Penicillin amidase (peptidase S45 family)
Penicillin acylase is a widely distributed enzyme among bacteria, yeast and fungi. It is used industrially in the production of 6-aminopenicillanic acid, the starting point for the synthesis of penicillins. In vivo it is thought to have a role in the use of aromatic compounds as carbon sources.
Reference Protein and Structure
- Sequence
-
P06875
 (3.5.1.11)
(3.5.1.11)
 (Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
(Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
- Biological species
-
Escherichia coli (Bacteria)

- PDB
-
1pnl
- PENICILLIN ACYLASE HAS A SINGLE-AMINO-ACID CATALYTIC CENTRE
(2.5 Å)



- Catalytic CATH Domains
-
3.60.20.10
 (see all for 1pnl)
(see all for 1pnl)
Enzyme Reaction (EC:3.5.1.11)
Enzyme Mechanism
Introduction
The penicillin binds in the active site near to the reactive N-terminal serine. The amino group enhances the serines nucleophilic character (via a bridging water) allowing it to attack the carbonyl carbon at the amide bond to be cleaved. The tetrahedral intermediate is stabilised by the side chain of asparagine 241 and the main chain nitrogen of alanine 69. The bond is then cleaved and the two reaction products are released.
Catalytic Residues Roles
| UniProt | PDB* (1pnl) | ||
| Asn530 (main-C) | Asn241B (main-C) | Stabilises the N-terminus of Ser 290 and increases its pKa so it more willingly accepts a proton from the hydroxyl of Ser 290. | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Ser290 (N-term) | Ser1B (N-term) | Activates the serine side chain. | proton acceptor, proton donor |
| Ser290 | Ser1B | Acts as a catalytic nucleophile. | nucleofuge, nucleophile, proton acceptor, proton donor |
| Asn530 (main-N), Ala358 (main-N) | Asn241B (main-N), Ala69B (main-N) | Form the oxyanion hole, stabilising the reactive intermediates and transition states. | electrostatic stabiliser |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, bimolecular nucleophilic addition, enzyme-substrate complex formation, intermediate formation, overall reactant used, rate-determining step, unimolecular elimination by the conjugate base, heterolysis, intermediate collapse, enzyme-substrate complex cleavage, native state of enzyme regenerated, overall product formedReferences
- McVey CE et al. (2001), J Mol Biol, 313, 139-150. Crystal structures of penicillin acylase enzyme-substrate complexes: structural insights into the catalytic mechanism 1 1Edited by K. Nagai. DOI:10.1006/jmbi.2001.5043. PMID:11601852.
- Grigorenko BL et al. (2014), ACS Catal, 4, 2521-2529. Catalytic Cycle of Penicillin Acylase from Escherichia coli: QM/MM Modeling of Chemical Transformations in the Enzyme Active Site upon Penicillin G Hydrolysis. DOI:10.1021/cs5002898.
- Suresh CG et al. (1999), Nat Struct Biol, 6, 414-416. Penicillin V acylase crystal structure reveals new Ntn-hydrolase family members. DOI:10.1038/8213. PMID:10331865.
- Done SH et al. (1998), J Mol Biol, 284, 463-475. Ligand-induced conformational change in penicillin acylase. DOI:10.1006/jmbi.1998.2180. PMID:9813130.
- Duggleby HJ et al. (1995), Nature, 373, 264-268. Penicillin acylase has a single-amino-acid catalytic centre. DOI:10.1038/373264a0. PMID:7816145.

Step 1. Ser 290 N-terminus deprotonates its own hydroxyl group which activates it to nucleophilically attack the carbonyl group of the amide bond of penicillin.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Ala69B (main-N) | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asn241B (main-N) | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asn241B (main-C) | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Ser1B | proton donor, nucleophile |
| Ser1B (N-term) | proton acceptor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, ingold: bimolecular nucleophilic addition, enzyme-substrate complex formation, intermediate formation, overall reactant used, rate-determining step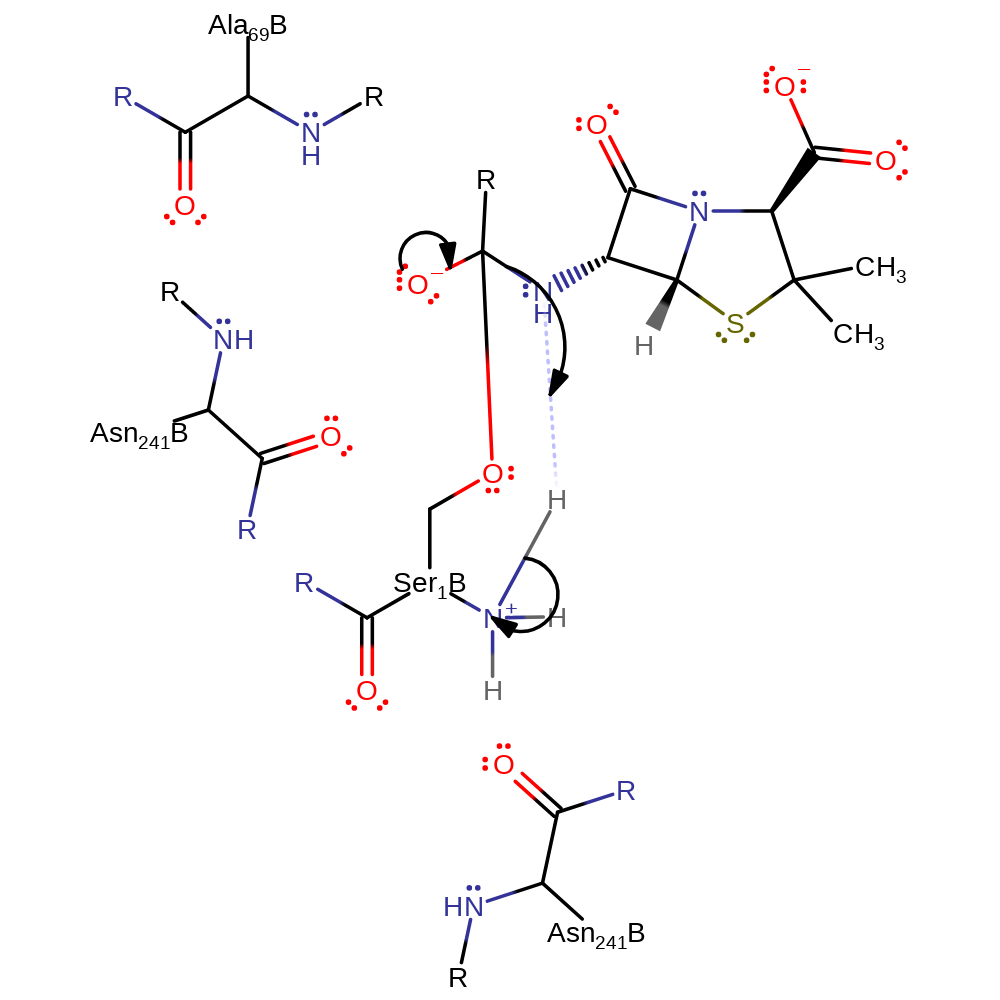
Step 2. The oxyanion initiates an elimination which results in the cleavage of the amide bond and the N-terminal product accepts a proton from the N-terminus of Ser290.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Ala69B (main-N) | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asn241B (main-N) | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asn241B (main-C) | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Ser1B (N-term) | proton donor |
Chemical Components
ingold: unimolecular elimination by the conjugate base, proton transfer, heterolysis, intermediate collapse
Step 3. The N-terminus of Ser290 abstracts a proton from a water molecule which activates it to nucleophilically attack the carbon of the carbonyl group.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Ala69B (main-N) | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asn241B (main-N) | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asn241B (main-C) | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Ser1B (N-term) | proton acceptor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, ingold: bimolecular nucleophilic addition, intermediate formation, overall reactant used
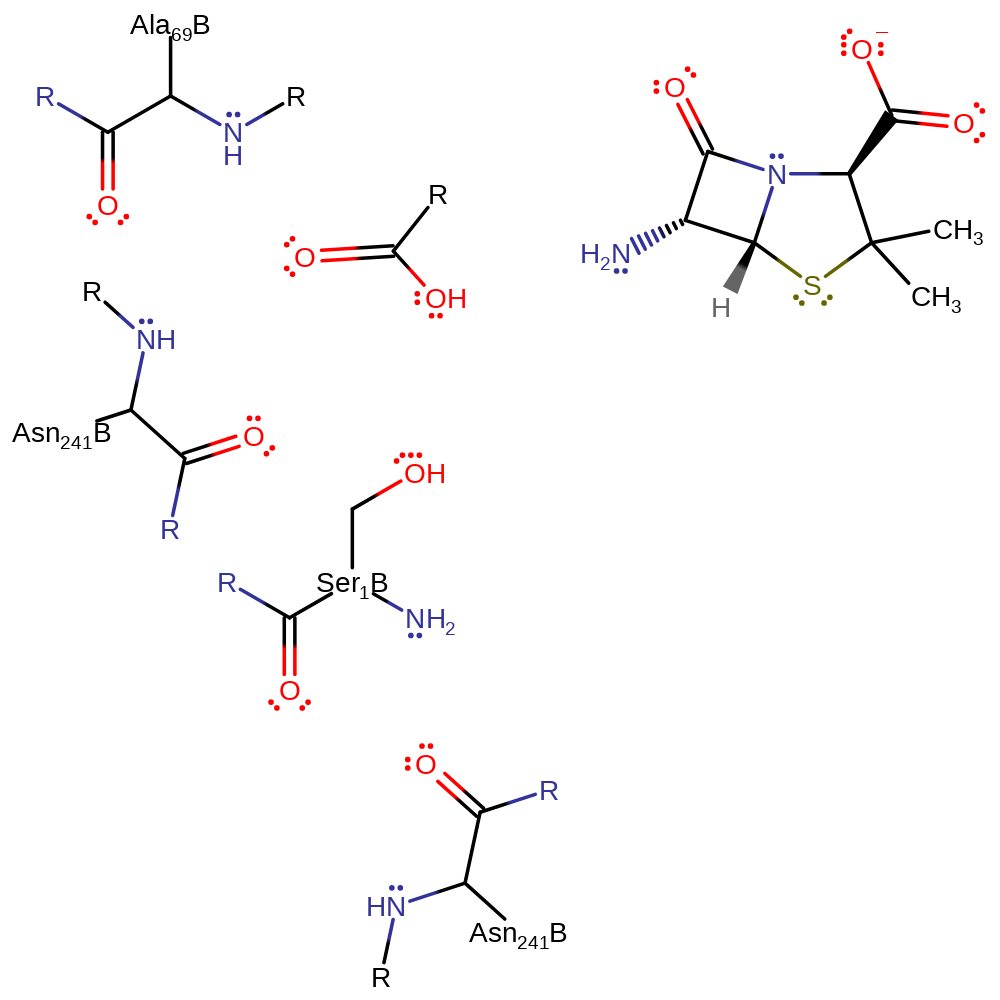
Step 4. The oxyanion initiates an elimination which results in the cleavage acyl-enzyme bond which releases Ser290 which then accepts a proton from its N-terminus and thus returns the active site to its native state.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Ala69B (main-N) | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asn241B (main-N) | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asn241B (main-C) | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Ser1B | nucleofuge |
| Ser1B (N-term) | proton donor |
| Ser1B | proton acceptor |




 Download:
Download: