Ulp1 peptidase
NEDP1 is a 211 residue cysteine-type peptidase of the Ulp family expressed in homo sapiens. It is a deneddylase enzyme involved in the processing of preNEDD8 to its mature form and the deconjugation of NEDD8 from modified substrates (eg. cullin). NEDP1 discrimates between NEDD8 and homologous ubiquitin, involving highly precise molecular recognition due to a single residue change in the C-terminus of NEDD8.
Reference Protein and Structure
- Sequences
-
Q96LD8
 (3.4.22.-)
(3.4.22.-)
Q15843
 (Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
(Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
- Biological species
-
Homo sapiens (Human)

- PDB
-
2bkr
- NEDD8 NEDP1 complex
(1.9 Å)



- Catalytic CATH Domains
-
3.40.395.10
 (see all for 2bkr)
(see all for 2bkr)
Enzyme Reaction (EC:3.4.22.68)
Enzyme Mechanism
Introduction
Deprotonation of the Cys 163 sulfhydryl by an adjacent histidine residue with a basic side chain. The thiolate ion is stabilised through the formation of an ion pair with the neighbouring imidazolium group of His 102. Asp 119 is adjacent to the catalytic His 102, and its side chain amide oxygen is hydrogen bonded to the N(e2)H of His 102. This effect of this is to both stabilise the ion pair and also keep the imidazole ring of the His residue in favourable orientation. The oxyanion is stabilised by an oxyanion hole.
Catalytic Residues Roles
| UniProt | PDB* (2bkr) | ||
| Asp119 | Asp119A | Asp 119 is adjacent to the catalytic His 102, and its side chain amide oxygen is hydrogen bonded to the N(e2)H of His 340. This effect of this is to both stabilise the ion pair and also keep the imidazole ring of the His residue in favourable orientation | electrostatic stabiliser |
| His102 | His102A | The basic side chain of the His residue deprotonates the cysteine thiol to activate it towards nucleophilic attack of the substrate peptide bond. The imidazole ring of His 102 forms an ion pair with Cys 163. His 102 forms a hydrogen bond to the Asn 91 side chain amide oxygen to stabilise the ion pair and keep the imidazole ring in favourable orientation. | proton acceptor, proton donor |
| Trp26 | Trp26A | Trp 26 forms van der Vaals with the C terminal Gly-Gly of NEDD8. It sits directly above the catalytic site with its side chain locking thr Gly-Gly into the active site. | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Trp103 | Trp103A | Trp 103 forms van der Vaals with Gly 75 of NEDD8. This stabilises the transition state. | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Cys163 | Cys163A | Deprotonation of the cysteine thiol by the His 102 basic side chain activates the cysteine S to carry out nucleophilic attack on the carbonyl carbon of the peptide bond in the substrate. The thiolate ion is stabilised by the formation of an active site ion pair with the His 102 imidazole ring. The main chain NH of Cys 163 forms part of the oxyanion hole, which stabilises the transition state. | nucleofuge, nucleophile, proton acceptor, proton donor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, bimolecular nucleophilic addition, enzyme-substrate complex formation, intermediate formation, overall reactant used, unimolecular elimination by the conjugate base, heterolysis, intermediate collapse, overall product formed, enzyme-substrate complex cleavage, native state of enzyme regeneratedReferences
- Shen LN et al. (2005), EMBO J, 24, 1341-1351. Structural basis of NEDD8 ubiquitin discrimination by the deNEDDylating enzyme NEDP1. DOI:10.1038/sj.emboj.7600628. PMID:15775960.
- Mendoza HM et al. (2003), J Biol Chem, 278, 25637-25643. NEDP1, a Highly Conserved Cysteine Protease That deNEDDylates Cullins. DOI:10.1074/jbc.m212948200. PMID:12730221.
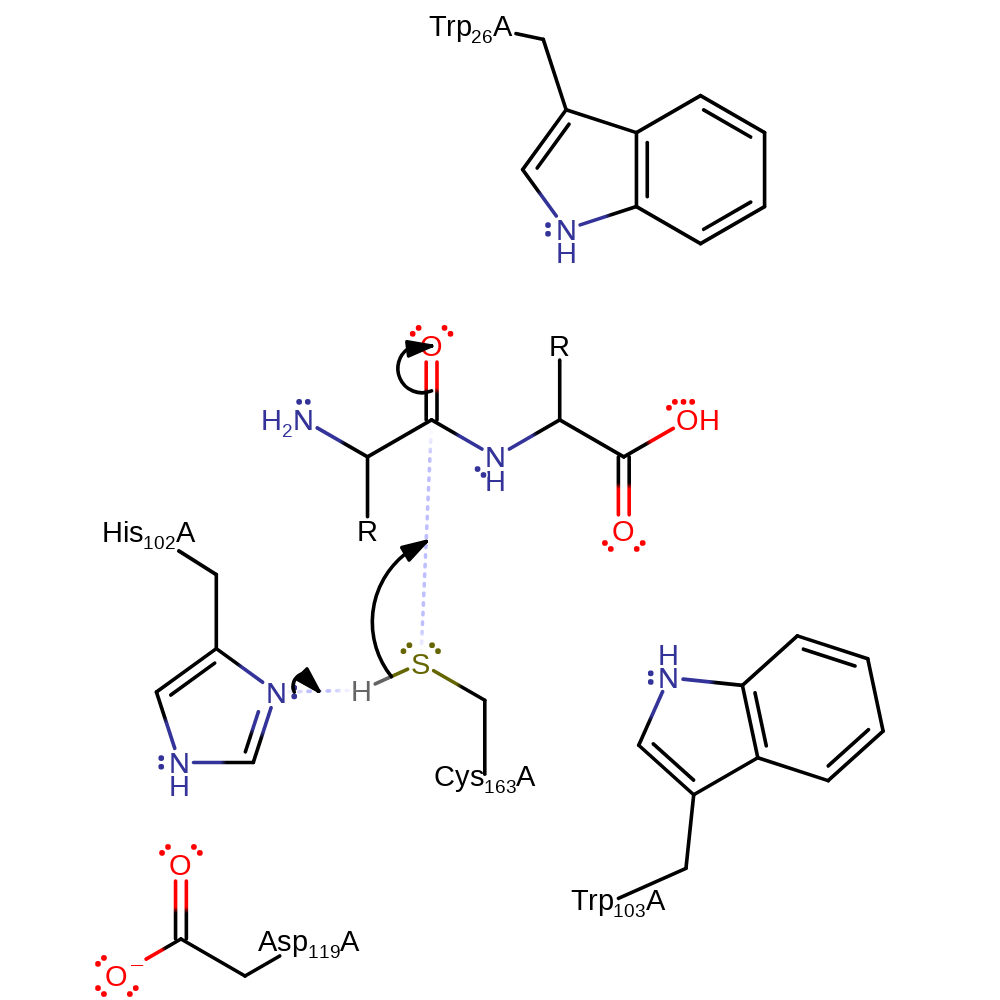
Step 1. His102 deprotonates Cys163 which activates it to nucleophilically attack the carbonyl carbon.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Trp103A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asp119A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Trp26A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Cys163A | proton donor, nucleophile |
| His102A | proton acceptor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, ingold: bimolecular nucleophilic addition, enzyme-substrate complex formation, intermediate formation, overall reactant used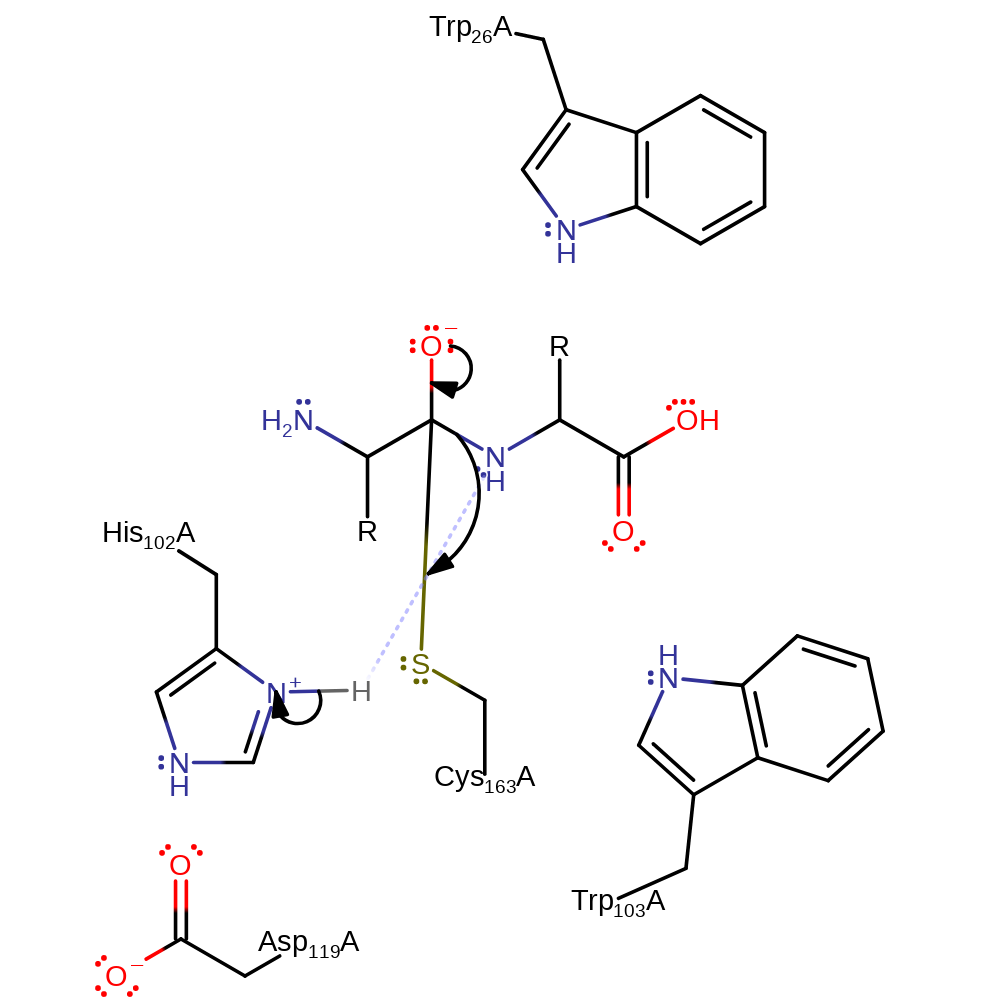
Step 2. His 102 protonates the amide nitrogen which initiates an elimination from the oxyanion which results in the cleavage of the peptide bond.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Trp26A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Trp103A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asp119A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| His102A | proton donor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, ingold: unimolecular elimination by the conjugate base, heterolysis, intermediate collapse, overall product formed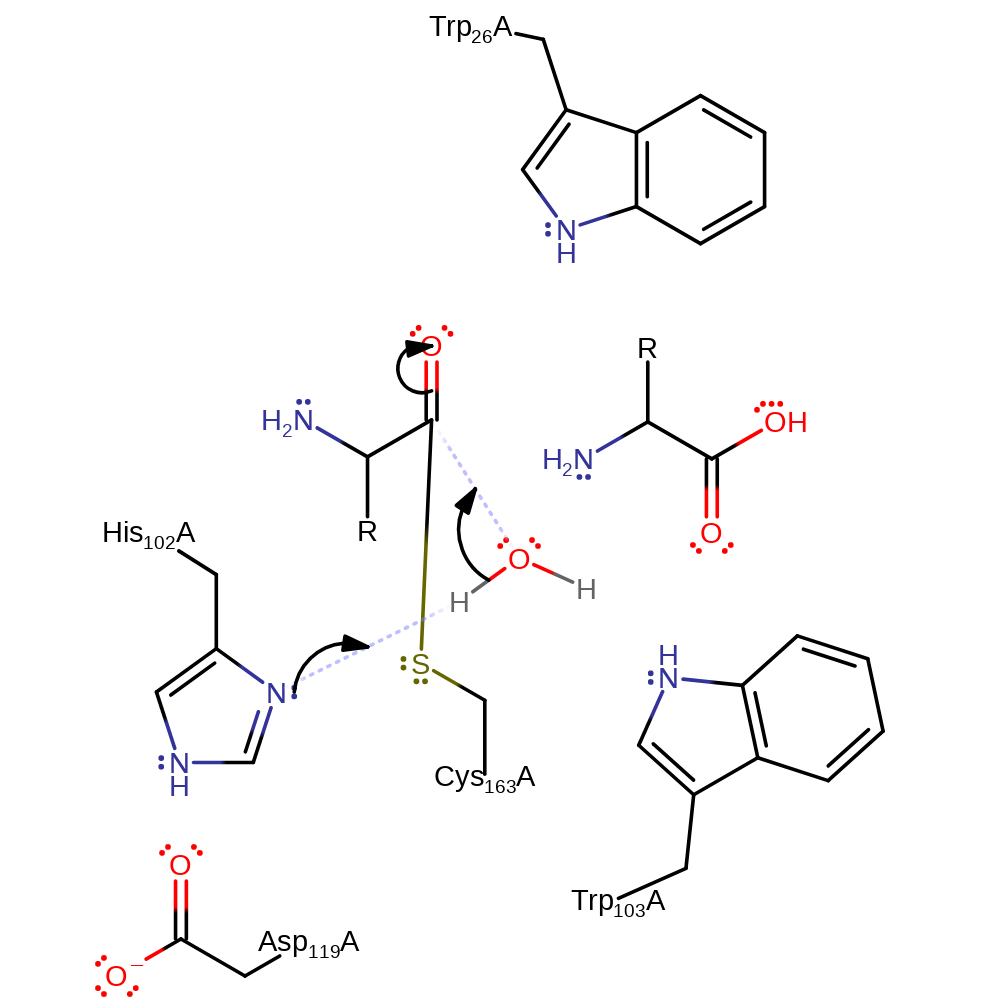
Step 3. His102 abstracts a proton from a water which activates it to nucleophilically attack the carbonyl carbon.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Trp26A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Trp103A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asp119A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| His102A | proton acceptor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, ingold: bimolecular nucleophilic addition, intermediate formation, overall reactant used
Step 4. The oxyanion initiates an elimination results in the cleavage of the acyl-enzyme intermediate and the released Cys163 accepts a proton from His102.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Trp26A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Trp103A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asp119A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Cys163A | nucleofuge |
| His102A | proton donor |
| Cys163A | proton acceptor |



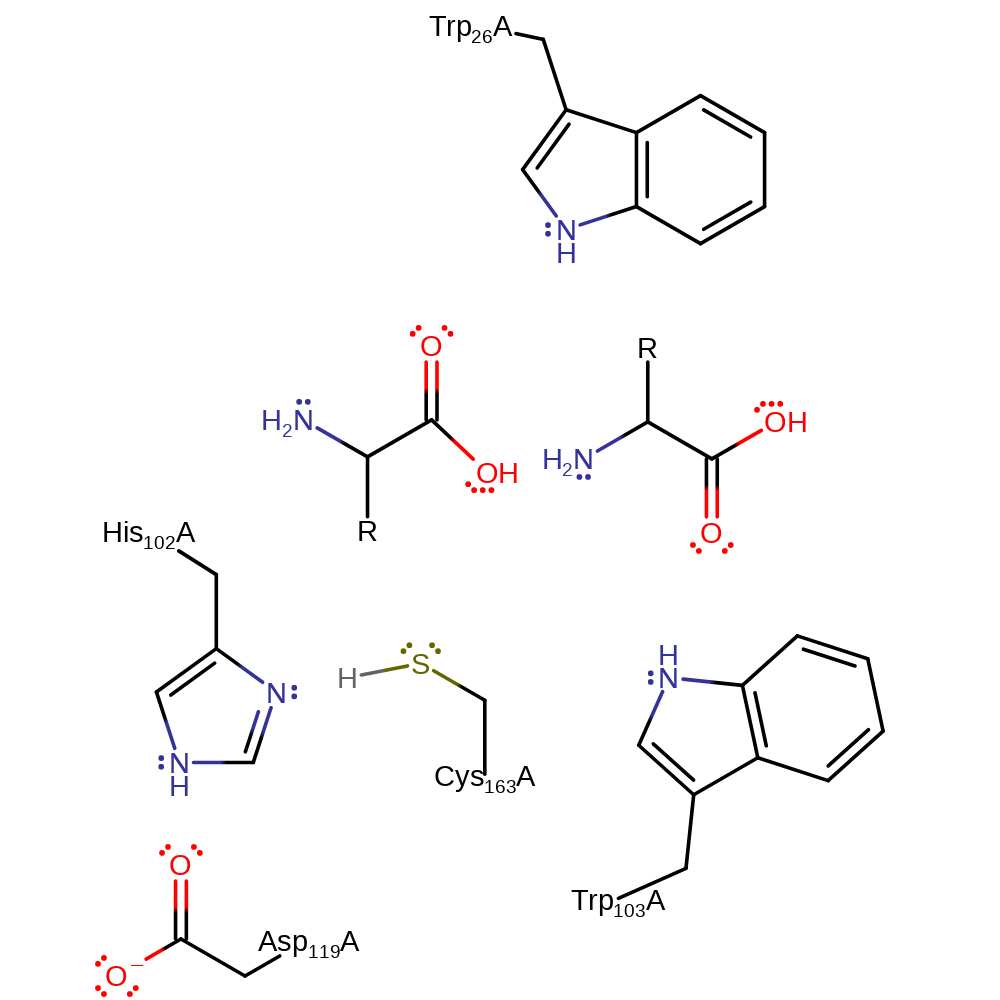 Download:
Download: