Hydroperoxide dehydratase
Coral allene oxide synthase (cAOS) is a fusion protein with 8R-lipoxygenase (LOX) from Plexura homomalia. cAOS is a hemoprotein with sequence homology to catalase, and is involved in the catalysis of the production of an unstable epoxide (an allene oxide) from the fatty acid hydroperoxide generated by the lipoxygenase activity (8R-HPETE). Despite the sequence homology to catalase, cAOS does not exhibit catalase activity as is does not catalyse the dismutation of hydrogen peroxide to water.
Reference Protein and Structure
- Sequence
-
O16025
 (1.13.11.40, 4.2.1.92)
(1.13.11.40, 4.2.1.92)
 (Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
(Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
- Biological species
-
Plexaura homomalla (Black sea rod)

- PDB
-
1u5u
- The structure of an Allene Oxide Synthase reveals a novel use for a catalase fold
(2.0 Å)



- Catalytic CATH Domains
-
2.40.180.10
 (see all for 1u5u)
(see all for 1u5u)
- Cofactors
- Heme b (1)
Enzyme Reaction (EC:4.2.1.92)
Enzyme Mechanism
Introduction
Despite sequence homology to catalase, the catalytic activities of cAOS and catalase are very different. 8R-HPETE is the fatty acid hydroperoxide derivative of arachidonic acid, produced by LOX activity. cAOS catalyses the conversion of 8R-HPETE into an allene oxide.
His 67 hydrogen bonds to the terminal peroxide hydrogen, favouring homolytic cleavage. His 67 hydrogen bonds to Thr 66 and Asn 137, which keeps the distal His imidazole ring in the correct orientation (flipped, relative to in catalase) for enzymatic activity. A hydrogen bond from the main chain amide of Asn 137 also helps to promote this cleavage. Cleavage results in the formation of an alkoxyl radical. One of the peroxide oxygens becomes bound to the heme group as a hydroxyl, with the other oxygen forming the radical. The alkoxyl radical forms a carbon radical, which reduces Fe-IV. The carbon radical is converted into a short-lived epoxy allylic carbocation. This carbocation is deprotonated by His 67 to form the allene oxide.
Catalytic Residues Roles
| UniProt | PDB* (1u5u) | ||
| Asn137 | Asn137A | Asn 137 hydrogen bonds to His 67 to ensure favourable orientation of the histidine. Hydrogen bonding to the non-terminal peroxide oxygen of the substrate favours homolytic cleavage. | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Thr66 | Thr66A | Thr 66 hydrogen bonds to His 67 to ensure favourable orientation of the His imidazole ring. | electrostatic stabiliser |
| His67 | His67A | His 67 promotes homolyic cleavage by hydrogen bonding to the terminal peroxide oxygen. The position of the His imidazole ring with respect to the heme group is achieved by hydrogen bonds of the His residue to Thr 66 and Asn 137. His 67 also deprotonates the carbocation intermediate to form the allene oxide product. | proton acceptor, electrostatic stabiliser, proton donor |
Chemical Components
intermediate formation, homolysis, radical formation, redox reaction, radical propagation, radical termination, proton transfer, overall product formed, native state of enzyme regenerated, inferred reaction stepReferences
- Oldham ML et al. (2005), Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, 102, 297-302. The structure of coral allene oxide synthase reveals a catalase adapted for metabolism of a fatty acid hydroperoxide. DOI:10.1073/pnas.0406352102. PMID:15625113.
- De Luna P et al. (2013), J Phys Chem B, 117, 14635-14641. A molecular dynamics examination on mutation-induced catalase activity in coral allene oxide synthase. DOI:10.1021/jp408486n. PMID:24164352.
- Tosha T et al. (2006), J Biol Chem, 281, 12610-12617. On the Relationship of Coral Allene Oxide Synthase to Catalase: A SINGLE ACTIVE SITE MUTATION THAT INDUCES CATALASE ACTIVITY IN CORAL ALLENE OXIDE SYNTHASE. DOI:10.1074/jbc.m600061200. PMID:16513636.
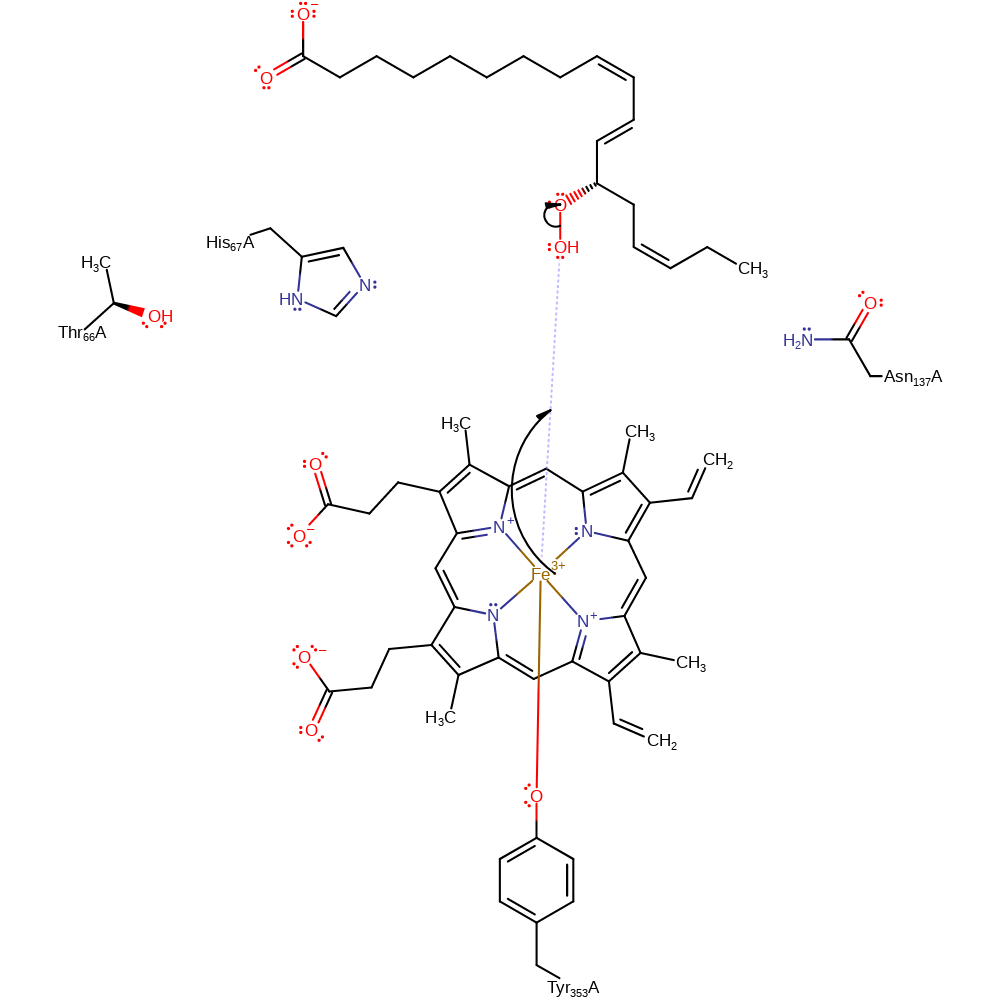
Step 1. The Fe(III) ion causes homolysis of the hydroperoxide O-O bond and generates a free radical intermediate. His67 and Asn137 hydrogen bond to the substrate.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Asn137A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Thr66A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| His67A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Tyr353A | metal ligand |
Chemical Components
intermediate formation, homolysis, radical formation, redox reactionCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Thr66A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| His67A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asn137A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Tyr353A | metal ligand |
Chemical Components
radical propagation
Step 3. An electron is transferred to Fe(IV) centre, forming a carbocation and Fe(III).
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Thr66A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| His67A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asn137A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Tyr353A | metal ligand |
Chemical Components
redox reaction, radical termination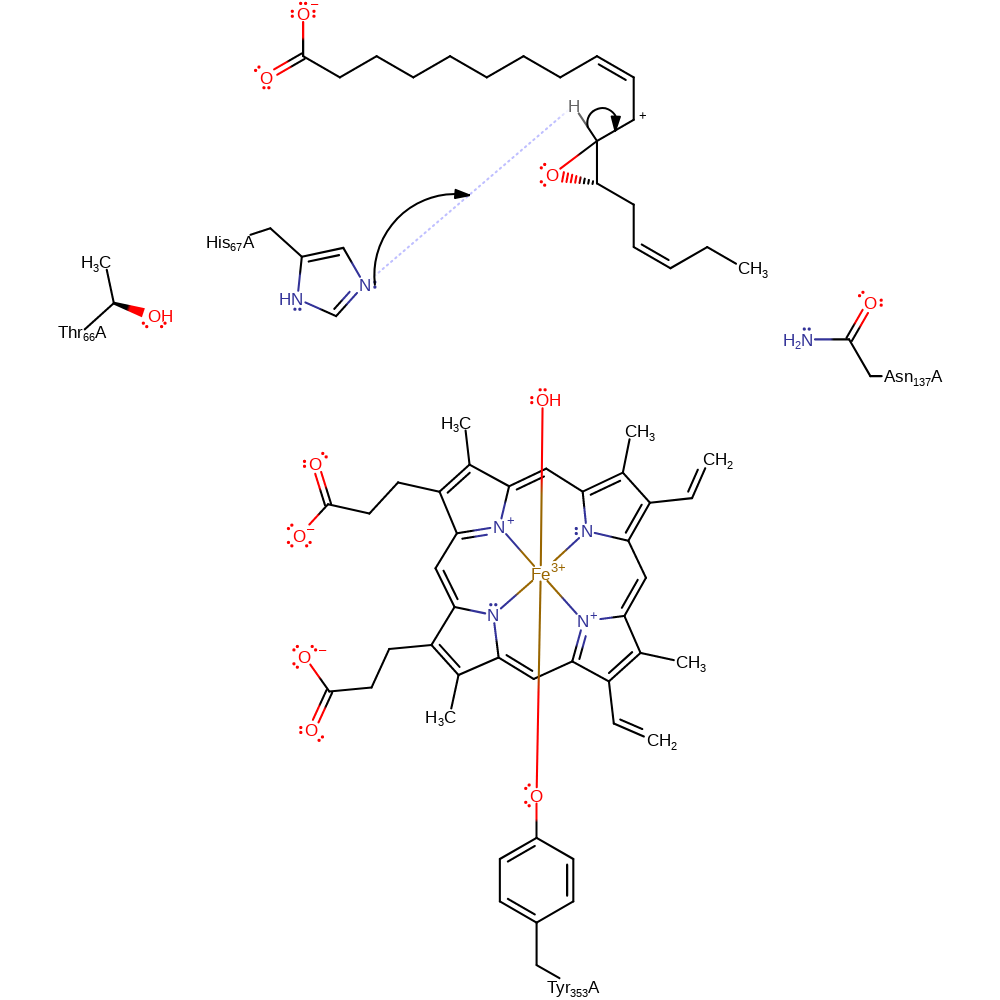
Step 4. His67 deprotonates the carbocation intermediate to form the product.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Thr66A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asn137A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Tyr353A | metal ligand |
| His67A | proton acceptor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, overall product formed
Step 5. The hydroxyl group accepts a proton from His67 and is released from the heme centre, restoring the active site.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Tyr353A | metal ligand |
| Thr66A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asn137A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| His67A | proton donor |




 Download:
Download: