Protein-glutamine gamma-glutamyltransferase (bacterial)
Transglutaminases, TGase, catalyse an acyl transfer reaction in which gamma-caboxyamide groups of the peptide-bound glutamine residues act as acyl donors with e-amino lysine groups as acyl acceptors. The microbial tranglutaminase, MTG, from Streptoverticllium mobaraense is Ca2+ independent unlike mammalian TGases and folds in to aplate-like shape with a deep cleft at the edge of the molecule. MTG is secreted from the cytoplasm and is activated by proteolytic processing. The additional pro-sequence consisting of 45 amino acid residues at the N terminus is cleaved off, resulting in the active form, the mature enzyme. Industrial applications of MTG include improving the physical and textural properties of protein-rich foods.
Reference Protein and Structure
- Sequence
-
P81453
 (2.3.2.13)
(2.3.2.13)
 (Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
(Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
- Biological species
-
Streptomyces mobaraensis (Streptoverticillium mobaraense)

- PDB
-
1iu4
- Crystal Structure Analysis of the Microbial Transglutaminase
(2.4 Å)



- Catalytic CATH Domains
-
3.90.1360.10
 (see all for 1iu4)
(see all for 1iu4)
Enzyme Reaction (EC:2.3.2.13)
Enzyme Mechanism
Introduction
MTG is involved in catalysing an acyl transfer reaction between protein glutamine and alkylamine, producing protein N(5)-alkylglutamine and ammonia. The residues Cys 64, Asp 255 and His 274 superimpose well on the 'Cys, His, Asp' catalytic triad of other transglutaminases, such as Factor XIII. However, the relative positions of MTG His and Asp seem to be reversed relative to the Cys residue and therefore the catalytic triad is not conserved in the active site of MTG, Hence, a cysteine-like protease mechanism is proposed, in which Asp 255 plays the role of the His residue in factor XIII-like TGases. Cys 64 is sufficiently exposed to the solvent and is deprotonated by water. The thiolate ion of Cys 64 nucleophilically attacks an acyl donor, the carbonyl C of the substrate Gln residue side chain. Electrostatic interaction of Asp 255 with water facilitates donation of a proton from Asp 255 to the resulting oxyanion from nucleophilic attack, and ammonia is released. The Asp 255 gamma-carboxyl group and the His 274 imidazole ring form a hydrogen bond to allow a favourable conformation. The Asp 255 oxygen is negatively charged and nucleophilically attacks a proton of a Lys residue acyl acceptor. Lys 269 side chain acts as an acyl acceptor as the NH attacks the transition state acyl group. Cys 64 N and Trp 272 Ne1 contribute to the stabilising oxyanion hole by forming hydrogen bonds. The product is released from the oxyanion intermediate.
Catalytic Residues Roles
| UniProt | PDB* (1iu4) | ||
| Cys140 | Cys64A | The Cys S is deprotonated by water and the resulting thiolate ion nucleophilically attacks the acyl group of the Gln substrate side chain. Cys 64 N forms part of the transition state-stabilising oxyanion hole. | covalently attached, nucleofuge, nucleophile, proton acceptor, proton donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| His350 | His274A | The carboxyl group of Asp 255 forms a hydrogen bond with His 274 imidazole ring to stabilise the transition state and ensure a favourable conformation | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asp331 | Asp255A | Electrostatic interaction with water initiates Asp 255 to donate a proton to the oxyanion intermediate. The carboxyl group of Asp 255 forms a hydrogen bond with His 275 imidazole ring to stabilise the transition state and ensure a favourable conformation. The negatively charged side chain oxygen on Asp 255 nucleophilically attacks a proton of the Cys residue acyl group. | proton acceptor, hydrogen bond acceptor, electrostatic stabiliser, proton donor |
| Trp348 | Trp272A | Cys 64 N and Trp 272 Ne1 contribute to the stabilising oxyanion hole by forming hydrogen bonds. | electrostatic stabiliser |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, bimolecular nucleophilic addition, enzyme-substrate complex formation, intermediate formation, overall reactant used, heterolysis, elimination (not covered by the Ingold mechanisms), overall product formed, intermediate collapse, bimolecular nucleophilic substitution, unimolecular elimination by the conjugate base, enzyme-substrate complex cleavage, intermediate terminated, native state of enzyme regeneratedReferences
- Kashiwagi T et al. (2002), J Biol Chem, 277, 44252-44260. Crystal Structure of Microbial Transglutaminase from Streptoverticillium mobaraense. DOI:10.1074/jbc.m203933200. PMID:12221081.
Catalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Trp272A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Cys64A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| His274A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asp255A | electrostatic stabiliser, hydrogen bond acceptor |
| His274A | hydrogen bond donor |
| Cys64A | proton donor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer
Step 2. Cys64 performs a nucleophilic attack on the carbonyl carbon of glutamine.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Trp272A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Cys64A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| His274A | hydrogen bond donor |
| Asp255A | hydrogen bond acceptor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| His274A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Cys64A | nucleophile |
Chemical Components
ingold: bimolecular nucleophilic addition, enzyme-substrate complex formation, intermediate formation, overall reactant used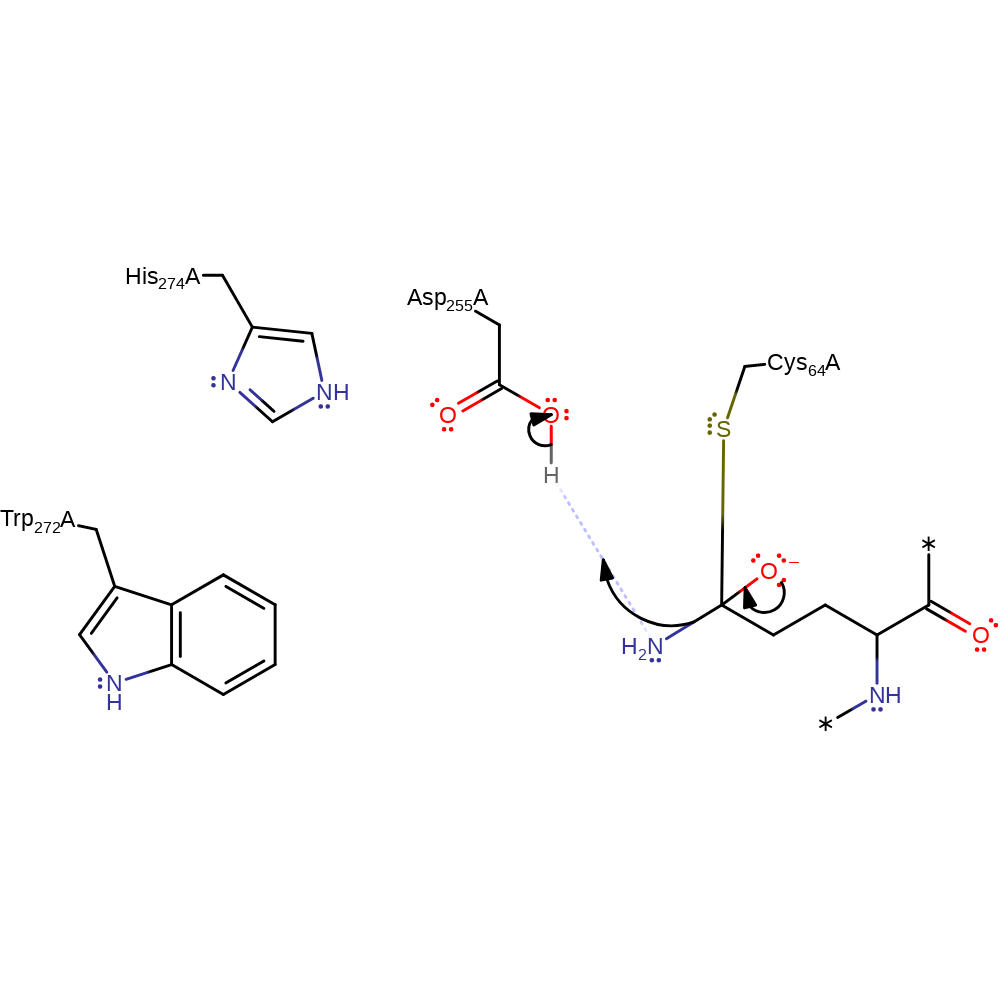
Step 3. Asp255 protonates the oxyanion to release the ammonia leaving group.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Cys64A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Trp272A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| His274A | hydrogen bond donor |
| Asp255A | hydrogen bond acceptor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| His274A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asp255A | proton donor |
Chemical Components
heterolysis, elimination (not covered by the Ingold mechanisms), overall product formed
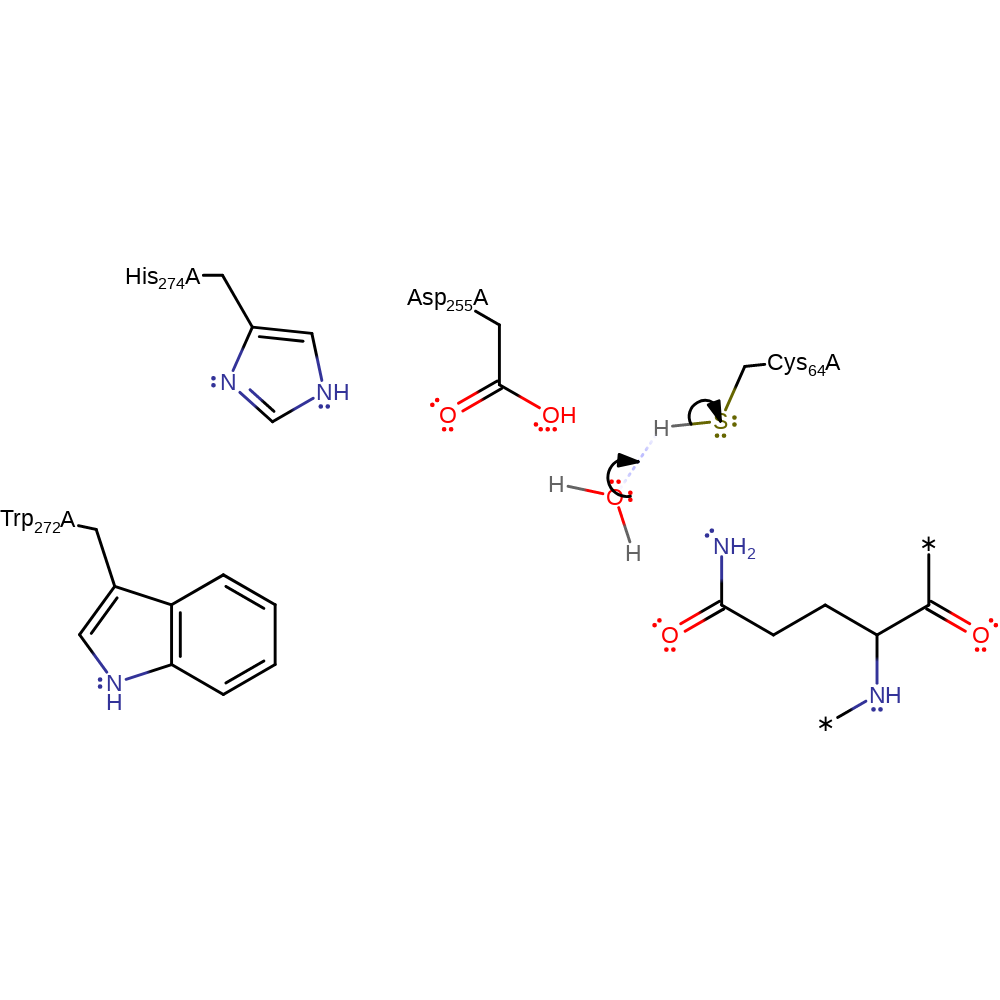
Step 4. Negatively charged Asp255 is protonated from nucleophilic attack on lysine amine group. Lysine amine group then attacks the carbonyl carbon.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Cys64A | covalently attached |
| Asp255A | hydrogen bond acceptor |
| His274A | hydrogen bond donor |
| Asp255A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| His274A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asp255A | proton acceptor |
Chemical Components
intermediate collapse, overall reactant used, ingold: bimolecular nucleophilic addition, ingold: bimolecular nucleophilic substitutionCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Cys64A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Trp272A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asp255A | hydrogen bond acceptor |
| His274A | hydrogen bond donor |
| Asp255A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| His274A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Cys64A | nucleofuge |
Chemical Components
ingold: unimolecular elimination by the conjugate base, enzyme-substrate complex cleavage, intermediate terminated, overall product formed, heterolysisCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Cys64A | proton acceptor |





 Download:
Download: