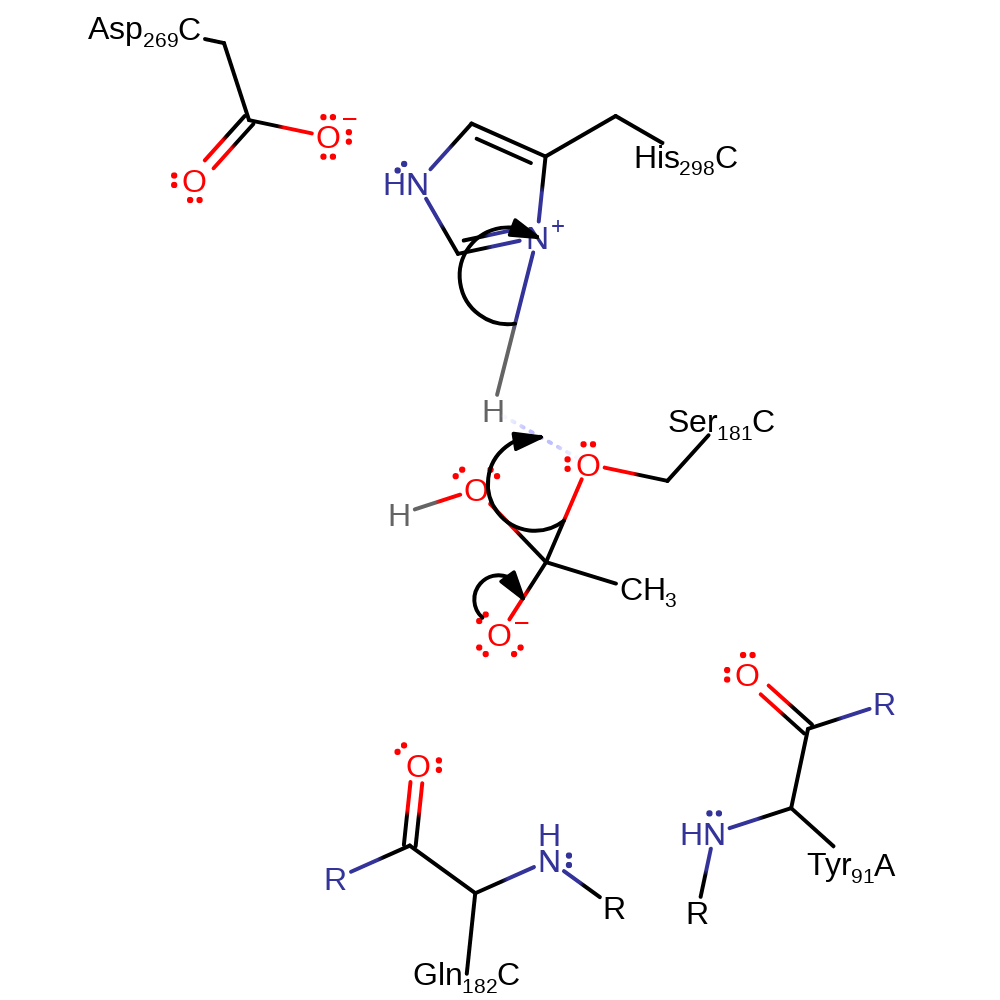
Step 4. The tetrahedral intermediate collapses and Ser181 is eliminated.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Tyr91A (main-N) | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Ser181A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asp269A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| His298A | proton donor |
| Ser181A | nucleofuge, proton acceptor |





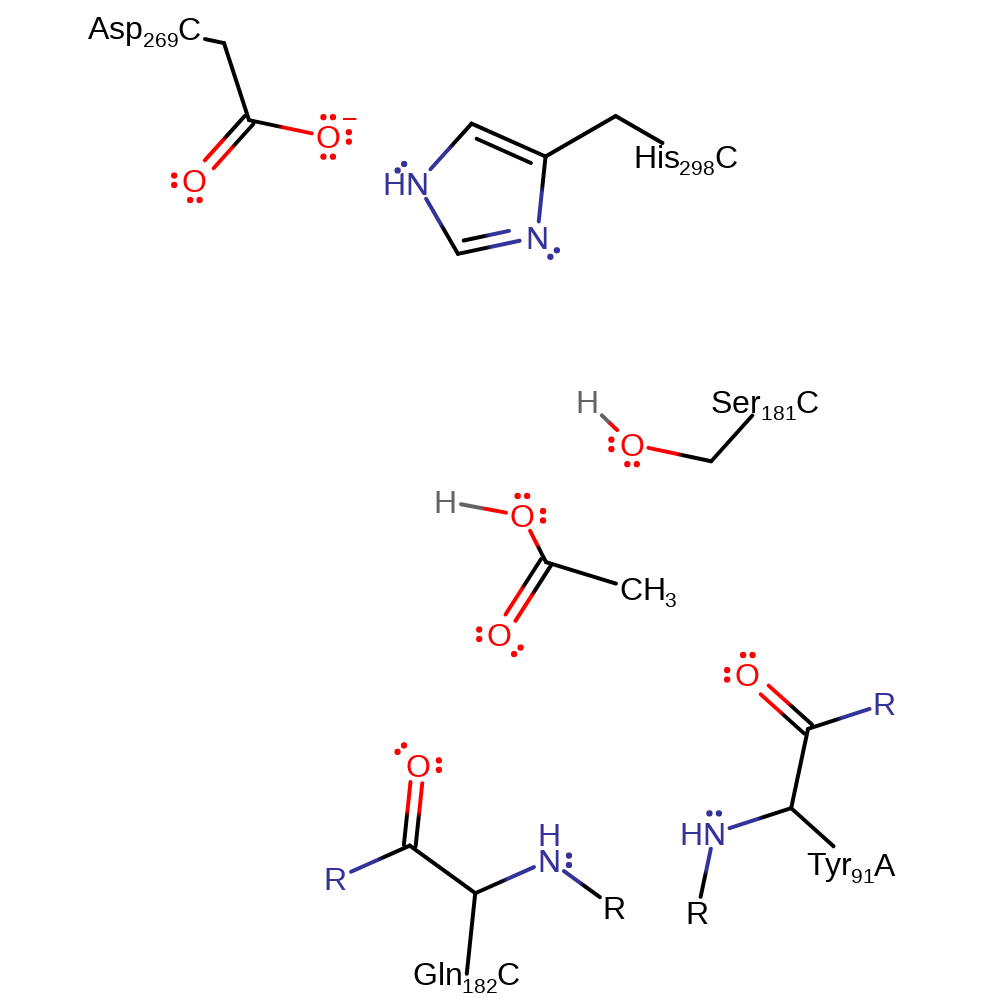 Download:
Download: