5'-nucleotidase (mitochondrial)
Mitochondrial 5'-(3') deoxyribonucleotidase (dNT-2) dephosphorylates thymidine and deoxyuridine monophosphates, thus regulates the precursors for mitochondrial DNA synthesis and protects mitochondrial DNA replication from excess dTTP.
Reference Protein and Structure
- Sequence
-
Q9NPB1
 (3.1.3.-)
(3.1.3.-)
 (Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
(Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
- Biological species
-
Homo sapiens (Human)

- PDB
-
1q91
- Crystal structure of human mitochondrial deoxyribonucleotidase in complex with the inhibitor DPB-T
(1.6 Å)



- Catalytic CATH Domains
-
3.40.50.1000
 (see all for 1q91)
(see all for 1q91)
- Cofactors
- Water (2), Magnesium(2+) (1)
Enzyme Reaction (EC:3.1.3.5)
Enzyme Mechanism
Introduction
A mechanism is proposed based on crystal structure. Asp41 nucleophilically attacks the phosphate to form a phosphoenzyme intermediate. Asp43 is positioned to firstly serve as an acid, promoting the protonation of the leaving deoxyribose moiety and then serves as a base to activate the water nucleophile which hydrolyse the covalent enzyme-substrate intermediate.
Catalytic Residues Roles
| UniProt | PDB* (1q91) | ||
| Asp41 | Asp41(10)A | It acts as a nucleophile to attack the phosphate to form a phosphoenzyme intermediate. | covalently attached, nucleophile, nucleofuge, metal ligand |
| Asp176, Asp43 (main-N), Asp41 | Asp176(145)A, Asp43(12)A (main-N), Asp41(10)A | Coordinate the magnesium ion. | metal ligand |
| Asp43 | Asp43(12)A | It acts as an acid, promoting the protonation of the leaving deoxyribose moiety and it serves as a base to activate the water nucleophile which hydrolyse the covalent enzyme-substrate intermediate. | increase nucleophilicity, proton acceptor, proton donor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, overall reactant used, intermediate formation, bimolecular nucleophilic substitution, overall product formed, intermediate terminatedReferences
- Rinaldo-Matthis A et al. (2002), Nat Struct Biol, 9, 779-787. Crystal structure of a human mitochondrial deoxyribonucleotidase. DOI:10.1038/nsb846. PMID:12352955.
- Seifried A et al. (2013), FEBS J, 280, 549-571. Human HAD phosphatases: structure, mechanism, and roles in health and disease. DOI:10.1111/j.1742-4658.2012.08633.x. PMID:22607316.
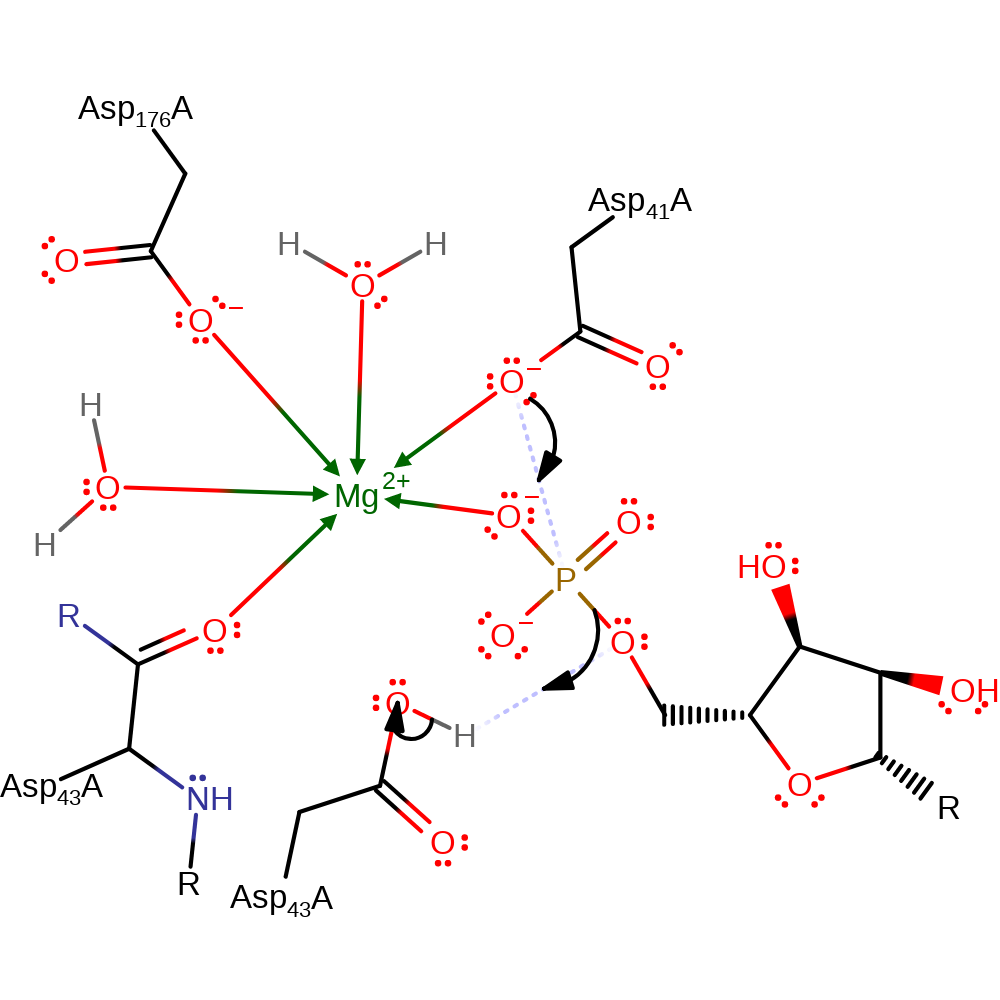
Step 1. Asp41 attacks the phosphate group leading to a phospho-enzyme intermediate being formed. Asp43 donates a proton to the nucleoside leaving group.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Asp41(10)A | covalently attached, metal ligand |
| Asp43(12)A (main-N) | metal ligand |
| Asp176(145)A | metal ligand |
| Asp43(12)A | proton donor |
| Asp41(10)A | nucleophile |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, overall reactant used, intermediate formation, ingold: bimolecular nucleophilic substitution, overall product formed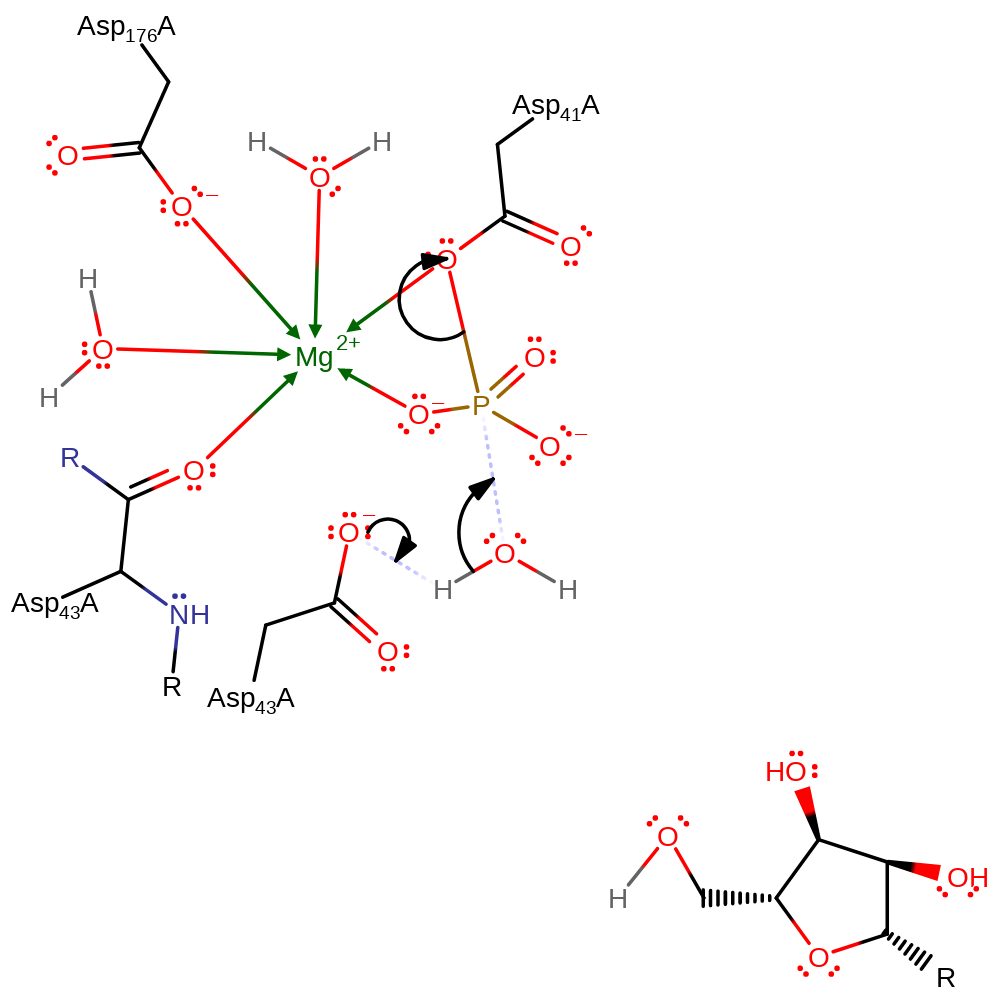
Step 2. Asp43 then activates a water molecule which attacks the phosphate, leading to the collapse of the intermediate.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Asp41(10)A | metal ligand |
| Asp43(12)A (main-N) | metal ligand |
| Asp176(145)A | metal ligand |
| Asp43(12)A | increase nucleophilicity |
| Asp43(12)A | proton acceptor |
| Asp41(10)A | nucleofuge |




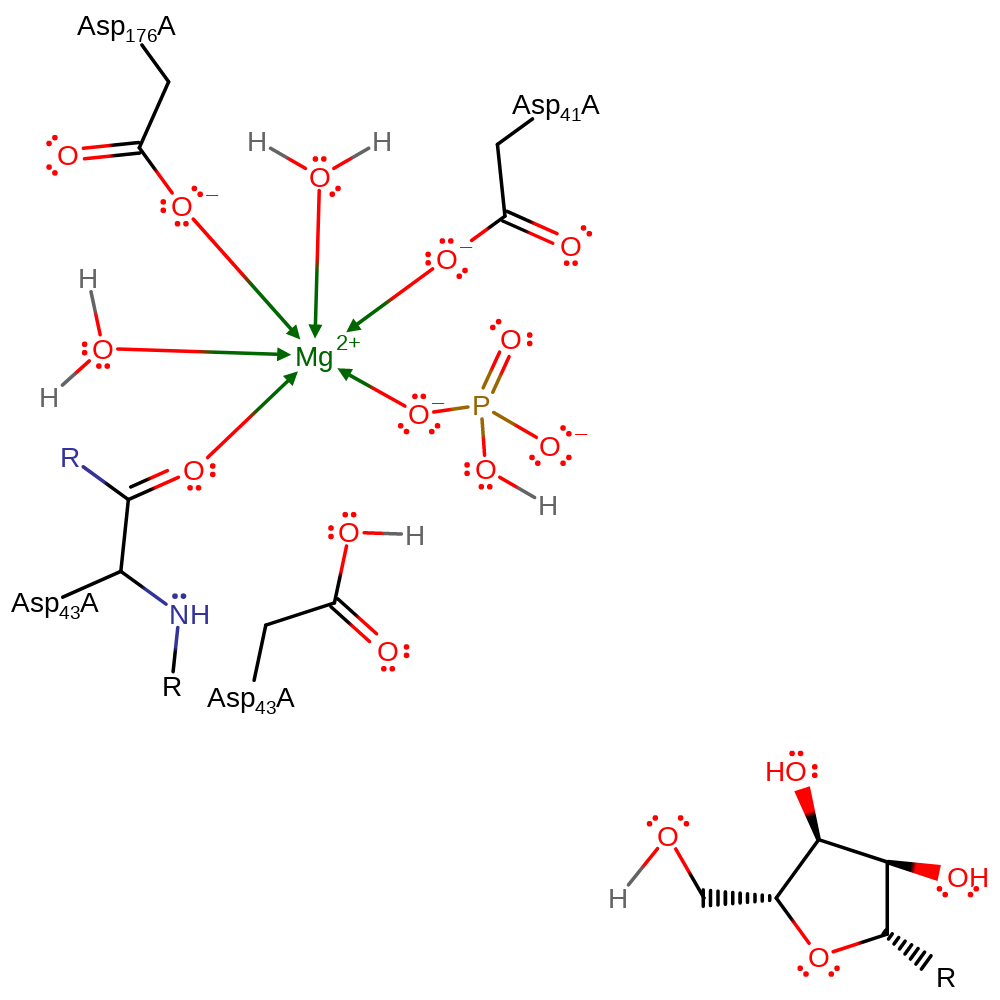 Download:
Download: