UDP-N-acetylglucosamine pyrophosphorylase
The bifunctional enzyme GlmU is able to catalyse two steps in the pathway of bacterial cell wall synthesis:
- The C-terminal domain converts glucosamine-1-phosphate to N-acetyl glucosamine-1-phosphate using Acetyl CoA as the donor
- The N-terminal domain (this entry) utilises UTP to activate the N-acetyl glucosamine-1-phosphate forming UDP-acetyl-glucosamine and pyrophosphate.
Interest in the processes catalysed by this enzyme stems from its potential as an antibiotic target.
Reference Protein and Structure
- Sequence
-
P0ACC7
 (2.3.1.157, 2.7.7.23)
(2.3.1.157, 2.7.7.23)
 (Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
(Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
- Biological species
-
Escherichia coli K-12 (Bacteria)

- PDB
-
1hv9
- STRUCTURE OF E. COLI GLMU: ANALYSIS OF PYROPHOSPHORYLASE AND ACETYLTRANSFERASE ACTIVE SITES
(2.1 Å)



- Catalytic CATH Domains
-
3.90.550.10
 (see all for 1hv9)
(see all for 1hv9)
- Cofactors
- Magnesium(2+) (1)
Enzyme Reaction (EC:2.7.7.23)
Enzyme Mechanism
Introduction
The mechanism of the transfer of UDP to N acetylglucosamine-1-phosphate proceeds via nucleophilic attack from the phosphate oxygen of the phosphate moiety on the alpha phosphate producing a pentavalent phosphate transition state. This is stabilised by Mg2+ at the active site and Arg 18, and collapses to release the beta and gamma phosphates as pyrophosphate.
Catalytic Residues Roles
| UniProt | PDB* (1hv9) | ||
| Arg18 | Arg18B | Stabilises the transition state by forming electrostatic contacts to the alpha phosphate of UTP. | electrostatic stabiliser |
Chemical Components
overall reactant used, overall product formed, bimolecular nucleophilic substitution, inferred reaction step, proton transferReferences
- Brown K et al. (1999), EMBO J, 18, 4096-4107. Crystal structure of the bifunctional N-acetylglucosamine 1-phosphate uridyltransferase from Escherichia coli: a paradigm for the related pyrophosphorylase superfamily. DOI:10.1093/emboj/18.15.4096. PMID:10428949.

Step 1. The phosphate of N-acetyl-alpha-D-glucosamine 1-phosphate attacks the alpha phosphate of UTP. This releases diphosphate and forms the product.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Arg18B | electrostatic stabiliser |
Chemical Components
overall reactant used, overall product formed, ingold: bimolecular nucleophilic substitution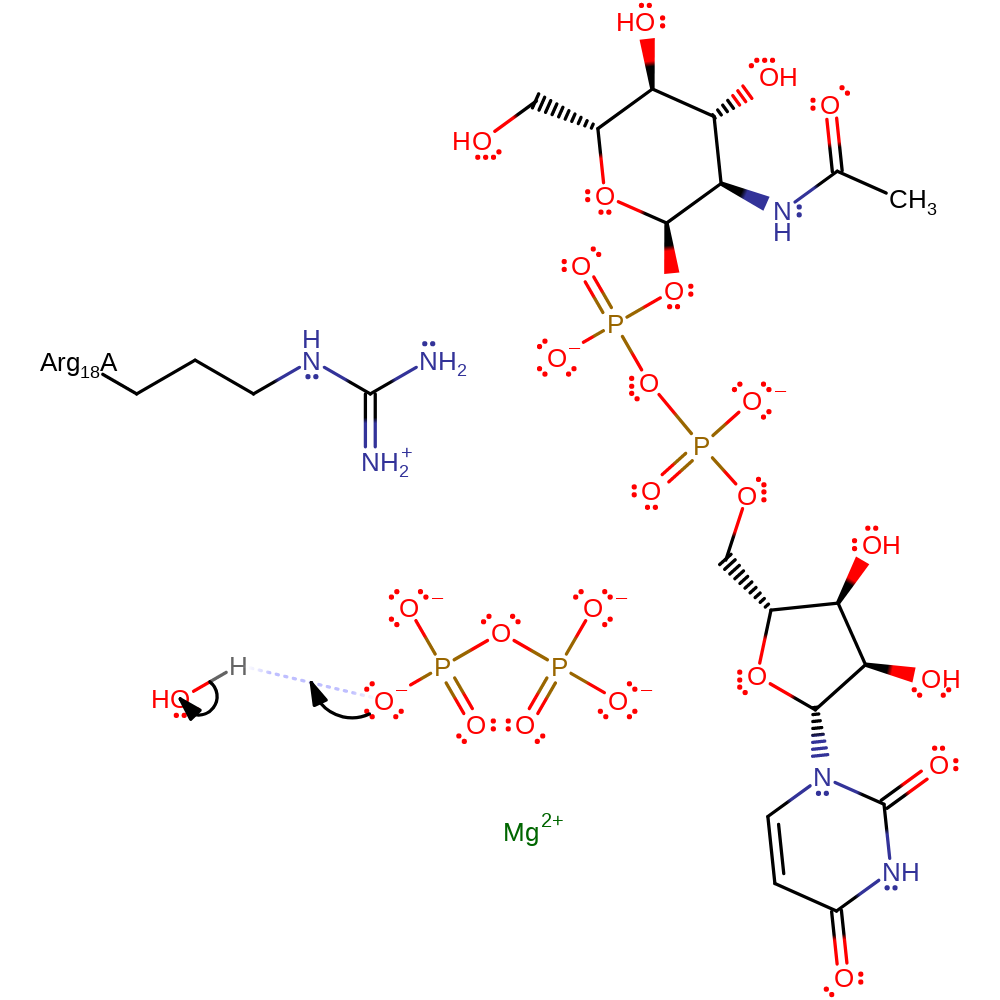
Step 2. The diphosphate group is protonated. The proton may be sourced from the solvent.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|





 Download:
Download: