Gamma-glutamyl hydrolase
gamma-glutamyl hydrolase is a lysosomal or secreted thiol-dependent peptidase most active at acidic pH that catalyses the cleavage of the gamma-glutamyl chain of folylpoly-gamma-glutamyl. Human gamma-glutamyl hydrolase (hGH) catalyses the hydrolysis of the gamma-linked polyglutamate chain of folyl- or antifolyl polyglutamates, releasing shorter chains of polyglutamates and diglutamates or glutamic acid.
Reference Protein and Structure
- Sequence
-
Q92820
 (3.4.19.9)
(3.4.19.9)
 (Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
(Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
- Biological species
-
Homo sapiens (Human)

- PDB
-
1l9x
- Structure of gamma-Glutamyl Hydrolase
(1.6 Å)



- Catalytic CATH Domains
-
3.40.50.880
 (see all for 1l9x)
(see all for 1l9x)
Enzyme Reaction (EC:3.4.19.9)
Enzyme Mechanism
Introduction
His220 activates Cys110 by abstracting a proton. The nucleophilic Cys110 attacks the gamma-carbonyl carbon of the of the susceptible Glu-Glu bond in the poly-gamma-glutamate substrate, forming a tetrahedral intermediate with an oxyanion. The carbonyl C-N bond is cleaved, forming the thioester intermediate and the gamma-linked glutamate leaving group which is protonated by His220. The thioester intermediate is hydrolysed by a water molecule which is activated by His220 acting as a base, yielding the product and regenerating the enzyme.
Catalytic Residues Roles
| UniProt | PDB* (1l9x) | ||
| Glu246 | Glu222(243)B | Raises the pKa of His 244 which enables the proton transfer between His 244 and Cys 132 | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Cys134 | Cys110(131)B | Activated Cys110 nucleophilically attacks the gamma-carbonyl carbon of the substrate to form the thioester intermediate. | nucleofuge, nucleophile, proton acceptor, proton donor |
| His244 | His220(241)B | His220 acts as a general acid/base catalyst. It activates the two nucleophiles in the reaction (Cys110 and water) as a base, and protonates the leaving group. | proton acceptor, proton donor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, bimolecular nucleophilic addition, intermediate formation, overall reactant used, rate-determining step, unimolecular elimination by the conjugate base, intermediate collapse, overall product formed, native state of enzyme regeneratedReferences
- Chave KJ et al. (2000), J Biol Chem, 275, 40365-40370. Molecular Modeling and Site-directed Mutagenesis Define the Catalytic Motif in Human gamma -Glutamyl Hydrolase. DOI:10.1074/jbc.m007908200. PMID:11005824.
- Alexander JP et al. (2008), Biochemistry, 47, 1228-1239. Gamma-glutamyl hydrolase: kinetic characterization of isopeptide hydrolysis using fluorogenic substrates. DOI:10.1021/bi701607v. PMID:18171026.
- Schneider E et al. (2006), Clin Chim Acta, 374, 25-32. Gamma-glutamyl hydrolase and drug resistance. DOI:10.1016/j.cca.2006.05.044. PMID:16859665.
- Li H et al. (2002), J Biol Chem, 277, 24522-24529. Three-dimensional structure of human gamma -glutamyl hydrolase. A class I glatamine amidotransferase adapted for a complex substate. DOI:10.1074/jbc.M202020200. PMID:11953431.
- Chave KJ et al. (1999), Biochem J, 343, 551-555. Site-directed mutagenesis establishes cysteine-110 as essential for enzyme activity in human γ-glutamyl hydrolase. DOI:10.1042/bj3430551. PMID:10527932.
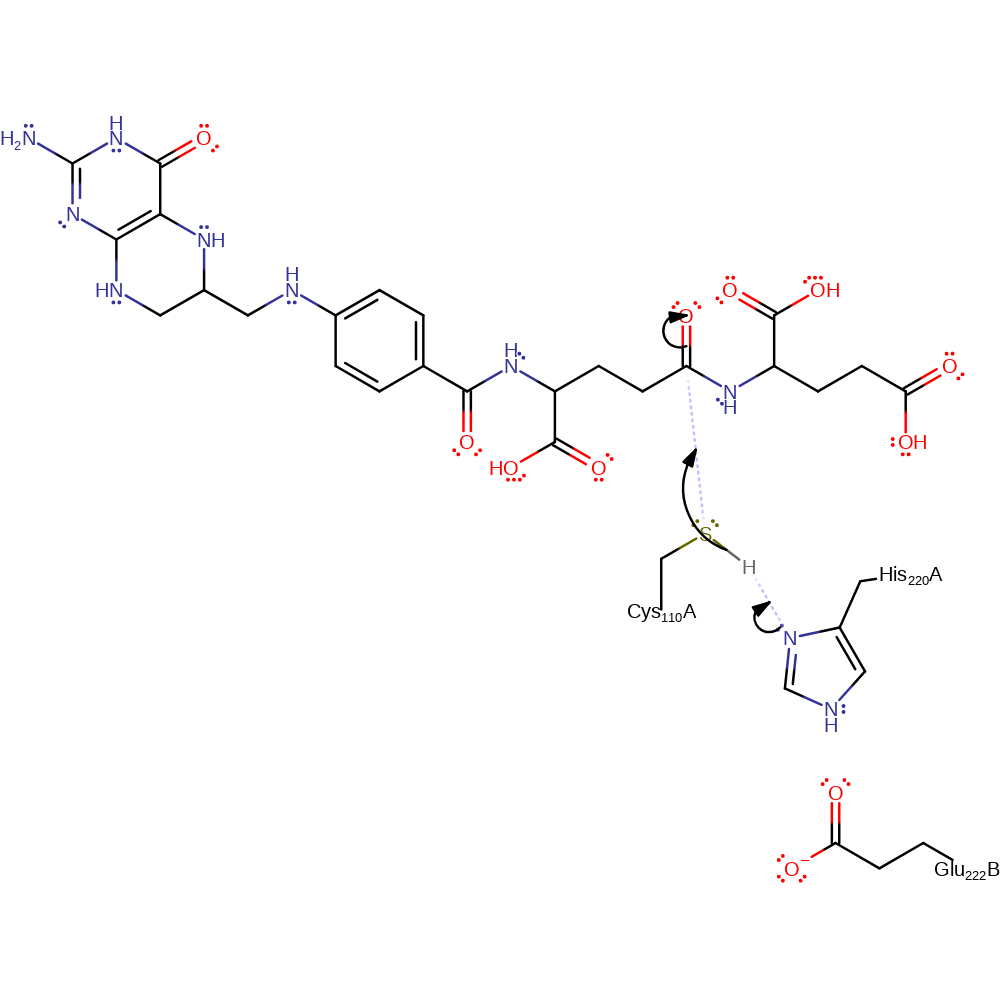
Step 1. His244 deprotonates Cys134 which activates it so it can attack the carbon of the peptide bond in a nucleophilic addition.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Glu222(243)B | electrostatic stabiliser |
| His220(241)B | proton acceptor |
| Cys110(131)B | proton donor, nucleophile |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, ingold: bimolecular nucleophilic addition, intermediate formation, overall reactant used, rate-determining step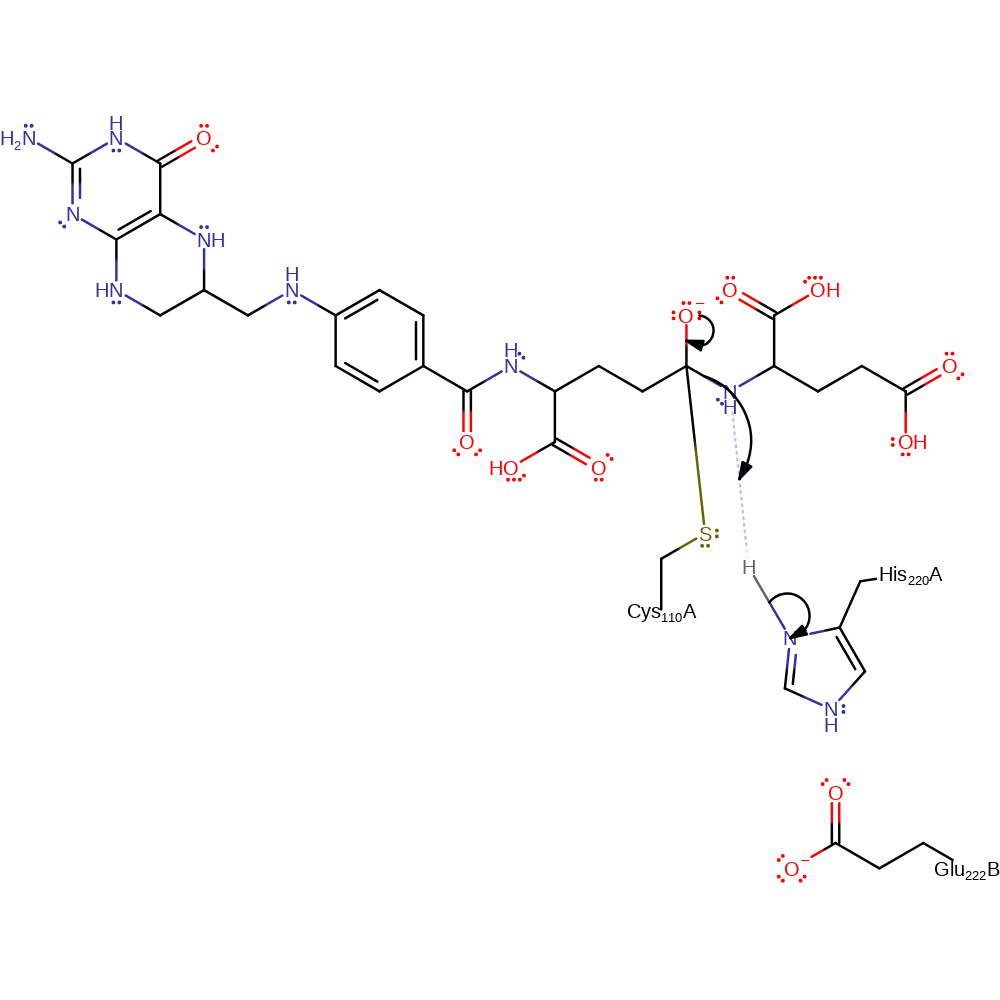
Step 2. The oxyanion initiates an elimination which results in the cleavage of the peptide bond. The N-terminal product then accepts a proton from His244.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Glu222(243)B | electrostatic stabiliser |
| His220(241)B | proton donor |
Chemical Components
ingold: unimolecular elimination by the conjugate base, proton transfer, intermediate collapse, overall product formed
Step 3. His244 abstracts a proton from a water which activates it so it can attack the carbon of the thioester bond in a nucleophilic addition.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Glu222(243)B | electrostatic stabiliser |
| His220(241)B | proton acceptor |
Chemical Components
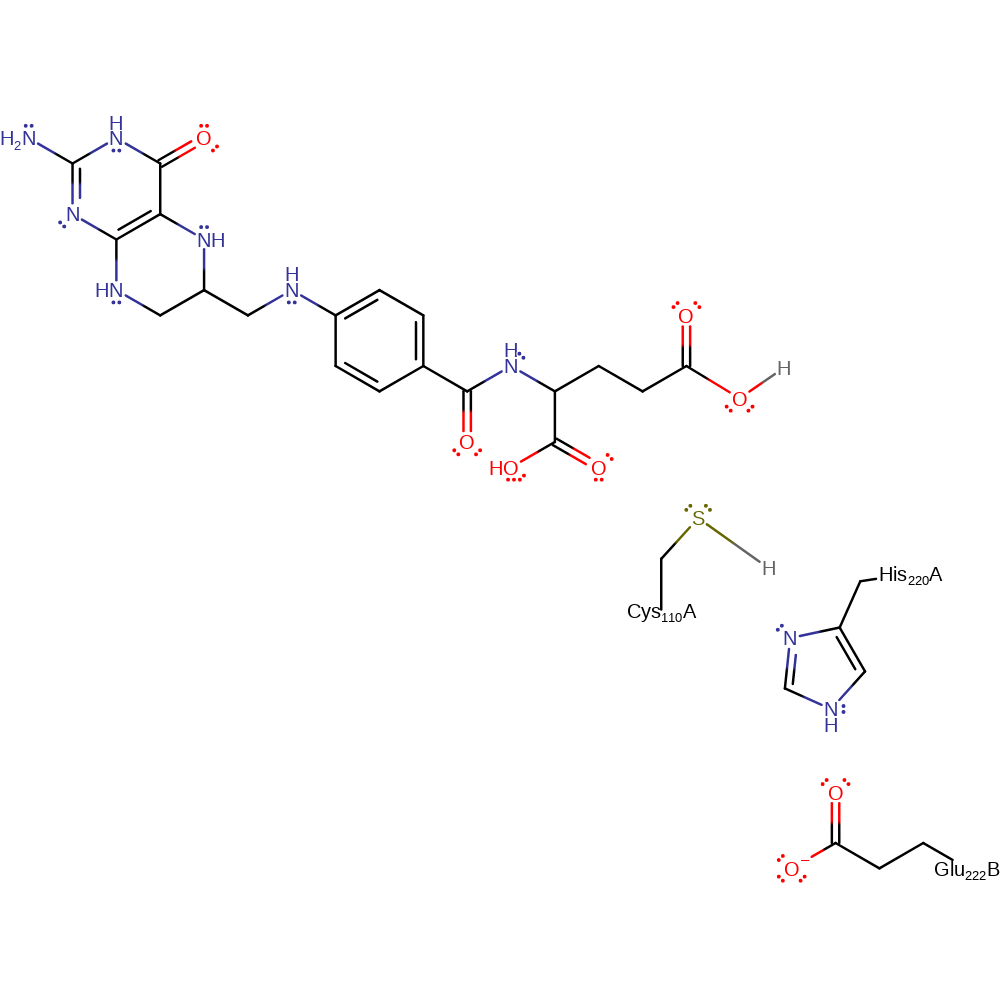
proton transfer, ingold: bimolecular nucleophilic addition, intermediate formation, overall reactant used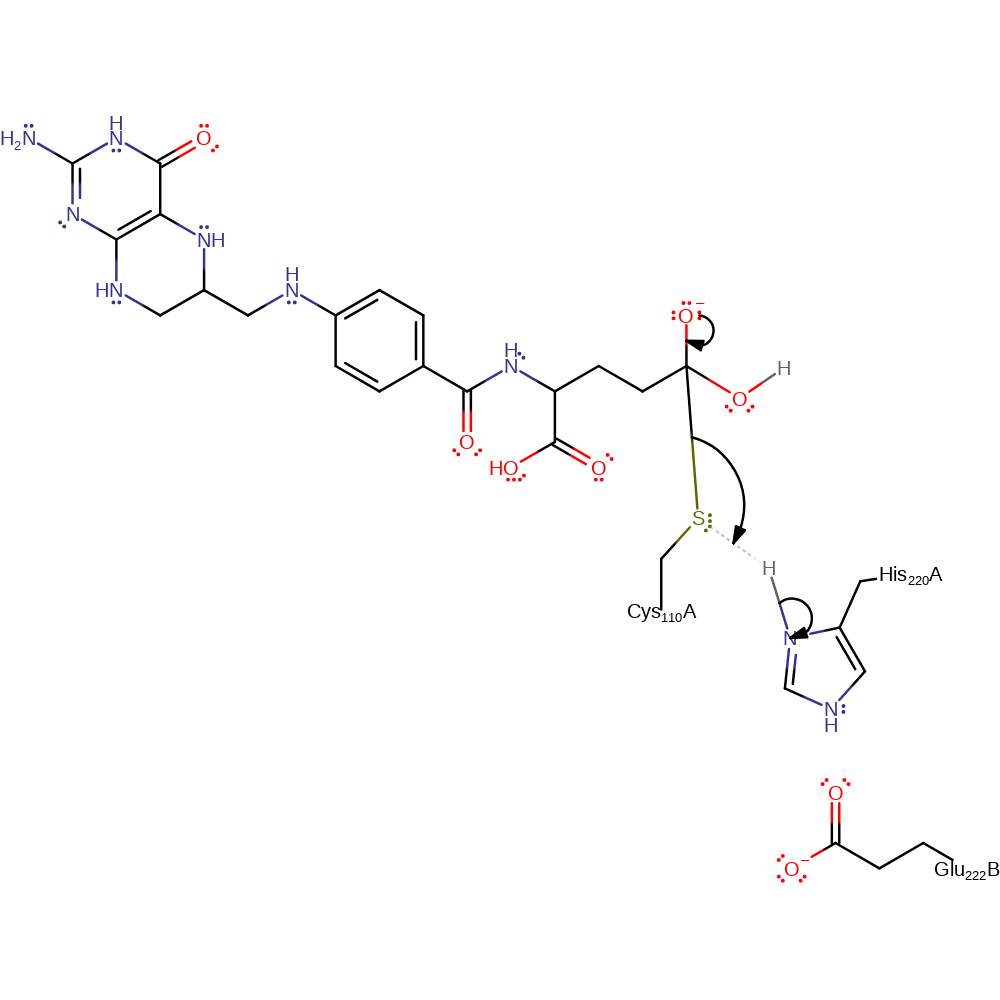
Step 4. The oxyanion initiates another elimination which results in the cleavage of the thioester bond. The released Cys134 can now accept a proton from His244 which returns the enzyme to its native state.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Glu222(243)B | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Cys110(131)B | proton acceptor |
| His220(241)B | proton donor |
| Cys110(131)B | nucleofuge |




 Download:
Download: