D-galactarolactone isomerase
Catalyses the isomerisation of D-galactaro-1,5-lactone to D-galactaro-1,4-lactone. This is a step in the oxidative degradation pathway of D-galacturonate, which allows Agrobacterium tumefaciens to utilise D-galacturonate as a sole carbon source. This enzyme belongs to the amidohydrolase superfamily. Unlike many members of the amidohydrolase superfamily, this protein does not require a divalent metal for its lactonase activity
Reference Protein and Structure
- Sequence
-
A9CEQ7
 (5.4.1.4)
(5.4.1.4)
 (Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
(Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
- Biological species
-
Agrobacterium fabrum str. C58 (Bacteria)

- PDB
-
4mup
- Crystal structure of Agrobacterium tumefaciens ATU3138 (EFI target 505157), apo structure
(1.6 Å)



- Catalytic CATH Domains
-
3.20.20.140
 (see all for 4mup)
(see all for 4mup)
Enzyme Mechanism
Introduction
The substrate undergoes auto-catalytic formation of the oxygen bridge, activated by Asn240. The formed oxyanion then collapses to form the five membered ring. The modest rate enhancement over the non-enzymatic reaction is thought to come from the preferential binding of the boat conformer of the delta-lactone ring to enforce the proximity of the 4-OH group and the lactone carbonyl group.
Catalytic Residues Roles
| UniProt | PDB* (4mup) | ||
| Asn240 | Asn240(260)A | This residue is the equivalent of the conserved aspartate in other amidohydrolase proteins; it is likely to stabilise and activate the substrate for auto-catalysis. | enhance reactivity, electrostatic stabiliser |
Chemical Components
cyclisation, overall reactant used, intramolecular nucleophilic addition, overall product formed, intramolecular elimination, decyclisationReferences
- Bouvier JT et al. (2014), Biochemistry, 53, 614-616. Galactaro δ-Lactone Isomerase: Lactone Isomerization by a Member of the Amidohydrolase Superfamily. DOI:10.1021/bi5000492. PMID:24450804.

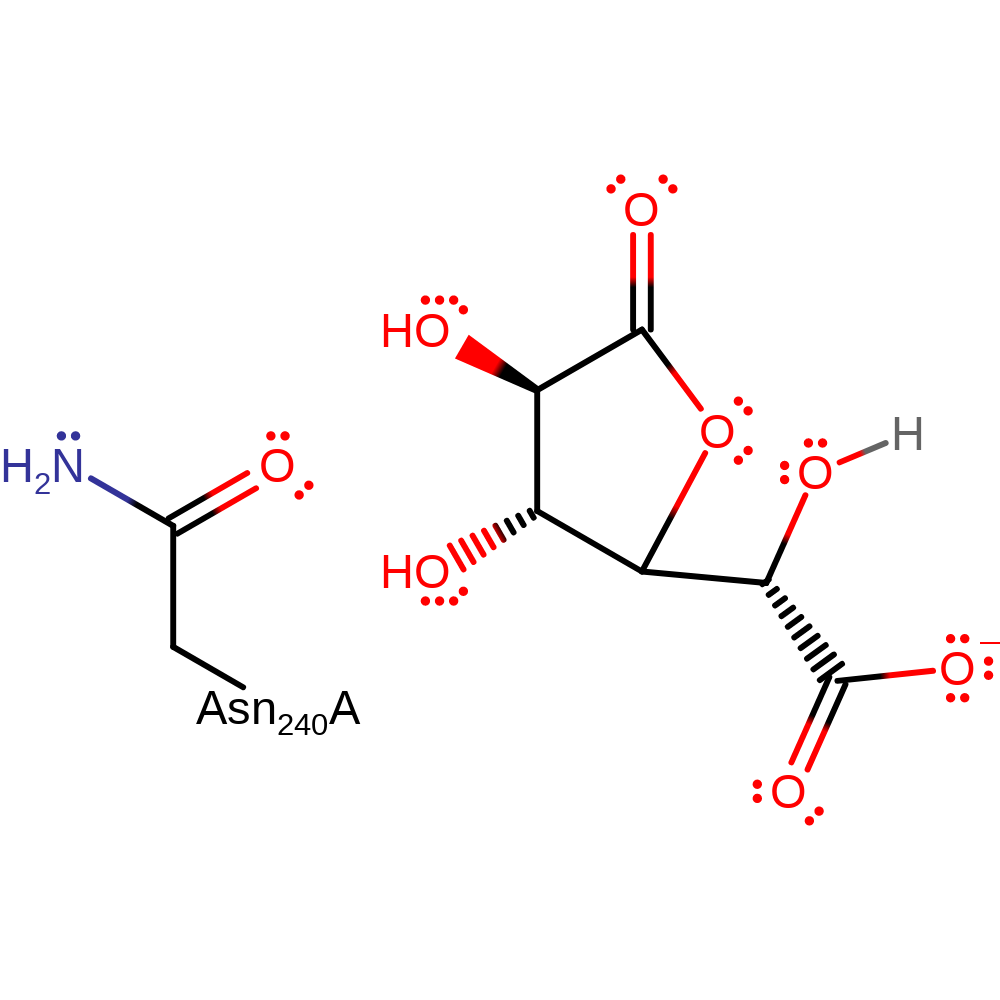
Step 1. The hydroxyl group opposite the lactone carbonyl initiates a nucleophilic attack to form the cyclic intermediate.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Asn240(260)A | enhance reactivity |
Chemical Components
cyclisation, overall reactant used, ingold: intramolecular nucleophilic addition
Step 2. The oxyanion collapses to form the 5-membered ring with deprotonation of the bridging oxygen.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Asn240(260)A | electrostatic stabiliser |


 Download:
Download: