Caspase-8
Caspase-8 from Homo sapiens is a cysteine dependent, aspartate specific protease. When activated, it will cleave peptide bonds of other downstream caspases in order to activate them. Caspase-8 must be activated in order to become a protease. It is involved in the process of apoptosis (programmed cell death) which is a central role in the development and homeostasis of an organism.
Reference Protein and Structure
- Sequence
-
Q14790
 (3.4.22.61)
(3.4.22.61)
 (Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
(Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
- Biological species
-
Homo sapiens (Human)

- PDB
-
1qtn
- CRYSTAL STRUCTURE OF THE COMPLEX OF CASPASE-8 WITH THE TETRAPEPTIDE INHIBITOR ACE-IETD-ALDEHYDE
(1.2 Å)



- Catalytic CATH Domains
-
3.40.50.1460
 (see all for 1qtn)
(see all for 1qtn)
Enzyme Reaction (EC:3.4.22.61)
Enzyme Mechanism
Introduction
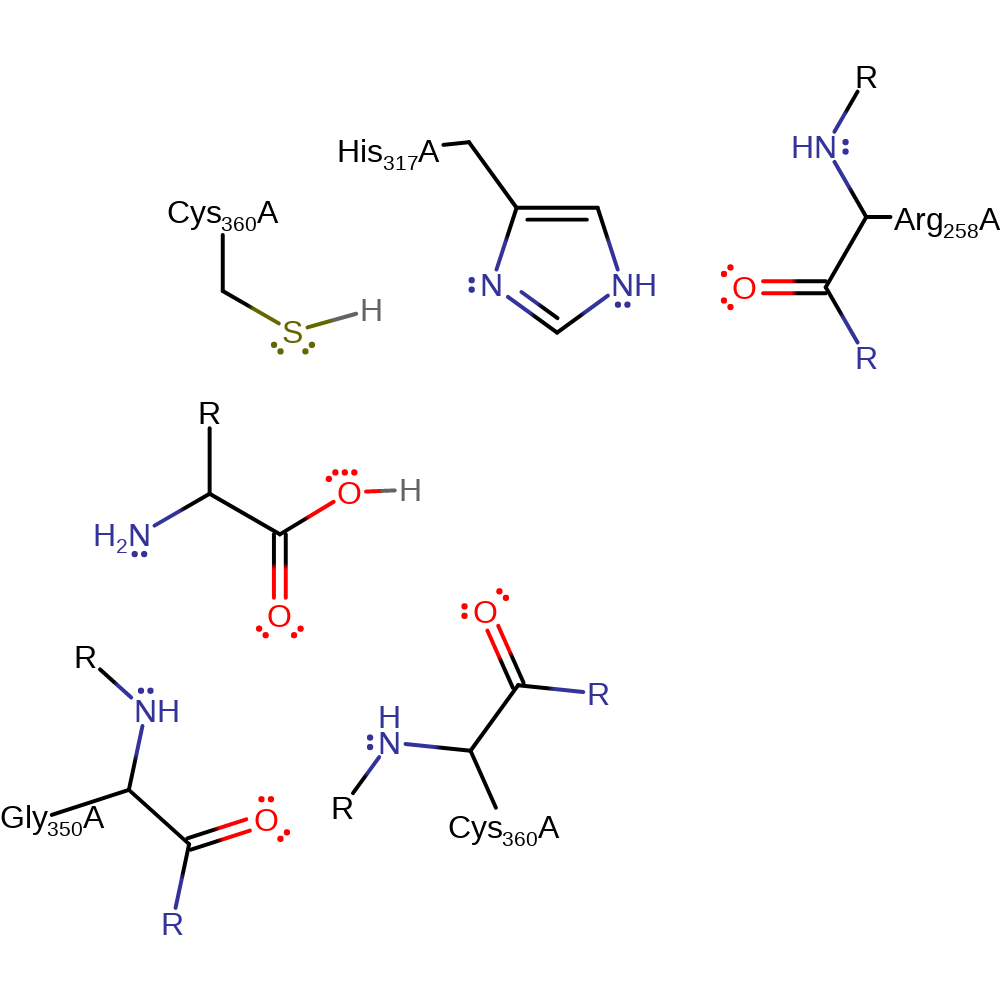
The backbone NH of Gly350 and Cys360 forms the oxyanion hole, and activates the scissile carbonyl bond for nucleophilic attack. His317 is made more basic through hydrogen bonding with the oxygen atom from the backbone carbonyl of Arg258. His317 deprotonates the Cys360 side chain, activating it so the S atom nucleophilically attacks the carbonyl of the scissile peptide bond, forming a negatively charged, tetrahedral intermediate. The intermediate is stabilised by hydrogen bonding to the backbone NH of Gly350 and Cys360. The carbonyl is reformed, and the leaving group amine is protonated by the previously protonated His317. His317 then activates a water molecule for nucleophilic attack on the carbonyl by deprotonating it. The negatively charged, tetrahedral intermediate is again stabilised by hydrogen bonding to the backbone NH of Gly350 and Cys360. The carbonyl is again reformed, and the protonated His317 donates a proton to the leaving group Cys360.
Catalytic Residues Roles
| UniProt | PDB* (1qtn) | ||
| Cys360 (main-N), Gly318 (main-N) | Cys360(150)A (main-N), Gly318(108)A (main-N) | The backbone NH of Gly350 and Cys360 hydrogen bonds to the carbonyl oxygen of the scissile peptide bond. This activates it for nucleophilic attack, and also helps to stabilise the negatively charged, tetrahedral intermediate. | electrostatic stabiliser |
| His317 | His317(107)A | His 317 deprotonates Cys 360, which then goes on to nucleophilically attack the substrate. The protonated form of His 317 then donates a proton to the leaving group amine as the carbonyl is reformed. His 317 then deprotonates a water molecule which goes on to nucleophilically attack the carbonyl. Protonated His 317 then donates a proton back to the leaving group Cys 360 as the carbonyl is once more reformed. | proton acceptor, proton donor |
| Cys360 | Cys360(150)A | The side chain SH of Cys 360 is deprotonated by His 317, and nucleophilically attacks the carbonyl of the scissile bond, forming a negatively charged, tetrahedral intermediate. | nucleofuge, nucleophile, proton acceptor, proton donor |
| Arg258 (main-C) | Arg258(48)A (main-C) | The carbonyl oxygen of Arg 258 acts electrostatically on His 317, making it more basic, and thereby making it more ready to accept a proton from Cys 360. | electrostatic stabiliser |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, bimolecular nucleophilic addition, intermediate formation, overall reactant used, unimolecular elimination by the conjugate base, intermediate collapse, overall product formed, native state of enzyme regeneratedReferences
- Watt W et al. (1999), Structure, 7, 1135-1143. The atomic-resolution structure of human caspase-8, a key activator of apoptosis. DOI:10.1016/s0969-2126(99)80180-4. PMID:10508785.
- Wang Z et al. (2010), Biochim Biophys Acta, 1804, 1817-1831. Kinetic and structural characterization of caspase-3 and caspase-8 inhibition by a novel class of irreversible inhibitors. DOI:10.1016/j.bbapap.2010.05.007. PMID:20580860.
- Sulpizi M et al. (2003), Proteins, 52, 212-224. Reaction mechanism of caspases: insights from QM/MM Car-Parrinello simulations. DOI:10.1002/prot.10275. PMID:12833545.
- Blanchard H et al. (2000), J Mol Biol, 302, 9-16. Caspase-8 specificity probed at subsite S(4): crystal structure of the caspase-8-Z-DEVD-cho complex. DOI:10.1006/jmbi.2000.4041. PMID:10964557.
- Stennicke HR et al. (1999), Cell Death Differ, 6, 1054-1059. Catalytic properties of the caspases. DOI:10.1038/sj.cdd.4400599. PMID:10578173.
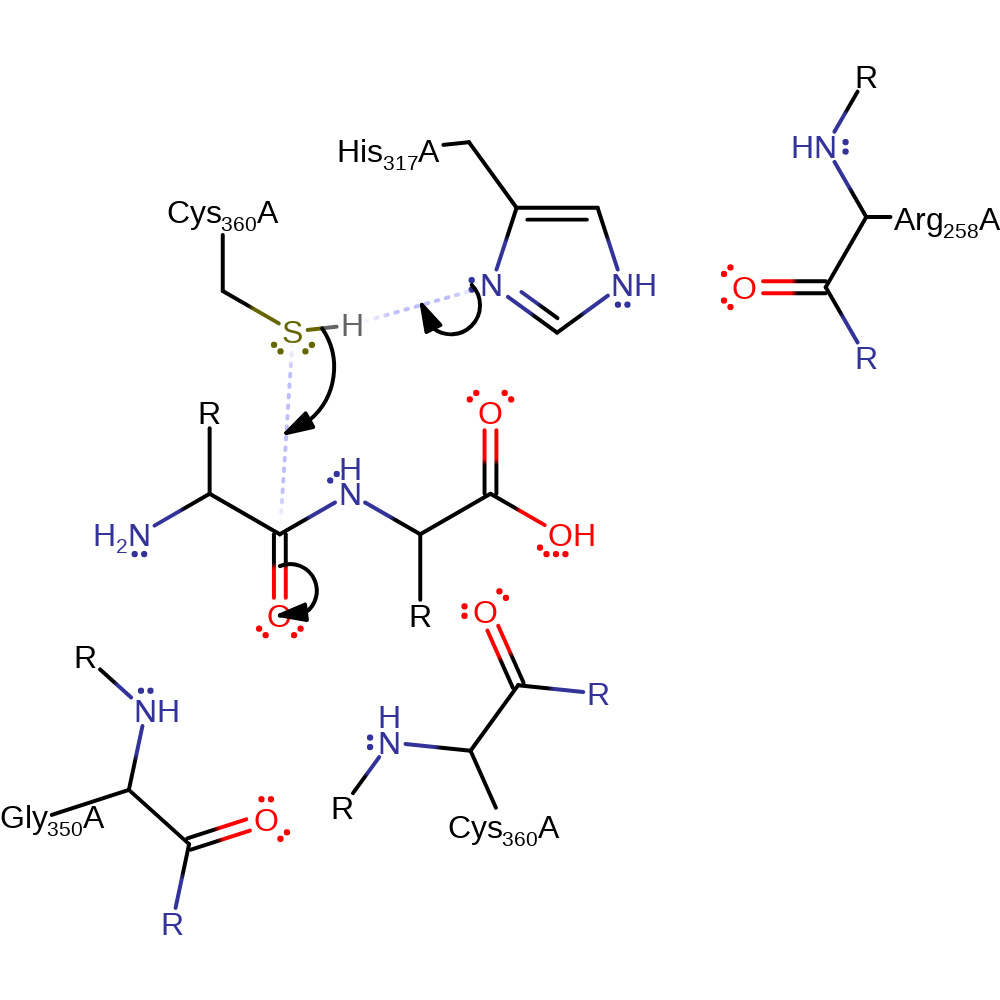
Step 1. His317 deprotonates Cys360 which activates it so that it can attack the carbon of the carbonyl in a nucleophilic addition which produces the oxyanion intermediate.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Gly318(108)A (main-N) | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Arg258(48)A (main-C) | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Cys360(150)A (main-N) | electrostatic stabiliser |
| His317(107)A | proton acceptor |
| Cys360(150)A | proton donor, nucleophile |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, ingold: bimolecular nucleophilic addition, intermediate formation, overall reactant used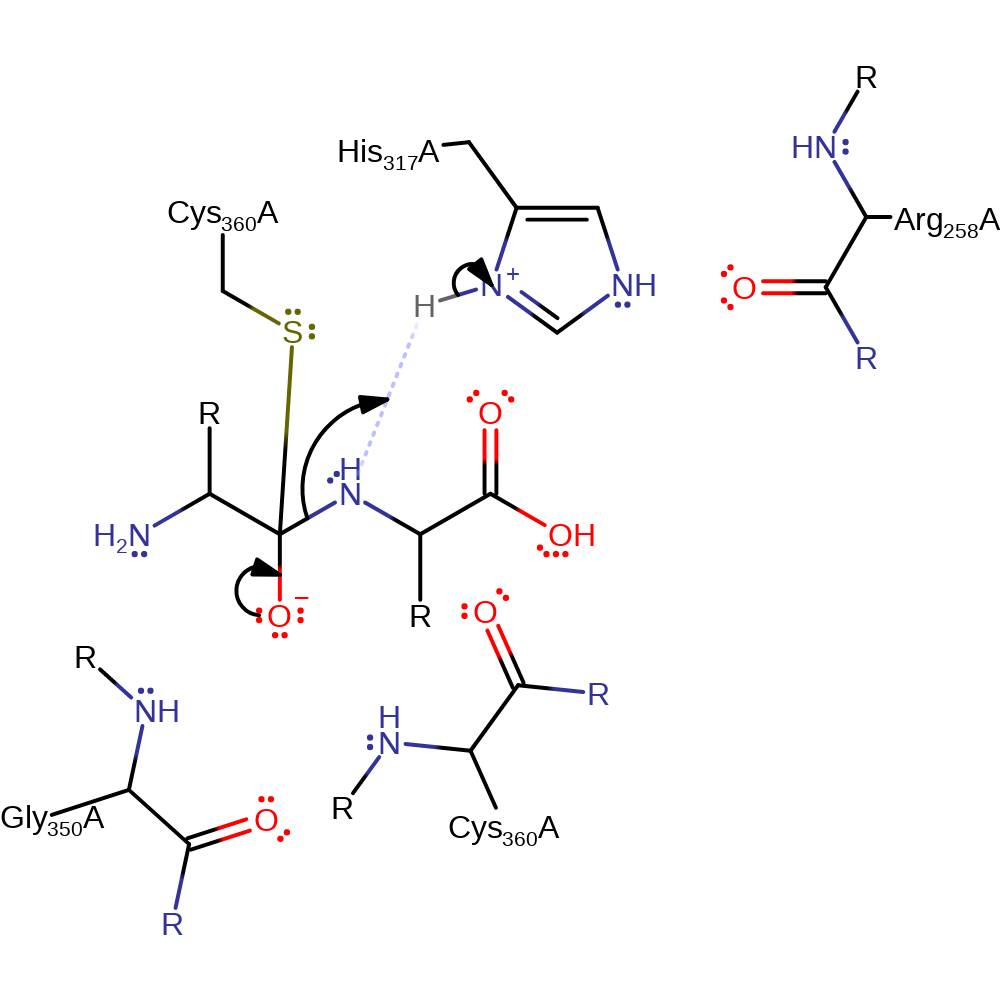
Step 2. The oxyanion initiates an elimination which results in cleavage of the peptide bond. His317 protonates the amino group of the N-terminal product which prevents the reformation of the peptide bond.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Arg258(48)A (main-C) | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Gly318(108)A (main-N) | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Cys360(150)A (main-N) | electrostatic stabiliser |
| His317(107)A | proton donor |
Chemical Components
ingold: unimolecular elimination by the conjugate base, proton transfer, intermediate collapse, overall product formed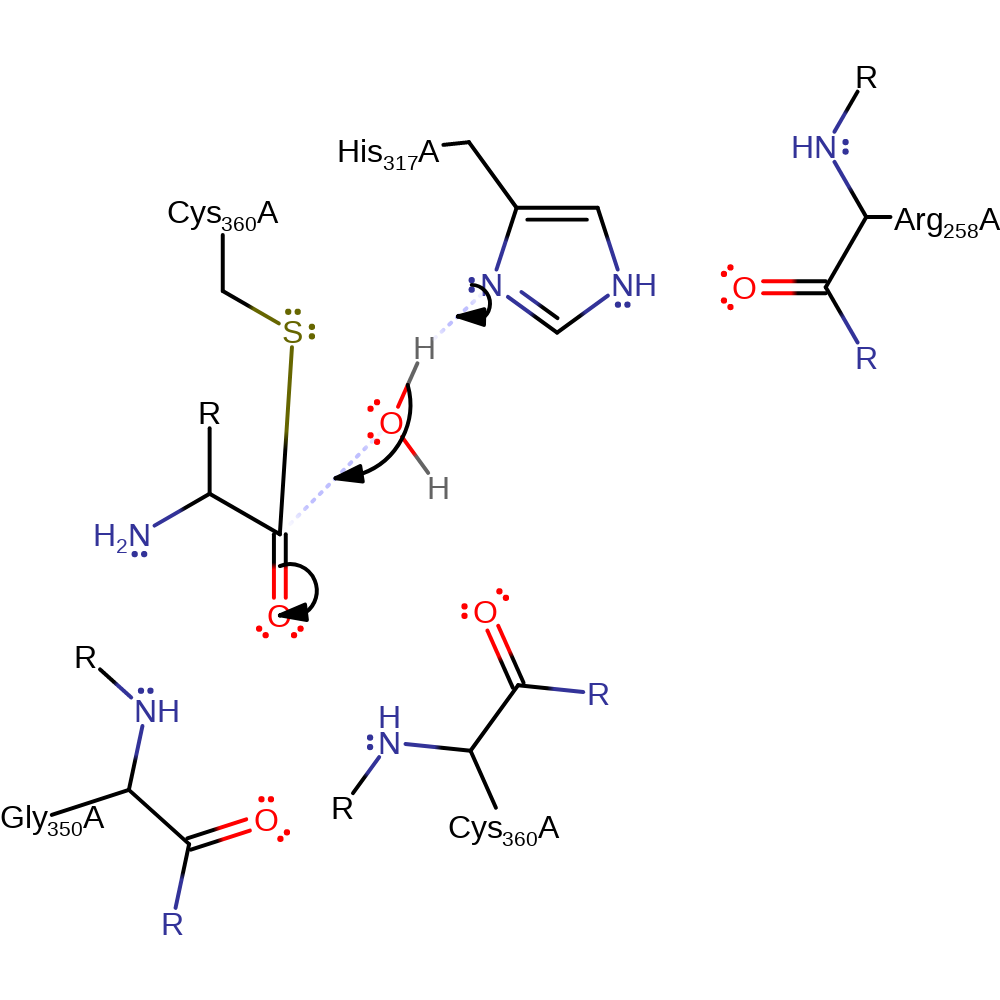
Step 3. His317 deprotonates a water which activates it allowing it to attack the carbon of the thioester bond in a nucleophilic addition.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Arg258(48)A (main-C) | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Gly318(108)A (main-N) | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Cys360(150)A (main-N) | electrostatic stabiliser |
| His317(107)A | proton acceptor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, ingold: bimolecular nucleophilic addition, intermediate formation, overall reactant used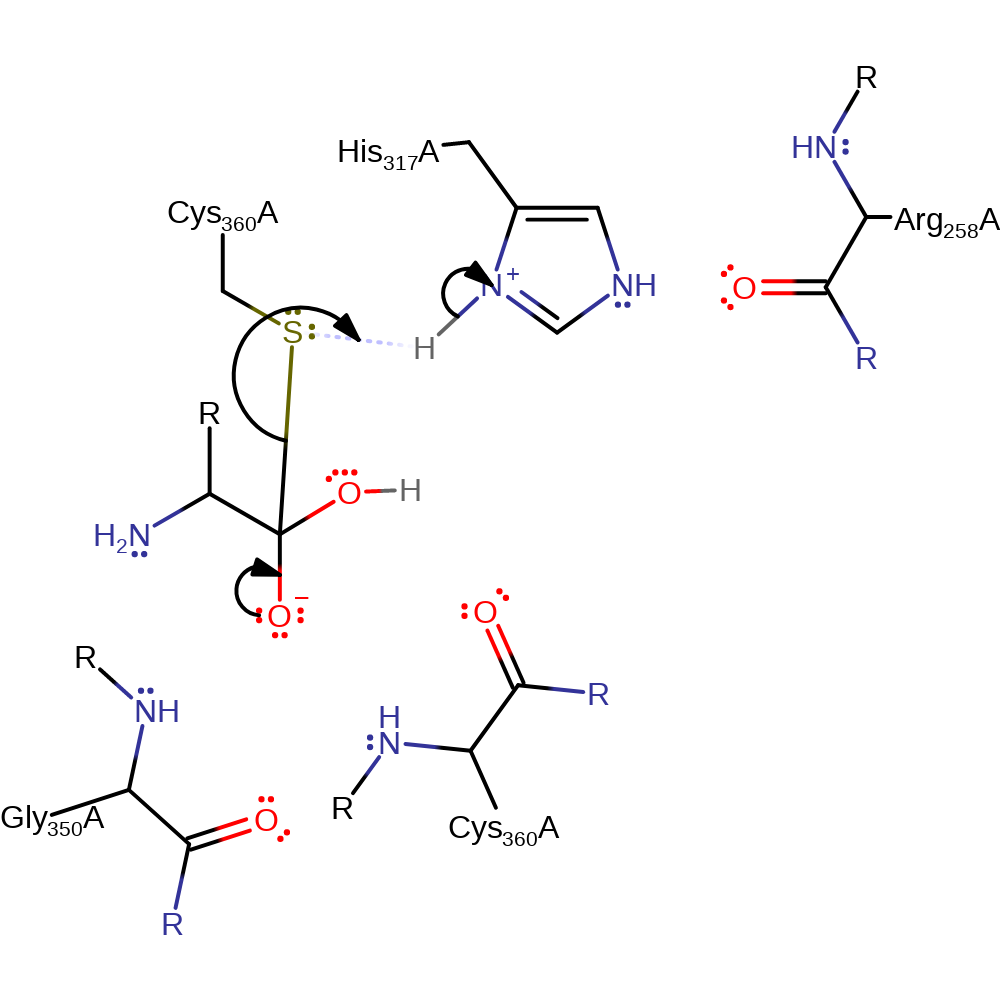
Step 4. The oxyanion initiates an elimination which results in the cleavage of the thioester bond. Cys360 now accepts a proton from His317 which regenerates the enzyme to its native state.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Arg258(48)A (main-C) | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Gly318(108)A (main-N) | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Cys360(150)A (main-N) | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Cys360(150)A | nucleofuge |
| His317(107)A | proton donor |
| Cys360(150)A | proton acceptor |



 Download:
Download: