Cholesterol oxidase
Cholesterol oxidase catalyses the oxidation and isomerisation of cholesterol to form cholest-4-en-3-one using FAD as a cofactor. The two forms of the enzyme found in Brevibacterium BCO1 and BCO2 do not show any structural or sequence homology, despite carrying out the same reaction. As a result their mechanisms are believed to be different. Study of the enzymes that degrade cholesterol is clearly of great relevance to medicine due to the role of the steroid in cardiovascular disease.
Reference Protein and Structure
- Sequence
-
Q7SID9

 (Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
(Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
- Biological species
-
Brevibacterium sterolicum (Bacteria)

- PDB
-
1i19
- CRYSTAL STRUCTURE OF CHOLESTEROL OXIDASE FROM B.STEROLICUM
(1.7 Å)



- Catalytic CATH Domains
-
3.30.43.10
 3.40.462.10
3.40.462.10  (see all for 1i19)
(see all for 1i19)
- Cofactors
- Fadh2(2-) (1)
Enzyme Mechanism
Introduction
The enzyme is able to carry out three interrelated reactions. First, in the oxidative half reaction, hydride transfer from the C3 of the steroid to N5 of FAD, with deprotonation of the 3C OH by Glu 475 oxidises cholesterol to form cholest-3-one. The proton is transferred to Glu 311, to allow Glu 475 to abstract a proton from the 4C and add it to the 6C to isomerise the cholest-3-one to cholest-4-en-3-one. Meanwhile, in the reductive half reaction, the reduced FAD, stabilised by contacts with Arg 477, transfers a hydride to a dioxygen molecule, which is protonated by Glu 311, forming H2O2.
Catalytic Residues Roles
| UniProt | PDB* (1i19) | ||
| His69 | His121(69)B | Forms a covalent attachment to the FAD cofactor and modifies its redox potential. | covalently attached, alter redox potential |
| Glu423 | Glu475(423)B | Acts as a general acid/base in the oxidative half reaction where it deprotonates the 3C OH group, and in the isomerisation step where it transfers a proton between the 4C and the 6C of the steroid ring system. | proton acceptor, proton donor |
| Arg425 | Arg477(425)B | Stabilises the negative charge that develops on the flavin ring system during its reduction. | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Glu259 | Glu311(259)B | Accepts a proton from Glu 475 in order to allow Glu 475 to function as a base in both the oxidation and isomerisation of cholesterol. Then transfers this proton to the oxygen molecule to allow it to be reduced to H2O2. | proton acceptor, proton donor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, hydride transfer, overall reactant used, overall product formed, native state of enzyme regenerated, native state of cofactor regeneratedReferences
- Coulombe R et al. (2001), J Biol Chem, 276, 30435-30441. Oxygen Access to the Active Site of Cholesterol Oxidase through a Narrow Channel Is Gated by an Arg-Glu Pair. DOI:10.1074/jbc.m104103200. PMID:11397813.
- Vrielink A et al. (2009), FEBS J, 276, 6826-6843. Cholesterol oxidase: biochemistry and structural features. DOI:10.1111/j.1742-4658.2009.07377.x. PMID:19843169.
- Lim L et al. (2006), Biochem J, 400, 13-22. Structural and kinetic analyses of the H121A mutant of cholesterol oxidase. DOI:10.1042/BJ20060664. PMID:16856877.
- Li J et al. (1993), Biochemistry, 32, 11507-11515. Crystal structure of cholesterol oxidase complexed with a steroid substrate: Implications for flavin adenine dinucleotide dependent alcohol oxidases. DOI:10.1021/bi00094a006. PMID:8218217.
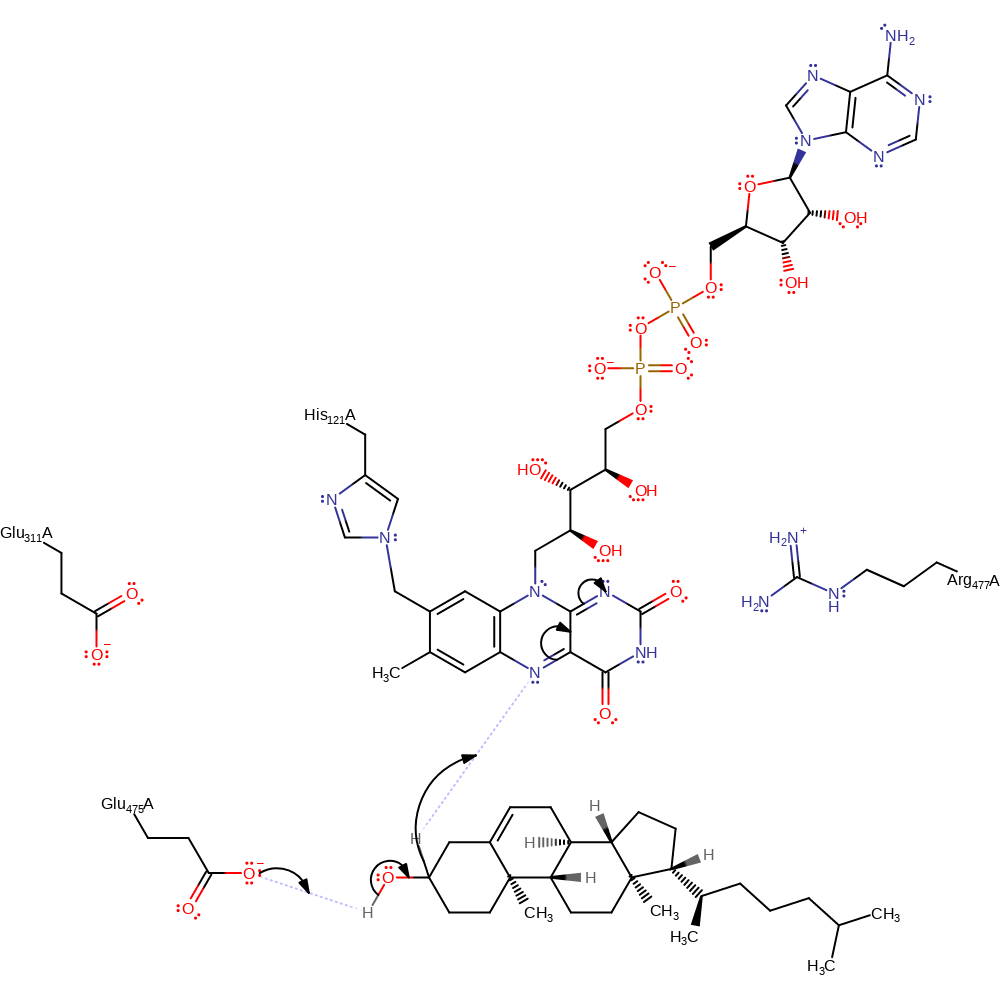
Step 1. In the oxidative half reaction the hydroxyl group of the substrate is deprotonated by Glu475 and a hydride is transferred from C3 of the steroid to N5 of FAD. Cholest-3-one is formed.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| His121(69)B | covalently attached |
| His121(69)B | alter redox potential |
| Arg477(425)B | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Glu475(423)B | proton acceptor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, hydride transfer, overall reactant usedCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Glu475(423)B | proton donor |
| Glu311(259)B | proton acceptor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer
Step 3. Glu475 abstracts a proton from C4 of the oxidised intermediate.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Glu475(423)B | proton acceptor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer
Step 4. The proton abstracted by Glu475 is transferred to C6 to isomerise cholest-3-one to the product, cholest-4-en-3-one.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Glu475(423)B | proton donor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, overall product formed
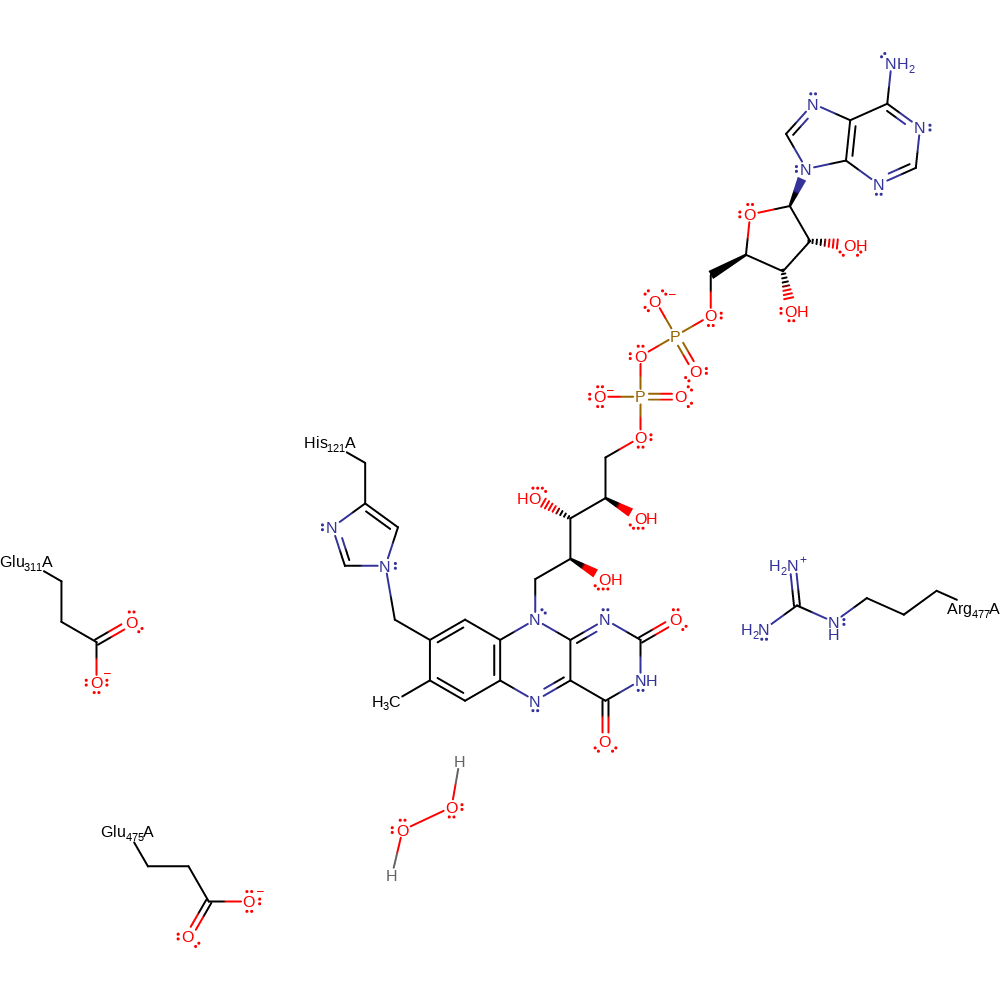
Step 5. In the reductive half reaction FADH- transfers a hydride to a dioxygen molecule which is simultaneously protonated by Glu311, forming H2O2 and restoring the active site.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| His121(69)B | alter redox potential |
| Arg477(425)B | electrostatic stabiliser |
| His121(69)B | covalently attached |
| Glu311(259)B | proton donor |





 Download:
Download: