Threonine synthase
Threonine synthase (TS) from Saccharomyces cerevisiae catalyses the conversion of O-phospho-L-homoserine (OPHS) into threonine and phosphate. This is the final step in threonine biosynthesis. The enzyme requires a pyridoxal 5'-phosphate (PLP) cofactor which binds at the interface of all three of the protein's domains.
Reference Protein and Structure
- Sequence
-
P16120
 (4.2.3.1)
(4.2.3.1)
 (Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
(Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
- Biological species
-
Saccharomyces cerevisiae S288c (Baker's yeast)

- PDB
-
1kl7
- Crystal Structure of Threonine Synthase from Yeast
(2.7 Å)



- Catalytic CATH Domains
-
3.40.50.1100
 (see all for 1kl7)
(see all for 1kl7)
- Cofactors
- Pyridoxal 5'-phosphate(2-) (1)
Enzyme Reaction (EC:4.2.3.1)
Enzyme Mechanism
Introduction
The catalytic cycle starts with a transaldimination reaction. Lys124 which is initially bound to the PLP cofactor is replaced by OPHS forming the external aldimine. Lys124 catalyses the abstraction of the C-alpha proton of the substrate and its transfer to the PLP C4' position. Next, Lys124 stereospecifically abstracts the beta-pro-S hydrogen leading to the non-hydrolytic elimination of the gamma-phosphate. The gamma-methylene group left after the elimination is reprotonated producing the PLP-derivative of E-aminocrotonate. Next, water is added at C-beta. Finally, reverse transaldimination yields L-threonine.
Catalytic Residues Roles
| UniProt | PDB* (1kl7) | ||
| Lys124 | Lys124A | Lys124 is the only residue in the immediate environment of the bound substrate that can act as an acid-base catalyst. It is involved in the abstraction of a proton from C-alpha and it's transfer to C4' as well as the abstraction of a proton from C-beta and the protonation of the C-gamma in the methylene intermediate. In the last step, Lys124 acts as a nucleophile attacking the external aldimine resulting in the release of the L-threonine. | covalently attached, nucleofuge, nucleophile, proton acceptor, proton donor, proton relay, increase nucleophilicity, electron pair acceptor, electron pair donor |
Chemical Components
bimolecular nucleophilic addition, intermediate formation, cofactor used, overall reactant used, intramolecular elimination, schiff base formed, intermediate collapse, proton relay, assisted tautomerisation (not keto-enol), proton transfer, overall product formed, native state of cofactor regenerated, native state of enzyme regenerated, intermediate terminatedReferences
- Garrido-Franco M et al. (2002), J Biol Chem, 277, 12396-12405. Structure and Function of Threonine Synthase from Yeast. DOI:10.1074/jbc.m108734200. PMID:11756443.
- Ujiie Y et al. (2017), J Phys Chem B, 121, 5536-5543. Molecular Mechanism of the Reaction Specificity in Threonine Synthase: Importance of the Substrate Conformations. DOI:10.1021/acs.jpcb.7b02932. PMID:28489381.

Step 1. The amino group of the serine performs a nucleophilic attack on the imine carbon of the lys-bound PLP forming a tetrahedral intermediate.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Lys124A | covalently attached |
| Lys124A | electron pair acceptor |
Chemical Components
ingold: bimolecular nucleophilic addition, intermediate formation, cofactor used, overall reactant usedCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Lys124A | nucleofuge |
Chemical Components
ingold: intramolecular elimination, schiff base formed, intermediate collapse
Step 3. Lys124 abstracts a proton from the alpha carbon of the substrate causing tautomerization of the imine.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Lys124A | proton relay |
| Lys124A | proton acceptor, proton donor |
Chemical Components
proton relay, assisted tautomerisation (not keto-enol)
Step 4. Lys124 abstracts a proton from the beta carbon causing a second tautomerization from imine to enamine.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Lys124A | proton acceptor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, assisted tautomerisation (not keto-enol)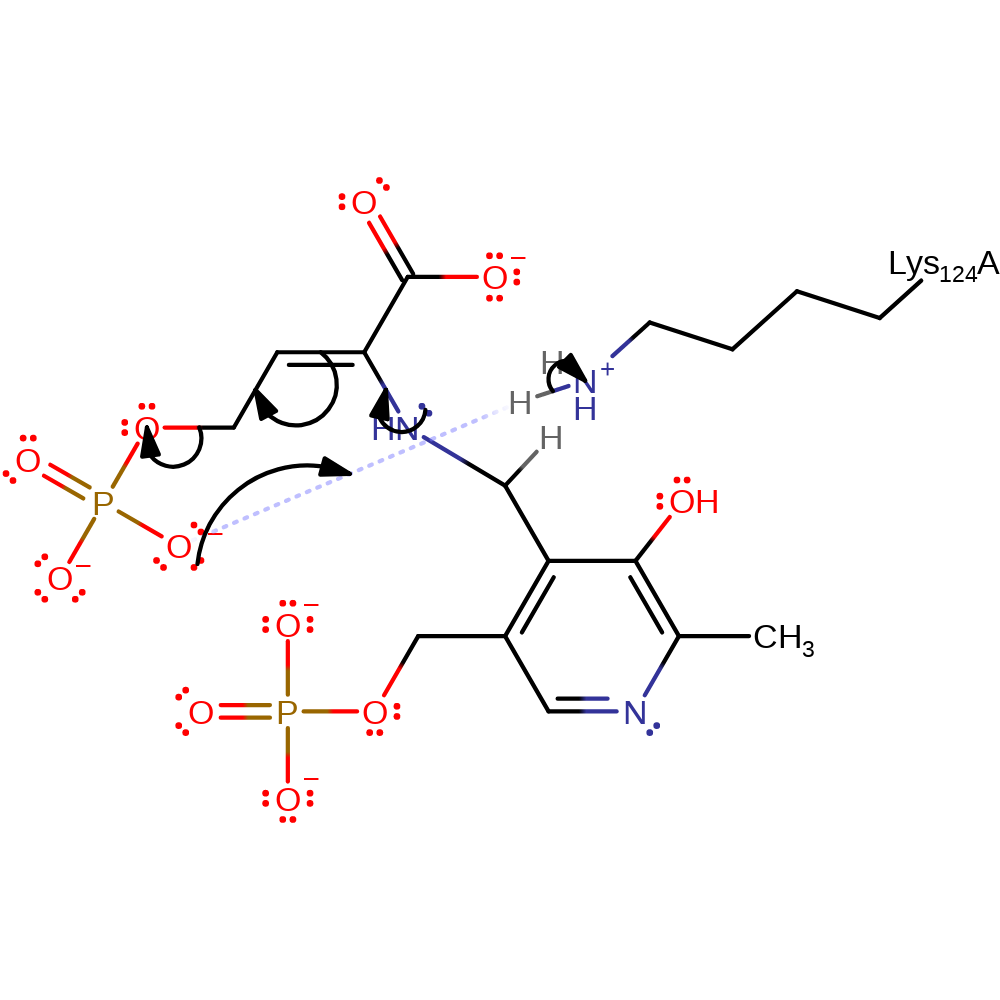
Step 5. Phosphate is eliminated from the homoserine and another imine is formed.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Lys124A | proton donor |
Chemical Components
schiff base formed, ingold: intramolecular elimination, proton transfer, assisted tautomerisation (not keto-enol)
Step 6. Lys124 acts as a proton relay causing another tautomerization reaction to occur.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Lys124A | proton relay, proton donor, proton acceptor |
Chemical Components
proton relay, assisted tautomerisation (not keto-enol)
Step 7. Water performs a nucleophilic attack on the C=C bond of the substrate, forming a carboanion. The water is activated by Lys124.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Lys124A | increase nucleophilicity, proton acceptor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, ingold: bimolecular nucleophilic additionCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Lys124A | proton donor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer
Step 9. The amino group of Lys124 performs a nucleophilic attack on the imine carbon of the thr-bound PLP forming a tetrahedral intermediate.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Lys124A | nucleophile |
Chemical Components
ingold: bimolecular nucleophilic addition, intermediate formationCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Lys124A | electron pair donor |





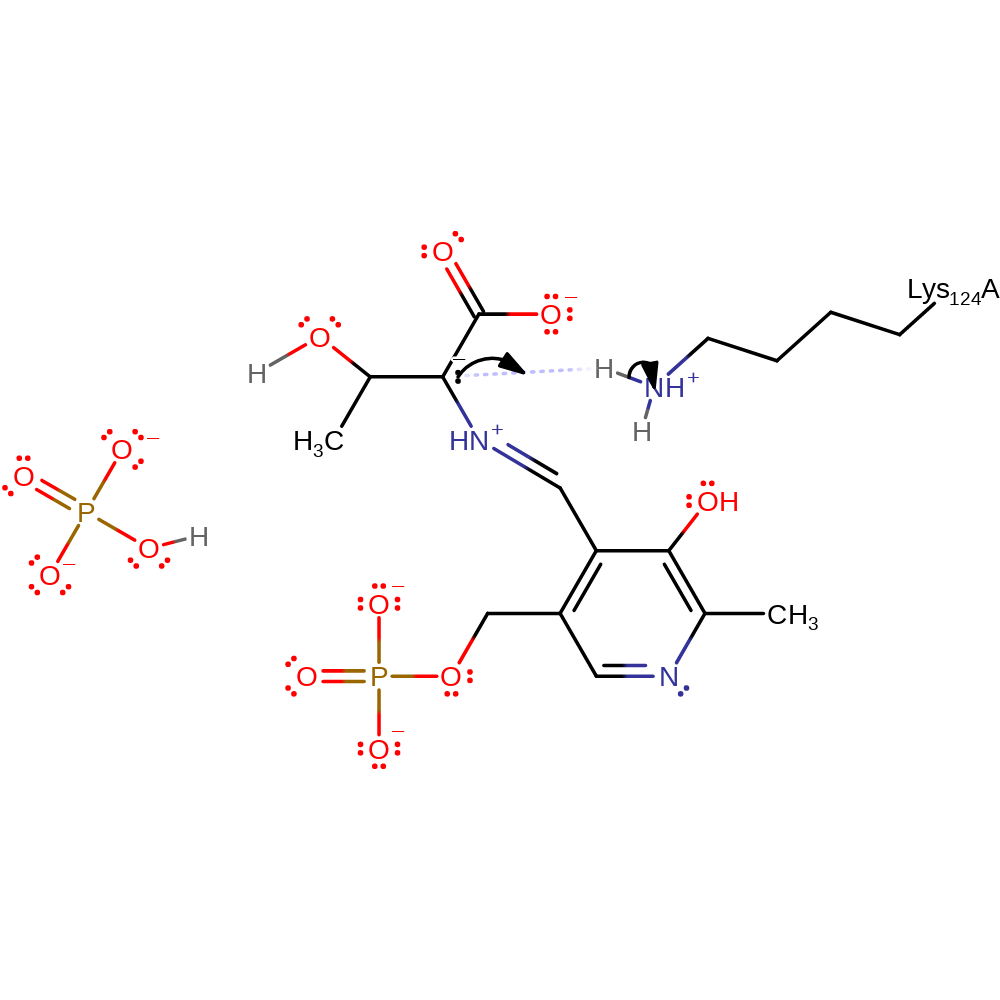
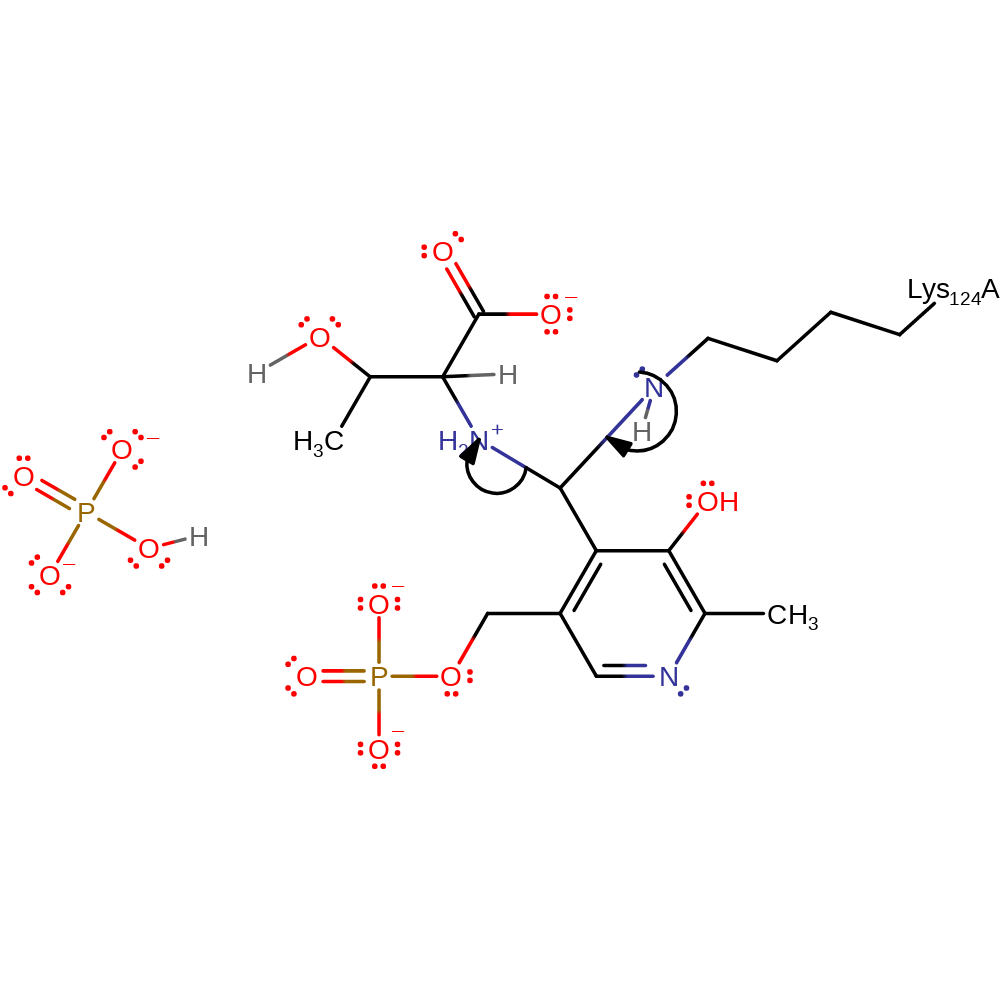
 Download:
Download: