Alpha-2,3-sialyltransferase
Sialyltransferase (CstII) from Campylobacter jejuni catalyses the transfer of the sialic acid moiety from cytidine-5'-monophospho-N-acetyl-neuramic acid (CMP-NeuAc) to the terminal positions of glycoconjugates. The products play critical roles in recognition and adherence. Campylobacter jejuni has been shown to express variable cell surface carbohydrate mimics of human gangliosides that are associated with virulence.
Reference Protein and Structure
- Sequence
-
Q9LAK3

 (Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
(Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
- Biological species
-
Campylobacter jejuni (Bacteria)

- PDB
-
1ro7
- Structural analysis of the sialyltransferase CstII from Campylobacter jejuni in complex with a substrate analogue, CMP-3FNeuAc.
(1.8 Å)



- Catalytic CATH Domains
-
3.90.1480.10
 (see all for 1ro7)
(see all for 1ro7)
Enzyme Reaction (EC:2.4.99.-)

Enzyme Mechanism
Introduction
Unlike other inverting glucosyltransferases, the reaction proceeds in an Sn1 manner, initiated by elimination of CMP (promoted by Tyr156 and Tyr162). His 188 is stabilised in its unprotonated state by Arg 129. His 188 accepts a proton from the O3' hydroxyl, activating it for nucleophilic attack on the donor C2' atom.
Catalytic Residues Roles
| UniProt | PDB* (1ro7) | ||
| Arg129 | Arg129A | Acts to provide an electrostatic shield favouring the deprotonated form of His188. | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Tyr156, Tyr162 | Tyr156A, Tyr162A | Stabilises the phosphate leaving group by hydrogen bonding to the non-bridging, pro-S oxygen which help prevents the reverse reaction. | electrostatic stabiliser |
| His188 | His188A | His 188 acts as a general base by deprotonating the O3' hydroxyl of the acceptor galactose, activating it for nucleophilic attack at the anomeric carbon of the donor sugar. | activator, proton acceptor, proton donor |
Chemical Components
heterolysis, intermediate formation, elimination (not covered by the Ingold mechanisms), overall reactant used, bimolecular nucleophilic addition, proton transfer, intermediate terminated, overall product formed, native state of enzyme regeneratedReferences
- Hamada Y et al. (2016), Biochemistry, 55, 5764-5771. Quantum Mechanics/Molecular Mechanics Study of the Sialyltransferase Reaction Mechanism. DOI:10.1021/acs.biochem.6b00267. PMID:27644888.
- Chiu CP et al. (2004), Nat Struct Mol Biol, 11, 163-170. Structural analysis of the sialyltransferase CstII from Campylobacter jejuni in complex with a substrate analog. DOI:10.1038/nsmb720. PMID:14730352.
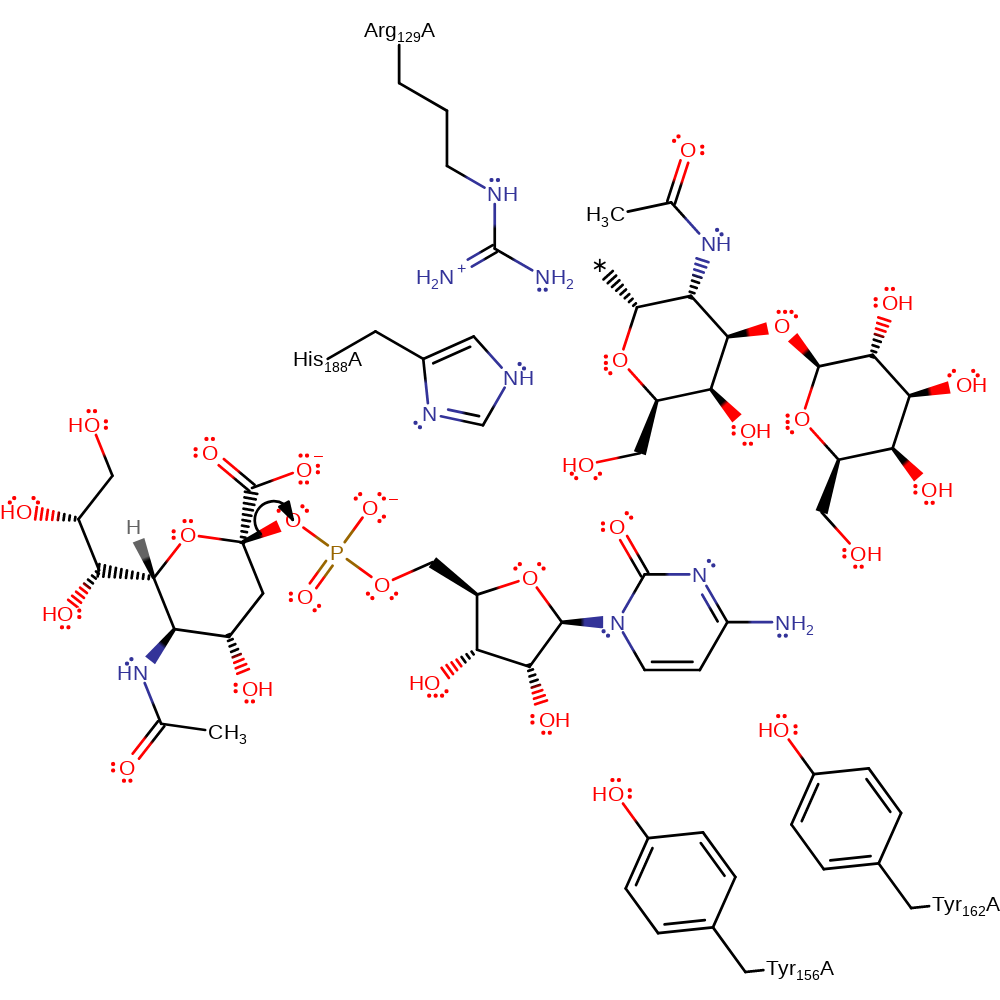
Step 1. Cleavage of C2-O glycosidic bond, stabilised by Tyr156 and Tyr162.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Tyr156A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Arg129A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Tyr162A | electrostatic stabiliser |
Chemical Components
heterolysis, intermediate formation, elimination (not covered by the Ingold mechanisms), overall reactant used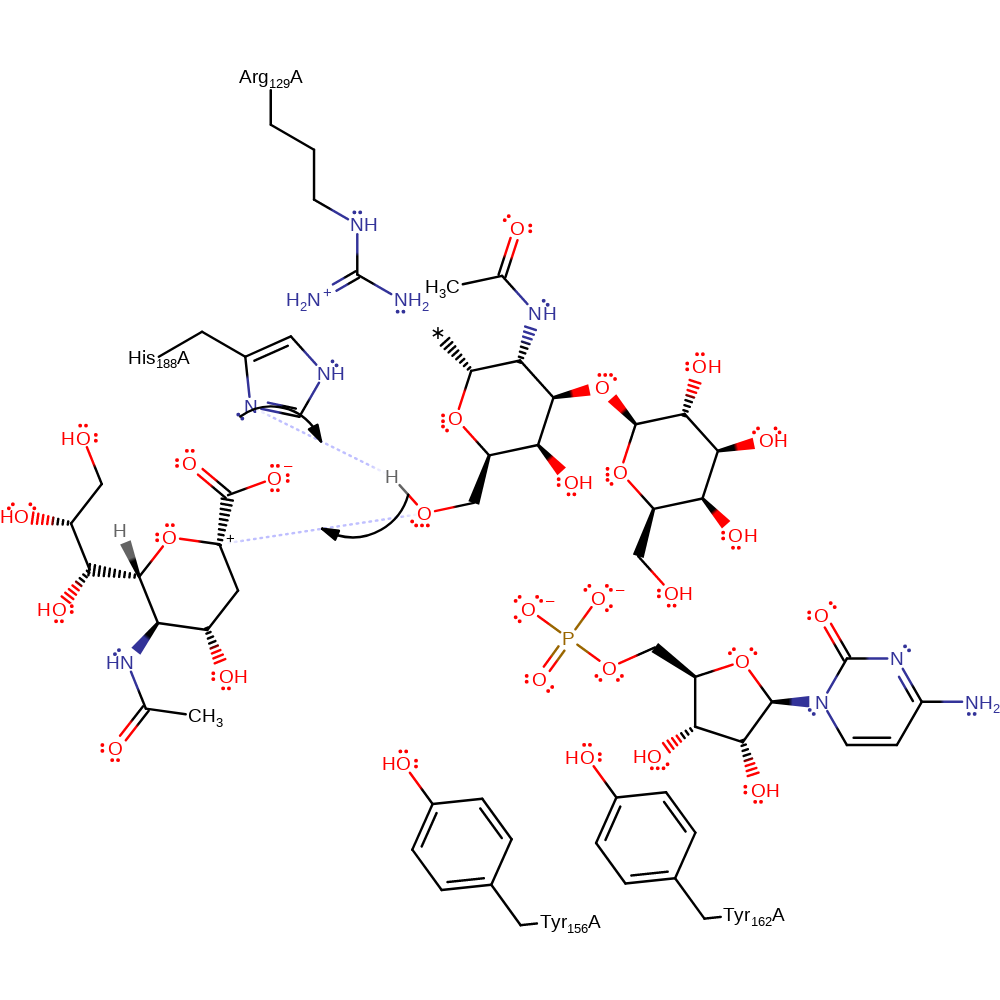
Step 2. His188 deprotonates the 3′-OH of galactose, increasing it's nucleophilicity to then attack the oxocarbenium ion intermediate.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| His188A | activator |
| His188A | proton acceptor |
Chemical Components
ingold: bimolecular nucleophilic addition, proton transfer, overall reactant used, intermediate terminated, overall product formedCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| His188A | proton donor |





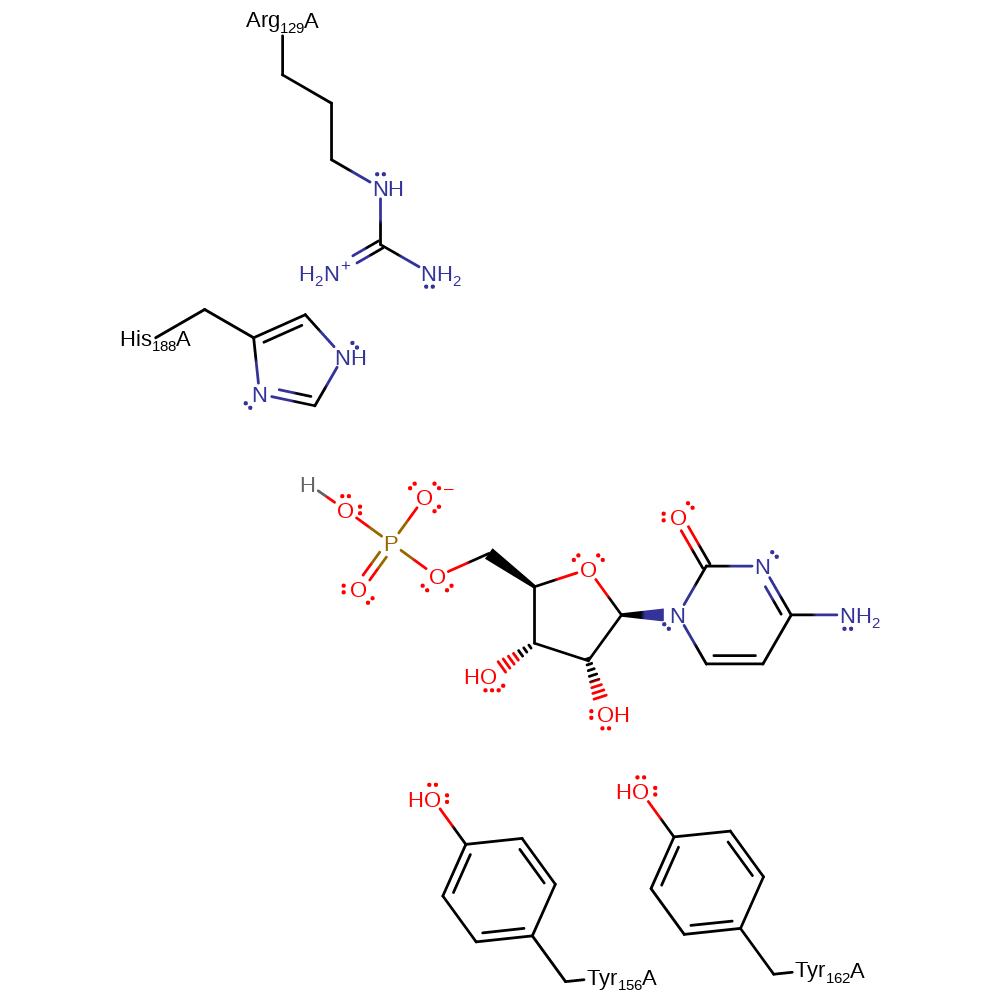 Download:
Download: