Peptide amidase
Peptide amidase (PAM) from Strenotrophomonas maltophilia (a gram-negative bacterium) catalyses the hydrolysis of the C-terminal amide bond in peptide amides. It is very regio-selective, and those terminal bonds in amino acid side chains are not hydrolysed. PAM belongs to the amidase signature (AS) family, most of which display hydrolase activity. The natural function of periplasmatic PAM is not known.
Reference Protein and Structure
- Sequence
-
Q9ZIV5

 (Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
(Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
- Biological species
-
Bradyrhizobium japonicum (Bacteria)

- PDB
-
1ocl
- THE CRYSTAL STRUCTURE OF MALONAMIDASE E2 COMPLEXED WITH MALONATE FROM BRADYRHIZOBIUM JAPONICUM
(2.0 Å)



- Catalytic CATH Domains
-
3.90.1300.10
 (see all for 1ocl)
(see all for 1ocl)
Enzyme Mechanism
Introduction
The catalytic mechanism of Ser-Ser-Lys catalytic triad contains five sequential steps: (i) nucleophilic attack of serine on the carbonyl group of the substrate, forming the first tetrahedral intermediate, (ii) formation of an acyl–enzyme complex, (ii) release of an ammonia product, (iv) nucleophilic attack of a water molecule forming the second tetrahedral intermediate, and (iv) the release of the product of the reaction, the carboxylic acid.
Catalytic Residues Roles
| UniProt | PDB* (1ocl) | ||
| Lys62 | Lys62A | Lys62 is a part of the Ser-Ser-Lys catalytic triad, responsible for accepting from Ser131 and transferring back the proton to Ser131. | proton acceptor, proton donor |
| Ser131 | Ser131A | Ser131 is a part of the Ser-Ser-Lys catalytic triad, responsible for proton transfer among catalytic residues as well as proton transfer to the amide group of the substrate. | proton acceptor, proton donor |
| Arg158 | Arg158A | Arg158 establishes an ionic interaction with the carboxyl group of the substrate to ensure correct orientation and alignment of the substrate inside the active site. | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Ser155 | Ser155A | Ser131 is a part of the Ser-Ser-Lys catalytic triad, responsible for nucleophilic attack for the formation of the acyl-enzyme tetrahedral intermediate. | nucleofuge, nucleophile, proton acceptor, proton donor |
| Thr150, Thr152 (main-N), Gly153 (main-N), Gly154 (main-N) | Thr150A, Thr152A (main-N), Gly153A (main-N), Gly154A (main-N) | Part of the oxyanion hole for the stabilization of the tetrahedral reaction intermediates. |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, bimolecular nucleophilic addition, overall reactant used, intermediate formation, intramolecular elimination, overall product formed, bimolecular eliminationReferences
- Cerqueira NMFSA et al. (2017), Phys Chem Chem Phys, 19, 12343-12354. The mechanism of the Ser-(cis)Ser-Lys catalytic triad of peptide amidases. DOI:10.1039/C7CP00277G. PMID:28453015.
- Labahn J et al. (2002), J Mol Biol, 322, 1053-1064. An Alternative Mechanism for Amidase Signature Enzymes. DOI:10.1016/s0022-2836(02)00886-0. PMID:12367528.

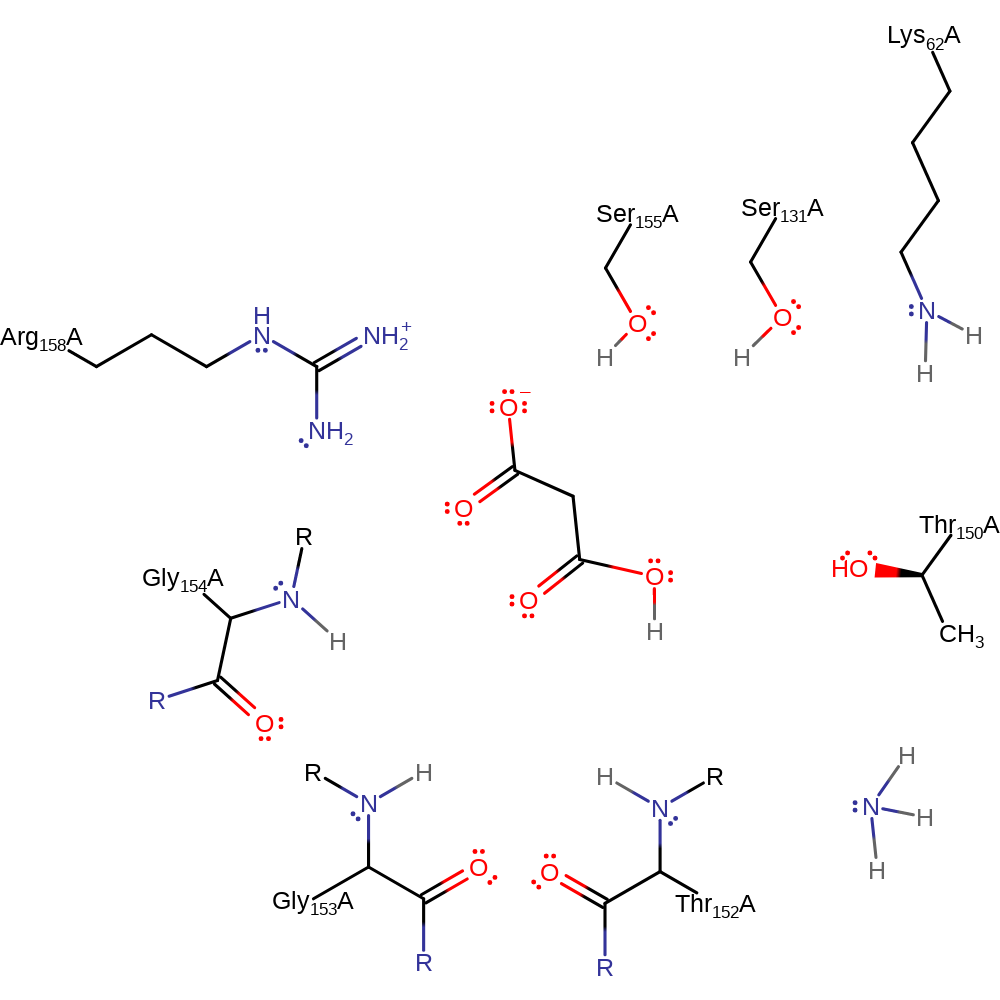
Step 1. Ser155 is ionized through proton transfer from this amino acid residue to (cis)Ser131. In the same step, the proton bonded to (cis)Ser131 migrates to Lys62.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Lys62A | proton acceptor |
| Ser131A | proton donor, proton acceptor |
| Ser155A | proton donor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer
Step 2. Ser155 performs nucleophilic attacks towards the carbonyl carbon of malonamate substrate, leading to formation of a tetrahedral adduct. The negatively charged carbonyl group of the amide of the substrate is stabilized by hydrogen bonding provided by the NH groups of the oxyanion pocket.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Ser155A | nucleophile |
| Thr152A (main-N) | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Gly153A (main-N) | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Gly154A (main-N) | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Arg158A | electrostatic stabiliser |
Chemical Components
ingold: bimolecular nucleophilic addition, overall reactant used, intermediate formation
Step 3. The amide group of the tetrahedral intermediate is protonated by (cis)Ser131. At the same time, one proton migrates back from the positively charged Lys62 to (cis)Ser131.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Gly154A (main-N) | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Gly153A (main-N) | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Thr152A (main-N) | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Arg158A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Ser131A | proton donor |
Chemical Components
proton transferCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|
Chemical Components
ingold: intramolecular elimination, overall product formed
Step 5. The hydroxyl group coming from the water molecule becomes attached to carbon C4 of the acyl–enzyme complex. At the same time, Ser131 and Lys62 are subsequently protonated.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Thr152A (main-N) | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Gly154A (main-N) | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Lys62A | proton acceptor |
| Ser131A | proton donor, proton acceptor |
| Gly153A (main-N) | electrostatic stabiliser |
Chemical Components
ingold: bimolecular nucleophilic addition, proton transferCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Ser155A | nucleofuge |
Chemical Components
ingold: bimolecular elimination, overall product formed
Step 7. Regeneration of the original catalytic residues: Ser155 is protonated by proton transfer from Ser131, (cis)Ser131 also become protonated and Lys62 returns to its neutral form.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Lys62A | proton donor |
| Ser131A | proton donor, proton acceptor |
| Ser155A | proton acceptor |
Chemical Components
proton transferIntroduction
Ser 226 acts as the primary nucleophile and attacks the amide carbonyl carbon atom. Simultaneously, Ser 202 protonates the substrate carbonyl oxygen, and deprotonates Ser 226. A tetrahedral intermediate is formed. Lys 123 acts to decrease the nucleophilicity of Ser 202, and increase its ability to protonate the carbonyl oxygen. Lys 123 protonates Ser 202 which in turn protonates the amido group of the substrate, creating NH3, a good leaving group. Lys 123 deprotonates Ser 202 which in turn deprotonates the O atom of the substrate, causing the reformation of the carbonyl with the elimination of NH3. Hydrolysis of the enzyme-acyl intermediate is carried out by nucleophilic attack of a water molecule, which is simultaneously deprotonated by the leaving group Ser 226.
Catalytic Residues Roles
| UniProt | PDB* (1ocl) | ||
| Ser202 | Ser202(165)A | Acts as an acid/base. Donates a proton to the carbonyl oxygen of the substrate at the same time as abstracting a proton from Ser 226. Accepts a proton from Lys 123 while donating a proton to substrate N atom. Accepts a proton from substrate O atom while donating a proton back to Lys 123. | proton acceptor, proton relay, electrostatic stabiliser, proton donor |
| Lys123 | Lys123(86)A | Acts to decrease the nucleophilicity of Ser 202 by hydrogen bonding to it. Also acts as an acid/base to Ser 202. | proton acceptor, electrostatic stabiliser, proton donor |
| Ser226 | Ser226(189)A | Acts as the primary nucleophile on the substrate carbonyl. Acts as a base by deprotonating a water molecule as it nucleophilically attacks the substrate carbonyl. | nucleofuge, nucleophile, proton acceptor, proton donor |
Chemical Components
bimolecular nucleophilic addition, proton transfer, enzyme-substrate complex formation, intermediate formation, overall reactant used, unimolecular elimination by the conjugate base, intermediate collapse, overall product formed, enzyme-substrate complex cleavage, hydrolysis, native state of enzyme regeneratedReferences
- Labahn J et al. (2002), J Mol Biol, 322, 1053-1064. An Alternative Mechanism for Amidase Signature Enzymes. DOI:10.1016/s0022-2836(02)00886-0. PMID:12367528.
- Cerqueira NMFSA et al. (2017), Phys Chem Chem Phys, 19, 12343-12354. The mechanism of the Ser-(cis)Ser-Lys catalytic triad of peptide amidases. DOI:10.1039/C7CP00277G. PMID:28453015.

Step 1. Ser226 as the primary nucleophile attacks the amide carbonyl carbon atom. Simultaneously, the substrate carbonyl group is protonated by Ser202, which in turn deprotonates Ser226.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Lys123(86)A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Ser202(165)A | proton acceptor |
| Ser226(189)A | nucleophile |
| Ser202(165)A | proton donor, proton relay |
| Ser226(189)A | proton donor |
Chemical Components
ingold: bimolecular nucleophilic addition, proton transfer, enzyme-substrate complex formation, intermediate formation, overall reactant used
Step 2. The amido group is protonated by Ser202 to form a plausible leaving group. Ser202 accepts a proton from Lys123.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Lys123(86)A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Lys123(86)A | proton donor |
| Ser202(165)A | proton donor, proton acceptor, proton relay |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, intermediate formation
Step 3. Lys123 deprotonates Ser202 which allows it to deprotonate the hydroxyl group which initiates elimination resulting in the release of ammonia.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Lys123(86)A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Ser202(165)A | proton acceptor |
| Lys123(86)A | proton acceptor |
| Ser202(165)A | proton donor, proton relay |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, ingold: unimolecular elimination by the conjugate base, intermediate collapse, overall product formed
Step 4. Ser226 abstracts a protonf rom water enabling it to nucleophilically attack the carbon of the acyl-enzyme bond which results in the cleavage of the acyl-enzyme.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Lys123(86)A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Ser202(165)A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Ser226(189)A | nucleofuge, proton acceptor |






 Download:
Download: 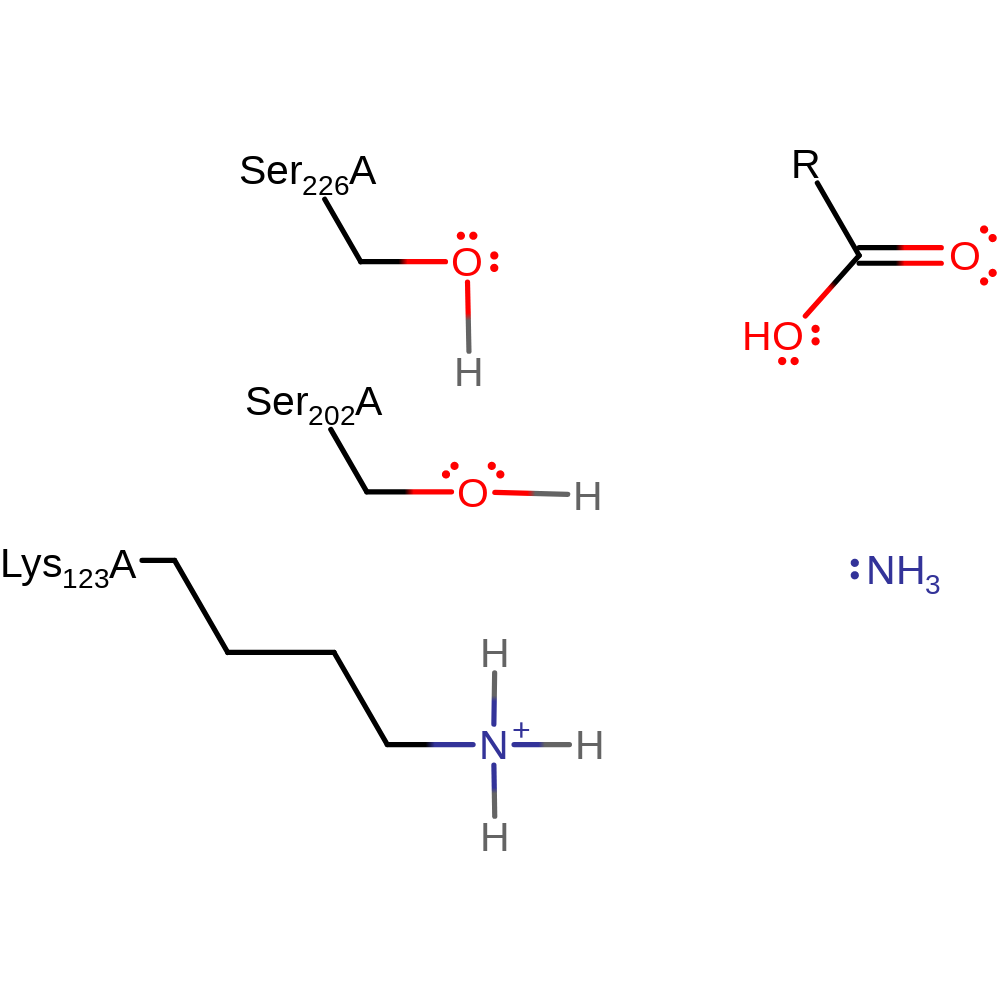 Download:
Download: