Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase
Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase (G6PDH) is a ubiquitous protein, present in bacteria and all eukaryotic cell types. The enzyme catalyses the the first step in the pentose pathway: the conversion of glucose-6-phosphate to gluconolactone 6-phosphate in the presence of NADP, producing NADPH. The ubiquitous expression of the enzyme gives it a major role in the production of NADPH for the many NADPH-mediated reductive processes in all cells. Deficiency of G6PDH is a common genetic abnormality affecting millions of people worldwide. Many sequence variants, most caused by single point mutations, are known, exhibiting a wide variety of phenotypes.
Reference Protein and Structure
- Sequence
-
P11411
 (1.1.1.363)
(1.1.1.363)
 (Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
(Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
- Biological species
-
Leuconostoc mesenteroides (Bacteria)

- PDB
-
1dpg
- GLUCOSE 6-PHOSPHATE DEHYDROGENASE FROM LEUCONOSTOC MESENTEROIDES
(2.0 Å)



- Catalytic CATH Domains
-
3.30.360.10
 (see all for 1dpg)
(see all for 1dpg)
Enzyme Reaction (EC:1.1.1.49)
Enzyme Mechanism
Introduction
The oxidation of glucose 6-phosphate by G6PD involves general base (His240) abstraction of a proton from the C1−OH, thereby allowing transfer of the hydride from C1 to the C4 position of the nicotinamide ring of the coenzyme.
Catalytic Residues Roles
| UniProt | PDB* (1dpg) | ||
| His179 | His178A | Binds the phosphate group of the substrate and helps stabilise the transition state. | transition state stabiliser |
| Asp178 | Asp177A | Hydrogen bonds with His240, lowering it's pKa to enable it to act as a general acid/base. | modifies pKa |
| His241 | His240A | Acts as a general acid/base. Its Nδ1 is hydrogen bonded to Asp177 Oδ1 while Nϵ2 is within hydrogen–bonding distance of two waters in each subunit of the unliganded enzyme. | proton acceptor, proton donor |
Chemical Components
hydride transfer, proton transfer, overall product formed, overall reactant used, inferred reaction step, native state of enzyme regeneratedReferences
- Cosgrove MS et al. (1998), Biochemistry, 37, 2759-2767. On the mechanism of the reaction catalyzed by glucose 6-phosphate dehydrogenase. DOI:10.1021/bi972069y. PMID:9485426.
- Cosgrove MS et al. (2002), Biochemistry, 41, 6939-6945. The Catalytic Mechanism of Glucose 6-Phosphate Dehydrogenases: Assignment and1H NMR Spectroscopy pH Titration of the Catalytic Histidine Residue in the 109 kDaLeuconostoc mesenteroidesEnzyme†. DOI:10.1021/bi0255219.
- Cosgrove MS et al. (2000), Biochemistry, 39, 15002-15011. An Examination of the Role of Asp-177 in the His-Asp Catalytic Dyad ofLeuconostoc mesenteroidesGlucose 6-Phosphate Dehydrogenase: X-ray Structure and pH Dependence of Kinetic Parameters of the D177N Mutant Enzyme†,‡. DOI:10.1021/bi0014608.
- Vought V et al. (2000), Biochemistry, 39, 15012-15021. Delineation of the Roles of Amino Acids Involved in the Catalytic Functions ofLeuconostoc mesenteroidesGlucose 6-Phosphate Dehydrogenase†. DOI:10.1021/bi0014610.
- Rowland P et al. (1994), Structure, 2, 1073-1087. The three–dimensional structure of glucose 6–phosphate dehydrogenase from Leuconostoc mesenteroides refined at 2.0 Å resolution. DOI:10.1016/s0969-2126(94)00110-3. PMID:7881907.
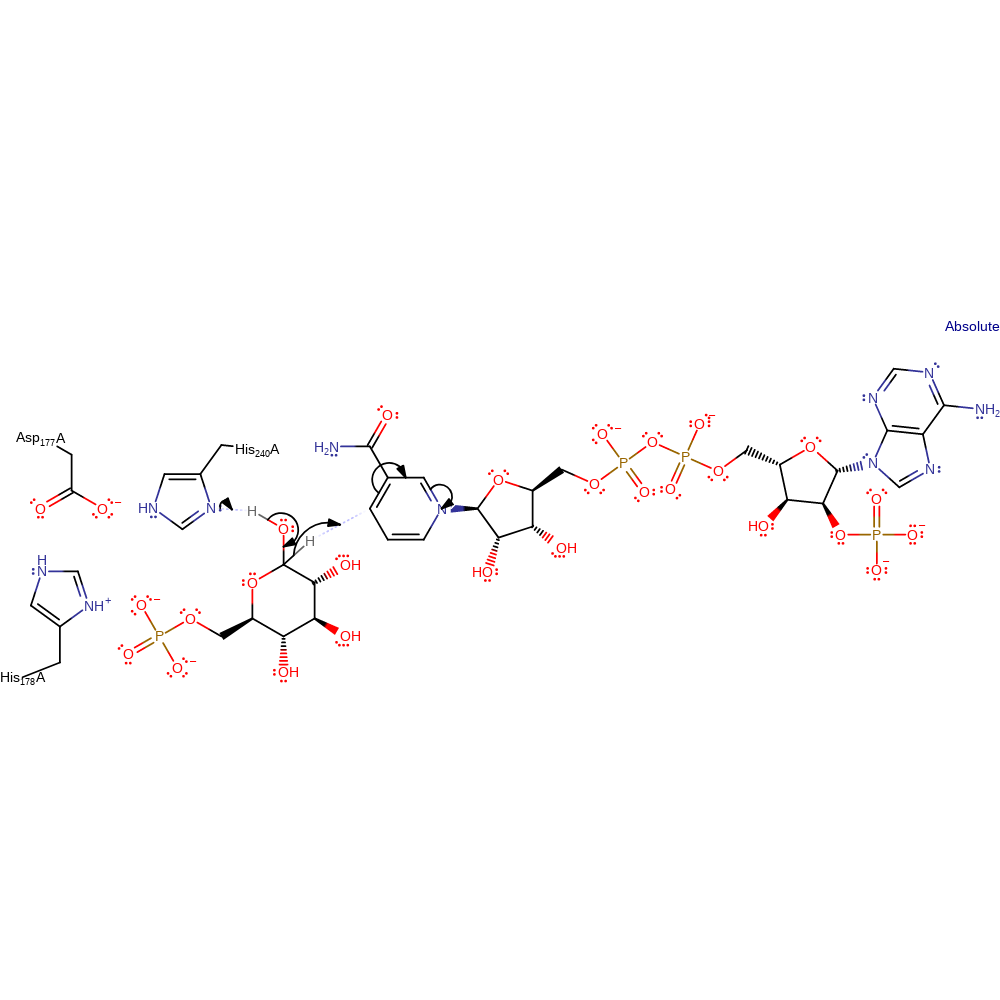
Step 1. His240 abstracts a proton from the substrate, eliminating a hydride that is added to NAD(P).
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Asp177A | modifies pKa |
| His178A | transition state stabiliser |
| His240A | proton acceptor |
Chemical Components
hydride transfer, proton transfer, overall product formed, overall reactant used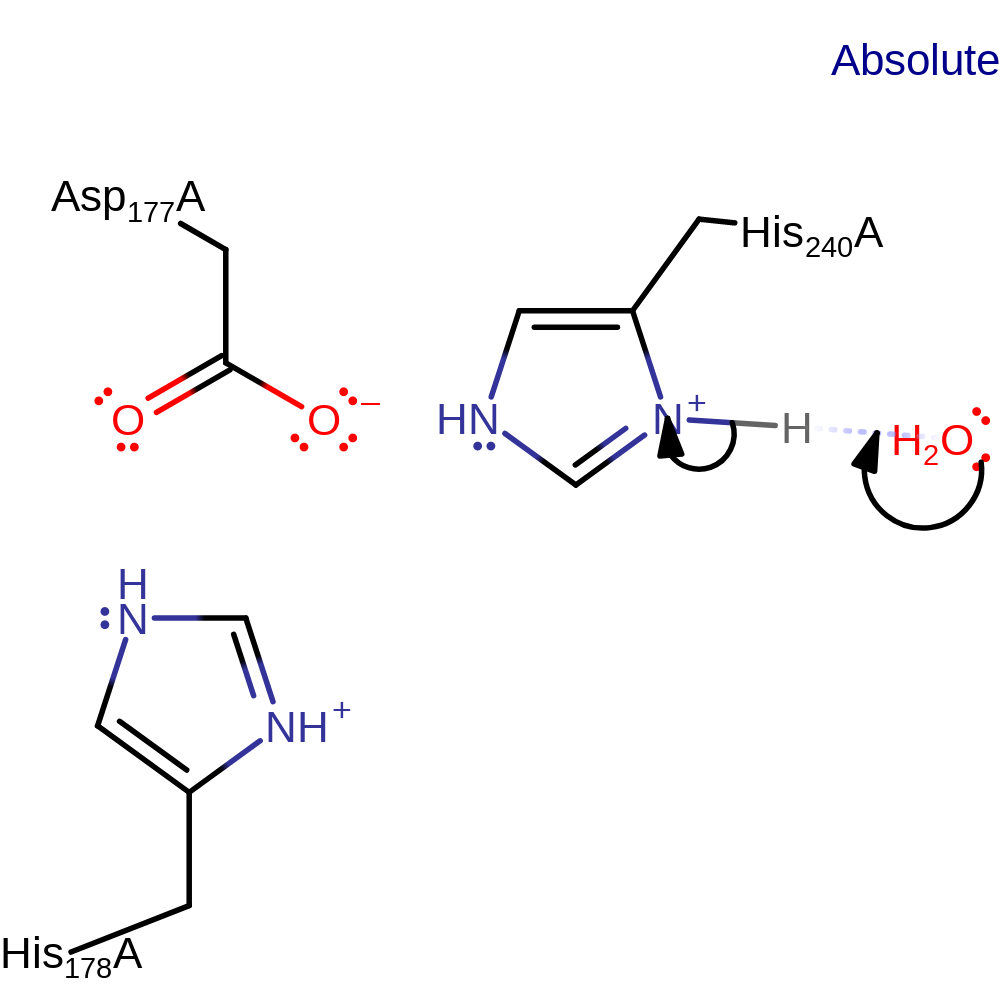
Step 2. Inferred return step to deprotonate His240, ready for another reaction cycle.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Asp177A | modifies pKa |
| His240A | proton donor |





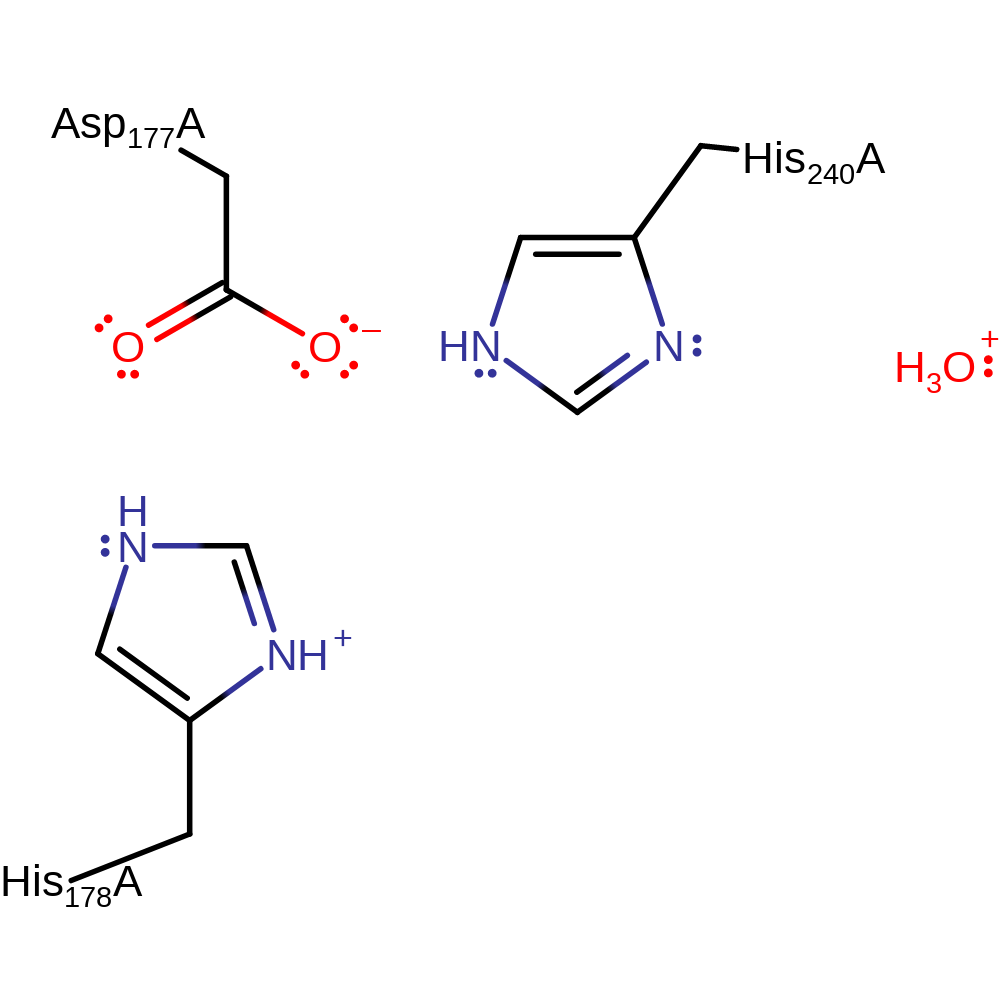 Download:
Download: