Cystathionine gamma-synthase
Cystathionine gamma-synthase (CGS) is a pyrodxial phosphate-dependent enzyme that catalyses a gamma-replacement reaction, in which the succinyl group of an O-succinyl-L-homoserine (L-OSHS) is displaced by the thiol of L-cysteine to form L-cystathionine, in the first step of the bacterial transsulphuration pathway. CGS is of interest as a potential target for antibiotics and herbicides.
Reference Protein and Structure
- Sequence
-
P00935
 (2.5.1.48)
(2.5.1.48)
 (Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
(Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
- Biological species
-
Escherichia coli K-12 (Bacteria)

- PDB
-
1cs1
- CYSTATHIONINE GAMMA-SYNTHASE (CGS) FROM ESCHERICHIA COLI
(1.5 Å)



- Catalytic CATH Domains
-
3.40.640.10
 (see all for 1cs1)
(see all for 1cs1)
- Cofactors
- Pyridoxal 5'-phosphate(2-) (1)
Enzyme Reaction (EC:2.5.1.48)
Enzyme Mechanism
- Summary
- Step 1
- Step 2
- Step 3
- Step 4
- Step 5
- Step 6
- Step 7
- Step 8
- Step 9
- Step 10
- Step 11
- Step 12
- Step 13
- Products
- All Steps
Introduction
The reaction proceeds via a series of steps, as is thought to follow a ping-pong mechanism, commonly encountered in PLP-dependent enzymes.
- Transaldimination: (i) OSHS binds through Arg 48*, Tyr 101 and Arg 361. (ii) The alpha-amino group of the substrate must be deprotonated for nucleophilic attack on C4' of the internal aldimine. Tyr 101 exists as phenolate due to two neighbouring positive charges (Arg 48* and NH of the internal aldimine). Therefore, Tyr 101 abstracts a proton from the incoming substrate and initiates transaldimination.
- Generation of the ketimine intermediate: (i) Lys 198 is responsible for proton transfer from the alpha-C to C4' of the PLP cofactor. The protonated amino group of Lys 198 is guided into a favourable position near C4' by Tyr 46*. After alpha-C deprotonation, a quinonoid intermediate is formed, which is stabilised by stacking interactions with Tyr 101. (ii) The Lys 198 e-amino group is positively charged and is therefore attracted to the negatively charged phosphate group of the PLP cofactor, orientating it into a favourable position for bond cleavage. (iii) Due to the new positioning of Lys 198, this residue is able to abstract a proton from the beta-C to initiate gamma-cleavage.
- Release of succinate Tyr 101 facilitates the release of succinate by and acid/base mechanism. The resulting beta-gamma unsaturated ketimine exhibits pronounced electron deficiency, caused by the protonated Schiff base, leading to activation of gamma-C towards Michael nucleophilic addition by L-cysteinate.
- Transaldimination: the reverse steps of 1-3 occur (beta-C protonation, C4' deprotonation, alpha-C protonation.)
Catalytic Residues Roles
| UniProt | PDB* (1cs1) | ||
| Tyr101 | Tyr101A | The phenol group of Tyr 101 exists as phenolate, due to two neighbouring positive charges (Arg 48* and NH of the internal aldimine). Tyr 101 impedes vertical movement of PLP with respect to the pyridine ring since the phenol Tyr ring is positioned appropriately above the PLP pyridine to restrict the cofactor. The resulting stacking interactions also increase the electron sink character of the PLP cofactor. Tyr 101 abstracts a proton from the incoming substrate to initiate transaldimination and also faciliates the release of succinate by and acid/base mechanism. | proton acceptor, electrostatic stabiliser, proton donor |
| Arg48 | Arg48C | Arg 48* allows binding of the PLP phophate and interaction with Tyr 101. Therefore increases the nucleophilicity of the Tyr residue. | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Lys198 (ptm) | Llp198A (ptm) | Lys 198 acts as a Schiff base with a protonated N, and is stabilised by interactions with the deprotonated PLP cofactor group at C3. Lys 198 abstracts a proton from the beta-C to initiate gamma-cleavage. | covalently attached, nucleofuge, nucleophile, proton acceptor, proton donor, electrostatic stabiliser, electron pair acceptor, electron pair donor |
| Asp173 | Asp173A | Asp 173 forms a strong hydrogen bond to the PLP pyridine N1, therefore stabilising its positive charge at this position, and increasing the electrophilic character of the cofactor. The carboxylate group of Asp 173 is fixed in the geometrically optimal position for contact with the substrate N1. | electrostatic stabiliser |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, intermediate formation, overall reactant used, bimolecular nucleophilic addition, cofactor used, enzyme-substrate complex formation, unimolecular elimination by the conjugate base, enzyme-substrate complex cleavage, intermediate collapse, overall product formed, michael addition, bimolecular electrophilic addition, intermediate terminated, native state of cofactor regenerated, native state of enzyme regeneratedReferences
- Clausen T et al. (1998), EMBO J, 17, 6827-6838. Crystal structure of Escherichia coli cystathionine γ-synthase at 1.5 Å resolution. DOI:10.1093/emboj/17.23.6827. PMID:9843488.
- Sato D et al. (2017), Sci Rep, 7, 4874-. X-Ray snapshots of a pyridoxal enzyme: a catalytic mechanism involving concerted [1,5]-hydrogen sigmatropy in methionine γ-lyase. DOI:10.1038/s41598-017-05032-6. PMID:28687762.
- Aitken SM et al. (2003), Biochemistry, 42, 11297-11306. Escherichia coliCystathionine γ-Synthase Does Not Obey Ping-Pong Kinetics. Novel Continuous Assays for the Elimination and Substitution Reactions†. DOI:10.1021/bi035107o. PMID:14503880.
- Clausen T et al. (1996), J Mol Biol, 262, 202-224. Crystal Structure of the Pyridoxal-5′-phosphate Dependent Cystathionine β-lyase fromEscherichia coliat 1.83 Å. DOI:10.1006/jmbi.1996.0508. PMID:8831789.

Step 1. Tyr101 initiates transaldimination by abstracting a proton from the substrate.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Tyr101A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asp173A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Arg48C | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Llp198A (ptm) | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Tyr101A | proton acceptor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, intermediate formation, overall reactant used
Step 2. The substrate amine nucleophilically attacks the C4' on the internal aldimine.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Tyr101A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asp173A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Llp198A (ptm) | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Arg48C | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Llp198A (ptm) | covalently attached, electron pair acceptor, proton acceptor |
Chemical Components
ingold: bimolecular nucleophilic addition, cofactor used, intermediate formation, enzyme-substrate complex formation
Step 3. The secondary aminethaat results from the initial attack initiates an elimination of Lys198.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Tyr101A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asp173A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Llp198A (ptm) | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Arg48C | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Llp198A (ptm) | covalently attached, nucleofuge |
Chemical Components
ingold: unimolecular elimination by the conjugate base, enzyme-substrate complex cleavage, intermediate collapse, intermediate formation
Step 4. Lys198 deprotonates the allylic Cα atom of intermediate which results in the rearrangement of double bonds and PLP acting as an electron sink.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Tyr101A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asp173A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Llp198A (ptm) | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Arg48C | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Llp198A (ptm) | proton acceptor |
Chemical Components
intermediate formation, proton transfer
Step 5. PLP feeds the electron back so that the C4' can accept a proton from Lys198.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Tyr101A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asp173A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Llp198A (ptm) | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Arg48C | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Llp198A (ptm) | proton donor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, intermediate formationCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Tyr101A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asp173A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Llp198A (ptm) | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Arg48C | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Llp198A (ptm) | proton acceptor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, intermediate formation
Step 7. Tyr101 facilitates the release of succinate by protonating the oxygen which results in the cleavage of succinate from the substrate and the rearrangement of double bonds.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Tyr101A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asp173A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Llp198A (ptm) | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Arg48C | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Tyr101A | proton donor |
Chemical Components
ingold: unimolecular elimination by the conjugate base, intermediate collapse, intermediate formation, overall product formed, proton transfer
Step 8. The gamma carbon now has pronounced electron deficiency and so cysteine can attack it by Michael nucleophilic addition.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Tyr101A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asp173A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Llp198A (ptm) | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Arg48C | electrostatic stabiliser |
Chemical Components
ingold: bimolecular nucleophilic addition, michael addition, intermediate formation, overall reactant usedCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Tyr101A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asp173A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Llp198A (ptm) | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Arg48C | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Llp198A (ptm) | proton donor |
Chemical Components
ingold: bimolecular electrophilic addition, intermediate formation, proton transfer
Step 10. Lys198 deprotonates the C4' carbon which results in the arrangement of double bonds as PLP acts as an electron sink.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Tyr101A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asp173A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Llp198A (ptm) | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Arg48C | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Llp198A (ptm) | proton acceptor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, intermediate formation
Step 11. PLP feeds the electrons back which results in the protonation of the alpha carbon.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Tyr101A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asp173A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Llp198A (ptm) | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Arg48C | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Llp198A (ptm) | proton donor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, intermediate formation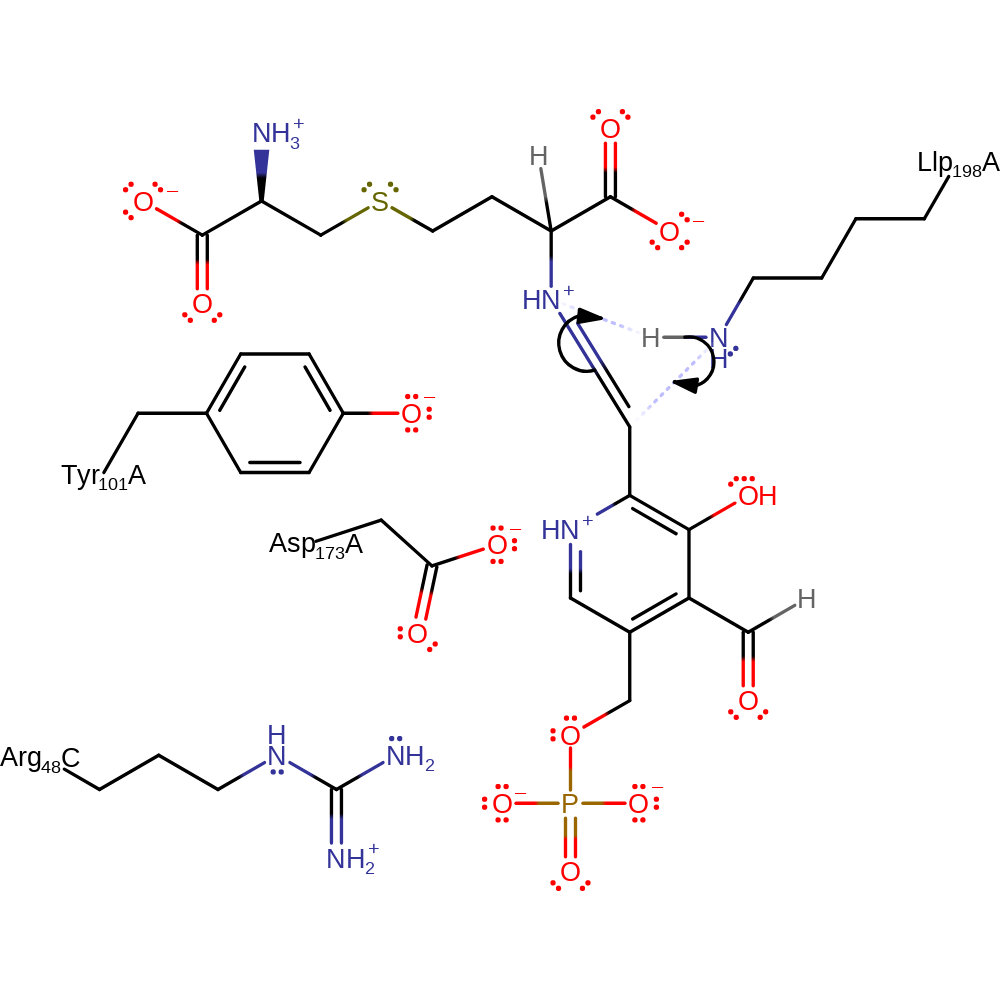
Step 12. The amine of Lys198 attacks the PLP in a nucleophilic addition reaction, the secondary amine of the attached substrate reprotonates from the bound Lys198.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Tyr101A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asp173A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Llp198A (ptm) | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Arg48C | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Llp198A (ptm) | nucleophile, proton donor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, ingold: bimolecular nucleophilic addition, enzyme-substrate complex formation, intermediate formation
Step 13. The secondary amine that results from the initial attack initiates an elimination of the covalently bound product, resulting in cystathionine and the regenerated PLP cofactor.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Tyr101A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asp173A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Llp198A (ptm) | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Arg48C | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Llp198A (ptm) | covalently attached, electron pair donor |







 Download:
Download: