4-hydroxybutanoyl-CoA dehydratase
4-hydroxybutyryl-CoA dehydratase (4-BUDH) catalyses the dehydration of 4-hydroxybutanoyl-CoA to crotonyl-CoA, as well as the isomerisation of vinylacetyl-CoA to crotonyl-CoA. The reaction is mechanistically the most demanding step in the fermentation of gamma-aminobutyrate to ammonia, acetate and butyrate by Clostridium aminobutyricum.
Reference Protein and Structure
- Sequence
-
P55792
 (4.2.1.120, 5.3.3.3)
(4.2.1.120, 5.3.3.3)
 (Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
(Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
- Biological species
-
Clostridium aminobutyricum (Bacteria)

- PDB
-
1u8v
- Crystal Structure of 4-Hydroxybutyryl-CoA Dehydratase from Clostridium aminobutyricum: Radical catalysis involving a [4Fe-4S] cluster and flavin
(1.6 Å)



- Catalytic CATH Domains
-
1.20.140.10
 1.10.3140.10
1.10.3140.10  2.40.110.10
2.40.110.10  (see all for 1u8v)
(see all for 1u8v)
- Cofactors
- Fadh2(2-) (1), Tetra-mu3-sulfido-tetrairon (1)
Enzyme Mechanism
Introduction
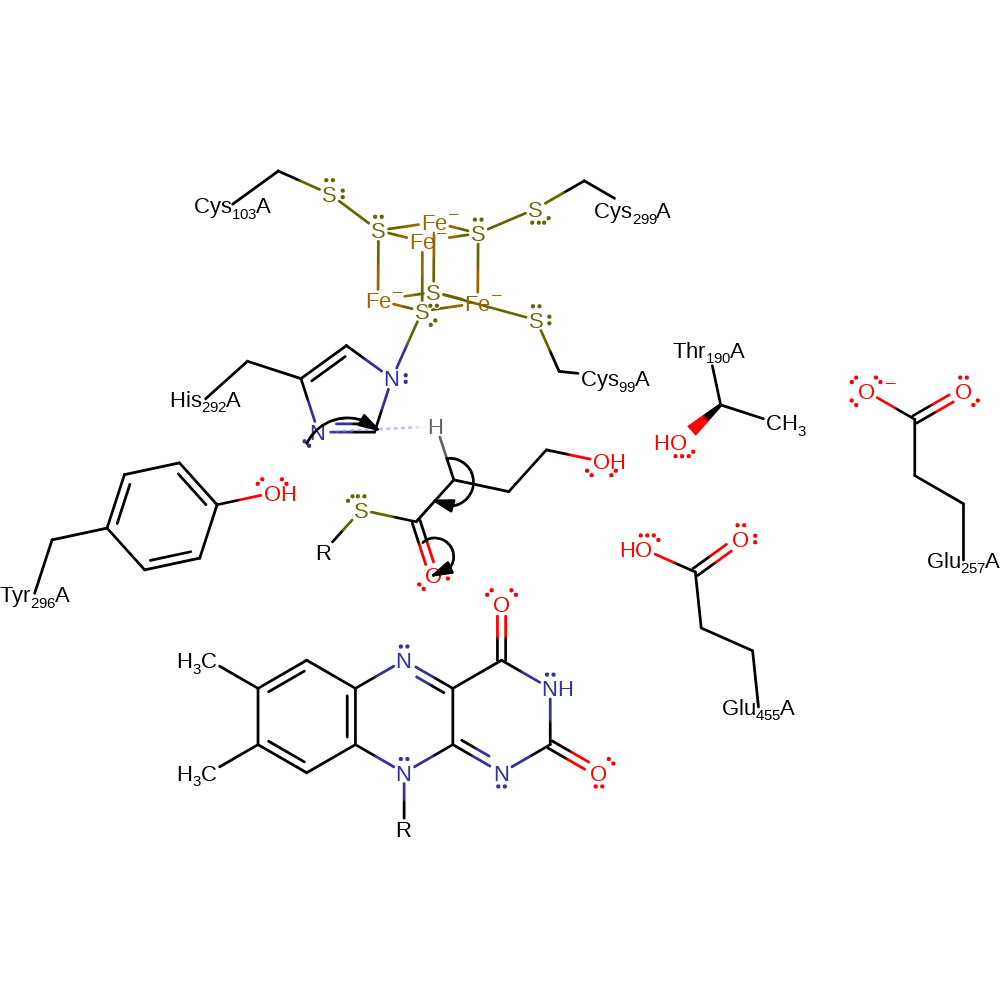
4-BUDH utilises an oxidised FAD quinone to carry out radical formation. This lowers the pKa of the C3 hydrogen, thus activating the usually unreactive C3-H bond. His 292 acts as a general base to enolise 4-hydroxybutanoyl-CoA by abstraction of the C2-proR-hydrogen. FAD removes an electron from the enolate oxygen to create the enoxy radical. The FAD-. semiquinone radical anion abstracts the substrate's C3-proS-hydrogen. The substrate is now a ketyl radical anion with the hydroxy group coordinated to an iron in the Fe-S cluster. This polarises the hydroxy group and enables the ketyl radical anion to eliminate water, with the extra proton coming from the FADH. semiquinone (i.e. the proton that was removed from C3 by FAD-.). The dienoxy radical produced undergoes one electron reduction by FAD-. to yield a dienolate. Glu455 donates a proton to C4 of the dienolate to yield the product.
Catalytic Residues Roles
| UniProt | PDB* (1u8v) | ||
| Glu455 | Glu455A | Aids in the elimination of water at C4 and reprotonates C4 to generate the product. | proton donor |
| Glu257, Thr190 | Glu257A, Thr190A | Deprotonates the neutral semiquinone to regenerate the semiquinone anion | proton acceptor |
| Cys103, Cys299, Cys99 | Cys103A, Cys299A, Cys99A | Bond to the iron sulfur cluster | |
| His292 | His292A | His 292 is one of the ligands to the Fe-S cluster. It acts as a general acid/base to the substrate, converting substrate to the enol (deprotonating C2), and the dienolate to the product (protonating C4). | proton acceptor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, assisted keto-enol tautomerisation, overall reactant used, radical formation, intramolecular elimination, radical termination, native state of cofactor regenerated, overall product formedReferences
- Martins BM et al. (2004), Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, 101, 15645-15649. Crystal structure of 4-hydroxybutyryl-CoA dehydratase: Radical catalysis involving a [4Fe-4S] cluster and flavin. DOI:10.1073/pnas.0403952101. PMID:15496473.
- Buckel W et al. (2012), Biochim Biophys Acta, 1824, 1278-1290. Enzyme catalyzed radical dehydrations of hydroxy acids. DOI:10.1016/j.bbapap.2011.11.009. PMID:22178228.
Catalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Tyr296A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| His292A | proton acceptor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, assisted keto-enol tautomerisation, overall reactant used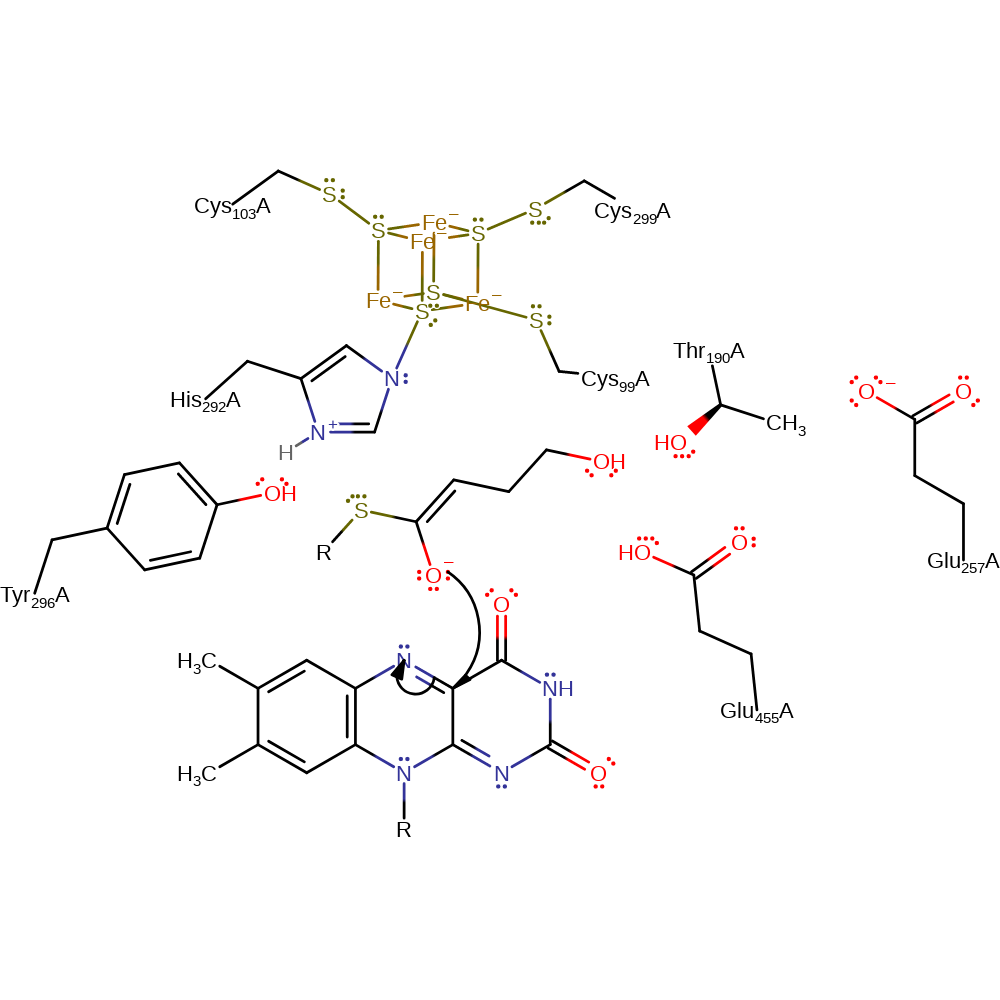
Step 2. FAD abstracts an electron from the enolate oxygen forming enoxy and semiquinone radicals.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Tyr296A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Tyr296A | radical stabiliser |
Chemical Components
radical formation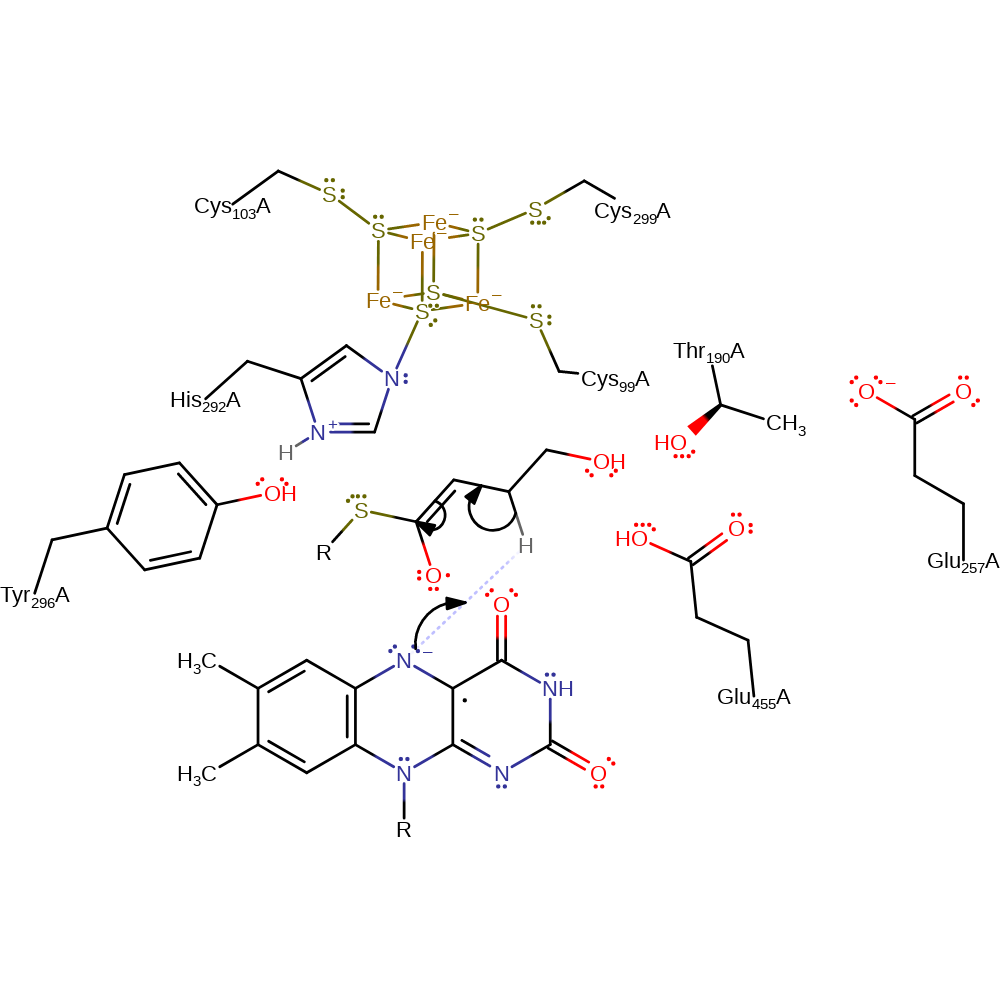
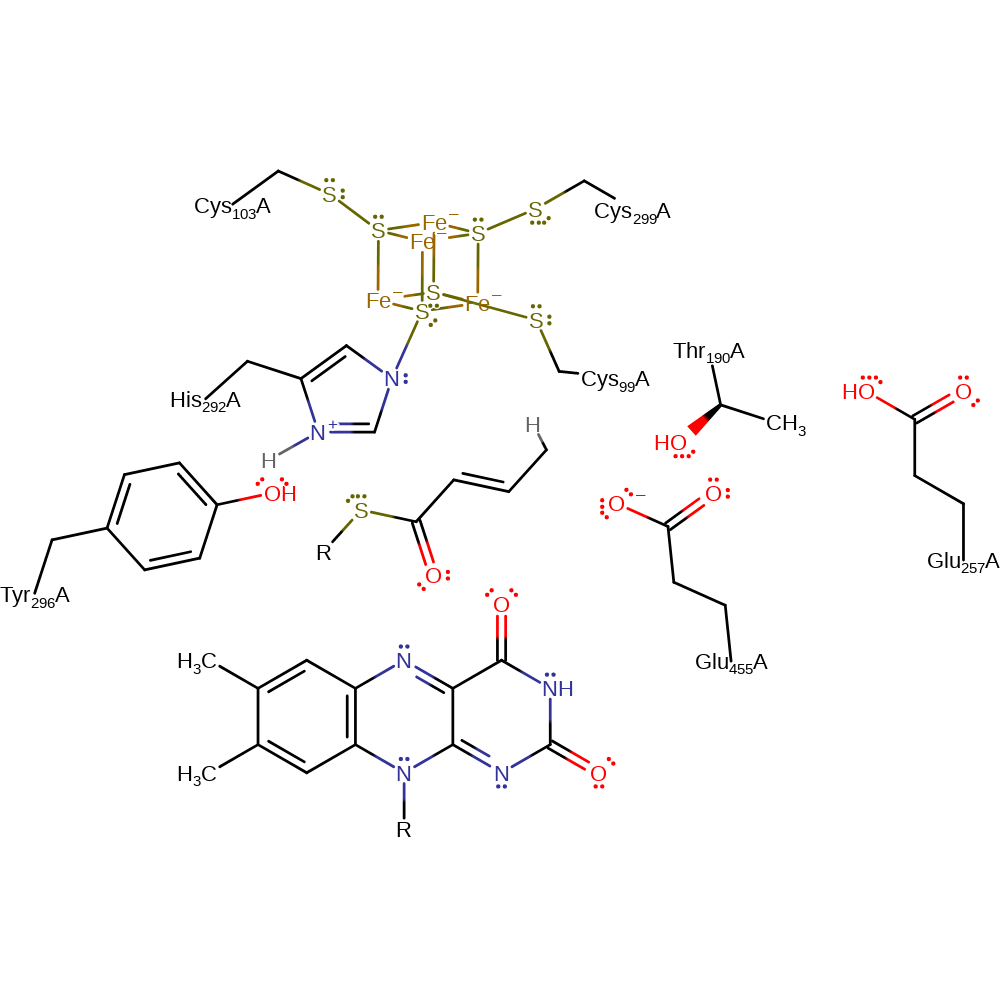
Step 3. The semiquinone anion abstracts a proton from C3, leading to the formation of a ketyl radical anion and a neutral semiquinone.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Tyr296A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Tyr296A | radical stabiliser |
Chemical Components
proton transfer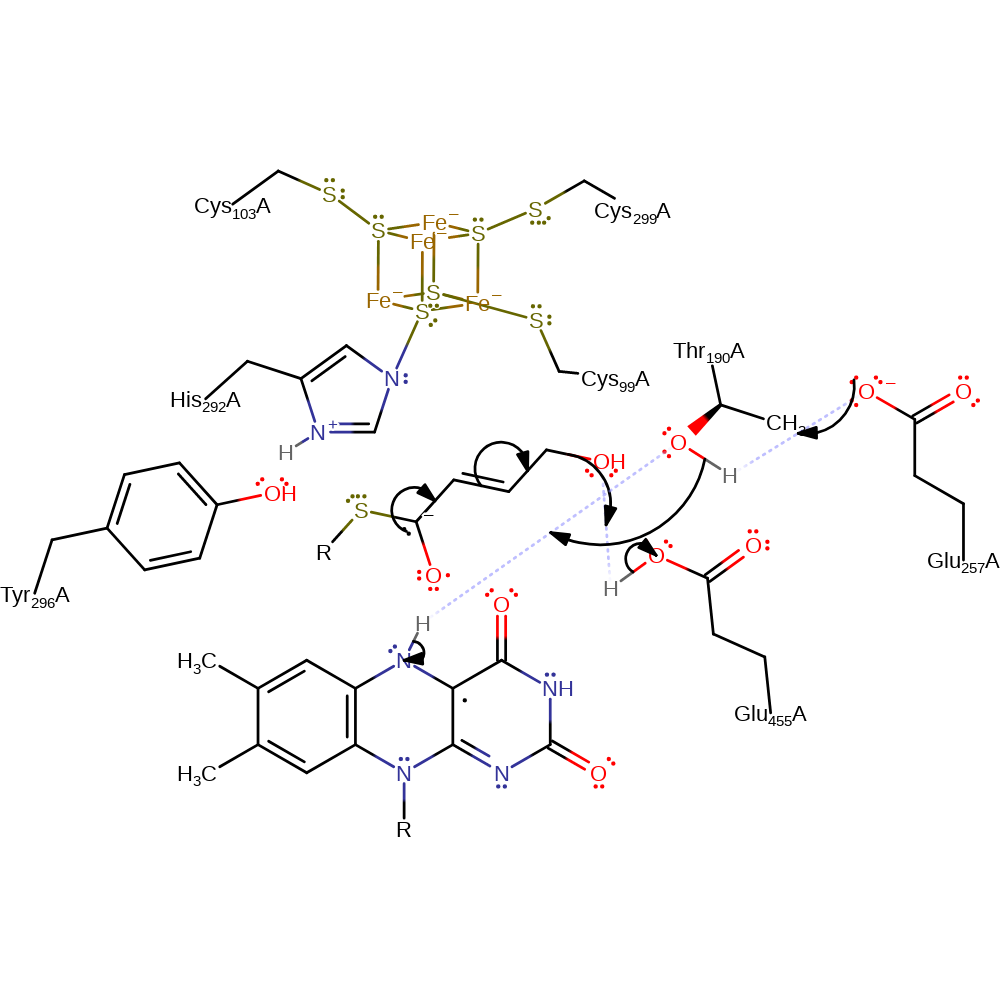
Step 4. The ketyl radical ion eliminates water at the C4 position to form a dienoxy radical, this is aided by protonation from Glu455. Thr190 and Glu257 both act to deprotonate the neutral semiquinone, reforming the semiquinone anion.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Tyr296A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Tyr296A | radical stabiliser |
| Thr190A | proton relay |
| Glu257A | proton acceptor |
| Glu455A | proton donor |
| Thr190A | proton acceptor, proton donor |
Chemical Components
ingold: intramolecular elimination, proton transfer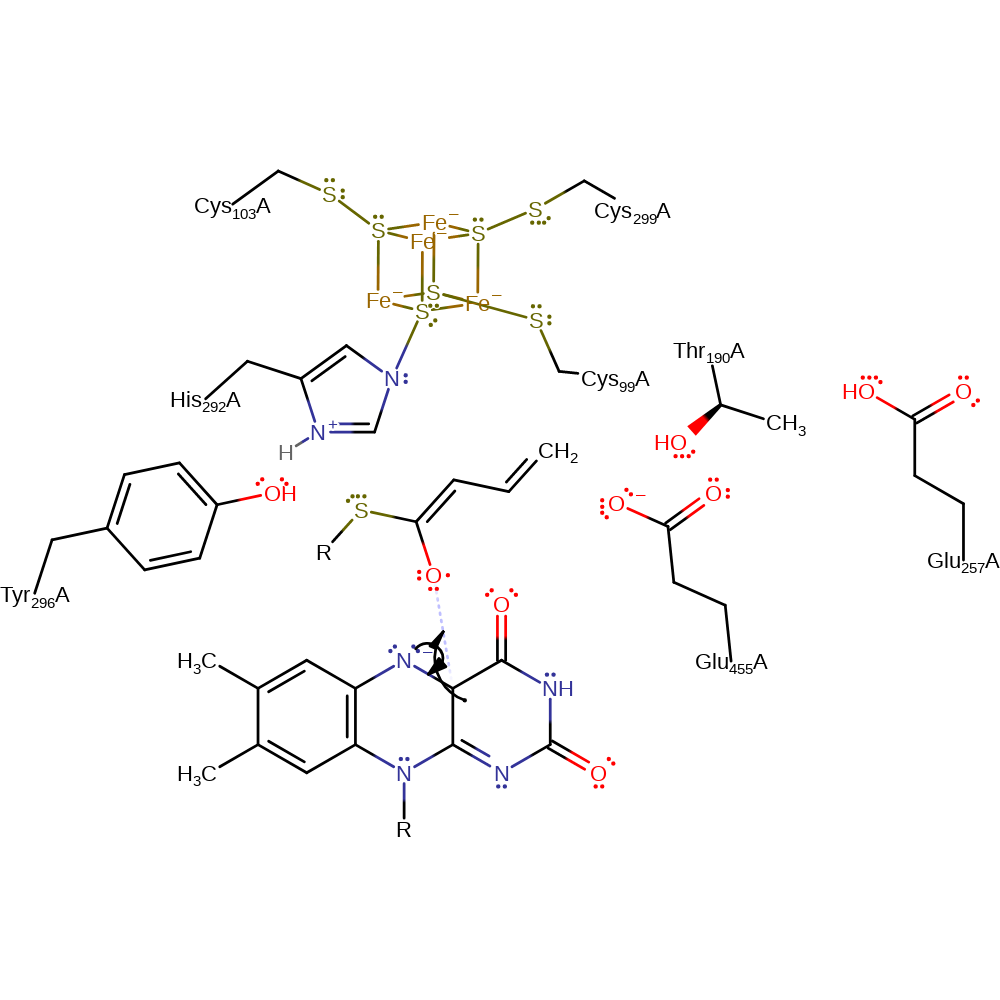
Step 5. The dienoxy radical abstracts an electron from the semiquinone forming a dienolate and quinone.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Tyr296A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Tyr296A | radical stabiliser |
Chemical Components
radical termination, native state of cofactor regenerated
Step 6. The dienolate tautomerizes via protonation at C4 from Glu455 to form the product crotonyl-CoA. It is not clear how Glu455 is protonated between this and the previous step.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Tyr296A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Glu455A | proton donor |



 Download:
Download: