Nicotinamidase
Pyrazinamide (PZA) is a prodrug used in the treatment of tuberculosis. PZA is converted to the active pyrazinoic acid by the bacterial PZAase enzyme; mutations in PZAase can therefore confer PZA resistance to M. tuberculosis. The gene product of Pyrococcus horikoshii 999 (PH999) shows PZAase and nicotinamidase activity, and extensive sequence homology to M. tuberculosis PZAase.
Reference Protein and Structure
- Sequence
-
O58727

 (Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
(Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
- Biological species
-
Pyrococcus horikoshii OT3 (Bacteria)

- PDB
-
1im5
- Crystal Structure of Pyrazinamidase of Pyrococcus horikoshii in Complex with Zinc
(1.65 Å)



- Catalytic CATH Domains
-
3.40.50.850
 (see all for 1im5)
(see all for 1im5)
- Cofactors
- Zinc(2+) (1)
Enzyme Reaction (EC:3.5.1.19)
Enzyme Mechanism
Introduction
The mechanism of PH999 can be inferred by homology to other enzymes like Arthrobacter sp. CSHase and E. coli YcaC. The mechanism of substrate amide hydrolysis is likely to be via an acylated cysteine intermediate. Asp 10 deprotonates Cys 133, activating Cys as a nucleophile. The Cys 133 thiolate attacks the amide group of pyrazinamide. The tetrahedral intermediate is stabilised by an oxyanion hole comprising the backbone amides of Ala 129 and Cys 133. The tetrahedral state collapses to yield the acylated Cys 133. The NH2 leaving group is protonated by Asp 10 to yield ammonia. A water molecule binds to Zn(II); Zn(II) acidifies the water so that Asp 10 can deprotonate it. The resulting hydroxide ion attacks the acyl-enzyme in the next catalytic cycle. The tetrahedral intermediate collapses. Asp 10 protonates the leaving Cys 133 thiolate. Lys 94 is likely to stabilise any charge on Cys 133 and Asp 10 during the reaction.
Catalytic Residues Roles
| UniProt | PDB* (1im5) | ||
| Asp52, His54, His71 | Asp52A, His54A, His71A | Coordinates to Zinc ion | metal ligand |
| Ser60, Glu101 | Ser60A, Glu101A | Stabilises water that are part of the Zinc coordination sphere | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Lys94 | Lys94A | Lys 94 stabilises the negative charges on the Cys 133 thiolate and Asp 10 carboxylate, tuning their pKas by hydrogen bonding. | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Cys133 (main-N), Ala129 (main-N) | Cys133A (main-N), Ala129A (main-N) | The backbone amide of Ala 129 forms part of the oxyanion hole. | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Cys133 | Cys133A | Cys 133 is the nucleophilic cysteine which becomes acylated in the intermediate. The backbone amide is part of the oxyanion hole. |
nucleofuge, nucleophile, proton acceptor, proton donor |
| Asp10 | Asp10A | Asp 10 deprotonates Cys 133 and water, both of which act as nucleophiles during the reaction. Asp 10 transfers this proton to the leaving group, i.e. the Cys 133 thiolate, and -NH2 to give ammonia. | proton acceptor, proton donor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, bimolecular nucleophilic addition, enzyme-substrate complex formation, intermediate formation, overall reactant used, rate-determining step, unimolecular elimination by the conjugate base, heterolysis, intermediate collapse, overall product formed, enzyme-substrate complex cleavage, native state of enzyme regeneratedReferences
- Du X et al. (2001), Biochemistry, 40, 14166-14172. Crystal Structure and Mechanism of Catalysis of a Pyrazinamidase fromPyrococcus horikoshii†. DOI:10.1021/bi0115479. PMID:11714269.
- Sheng X et al. (2014), Org Biomol Chem, 12, 1265-1277. A QM/MM study of the catalytic mechanism of nicotinamidase. DOI:10.1039/C3OB42182A. PMID:24413890.
- Lemaitre N et al. (1999), Antimicrob Agents Chemother, 43, 1761-1763. Characterization of new mutations in pyrazinamide-resistant strains of Mycobacterium tuberculosis and identification of conserved regions important for the catalytic activity of the pyrazinamidase PncA. PMID:10390238.
- Romão MJ et al. (1992), J Mol Biol, 226, 1111-1130. Crystal structure analysis, refinement and enzymatic reaction mechanism of N-carbamoylsarcosine amidohydrolase from Arthrobacter sp. at 2·0Åresolution. DOI:10.1016/0022-2836(92)91056-u. PMID:1381445.
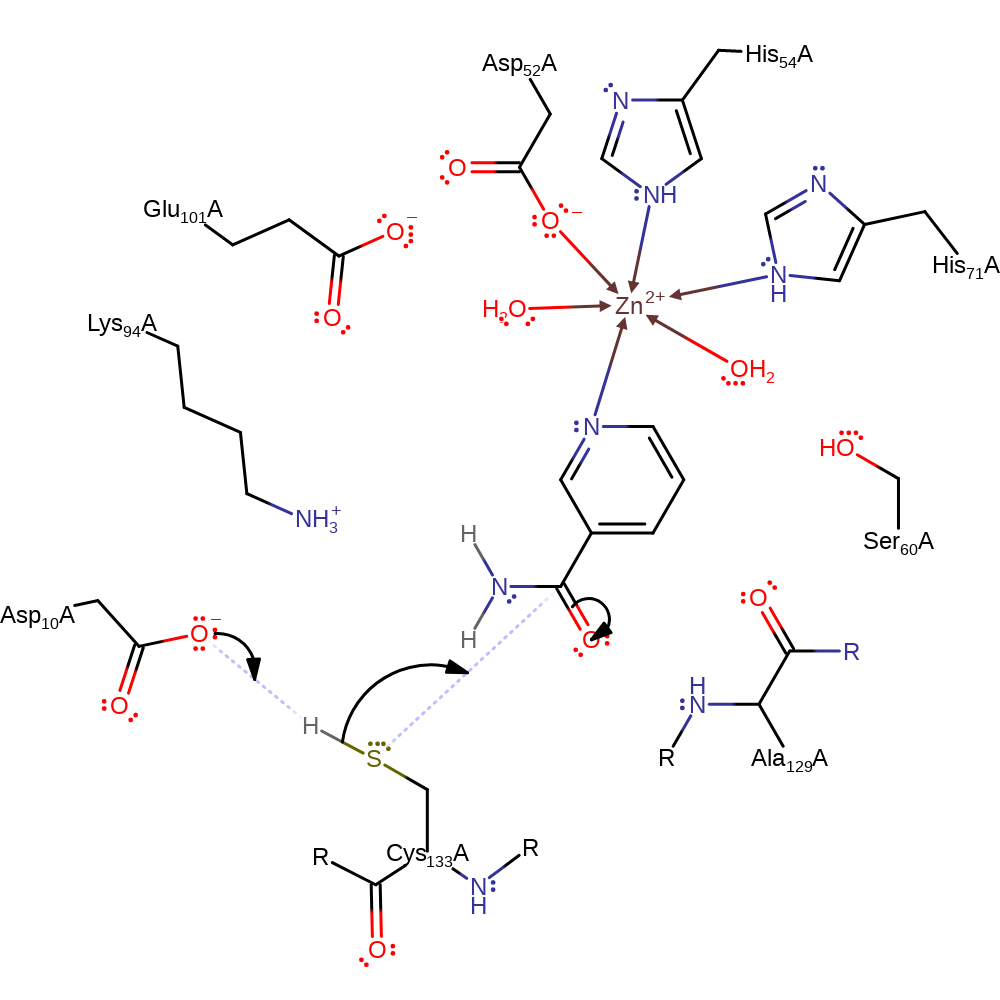
Step 1. Asp10 deprotonates Cys133 which then nucleophilically attacks the carbon of the carbonyl group of Nicotinamide.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Ala129A (main-N) | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Lys94A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Ser60A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Glu101A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asp52A | metal ligand |
| His54A | metal ligand |
| His71A | metal ligand |
| Cys133A (main-N) | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asp10A | proton acceptor |
| Cys133A | proton donor, nucleophile |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, ingold: bimolecular nucleophilic addition, enzyme-substrate complex formation, intermediate formation, overall reactant used, rate-determining step
Step 2. The amine group is protonated by Asp10 which initiates an elimination from the oxyanion which results in the cleavage of the amide bond an the release of ammonia.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Ser60A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Lys94A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Glu101A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Ala129A (main-N) | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Cys133A (main-N) | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asp52A | metal ligand |
| His54A | metal ligand |
| His71A | metal ligand |
| Asp10A | proton donor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, ingold: unimolecular elimination by the conjugate base, heterolysis, intermediate collapse, overall product formed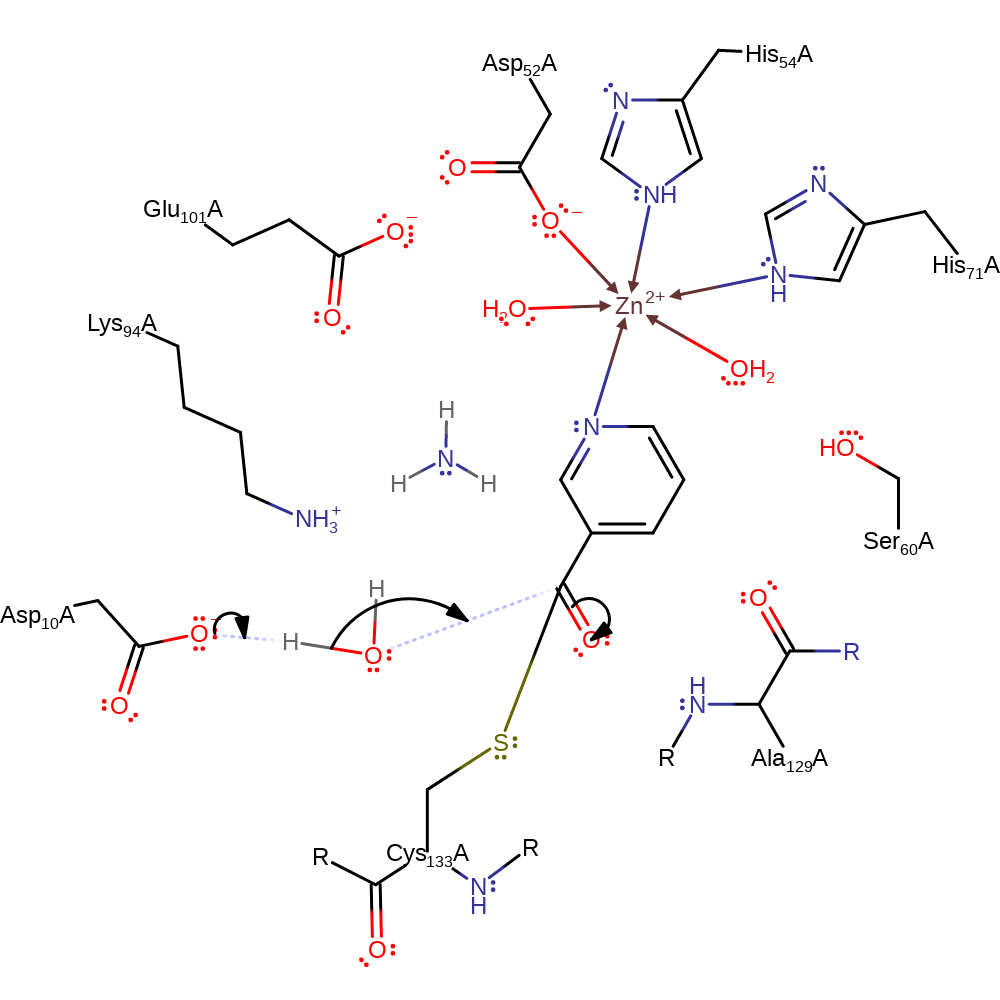
Step 3. Asp10 deprotonates water which activates it to nucleophilically attack the carbon of the carbonyl group.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Ser60A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Lys94A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Glu101A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Ala129A (main-N) | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Cys133A (main-N) | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asp52A | metal ligand |
| His54A | metal ligand |
| His71A | metal ligand |
| Asp10A | proton acceptor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, ingold: bimolecular nucleophilic addition, intermediate formation, overall reactant used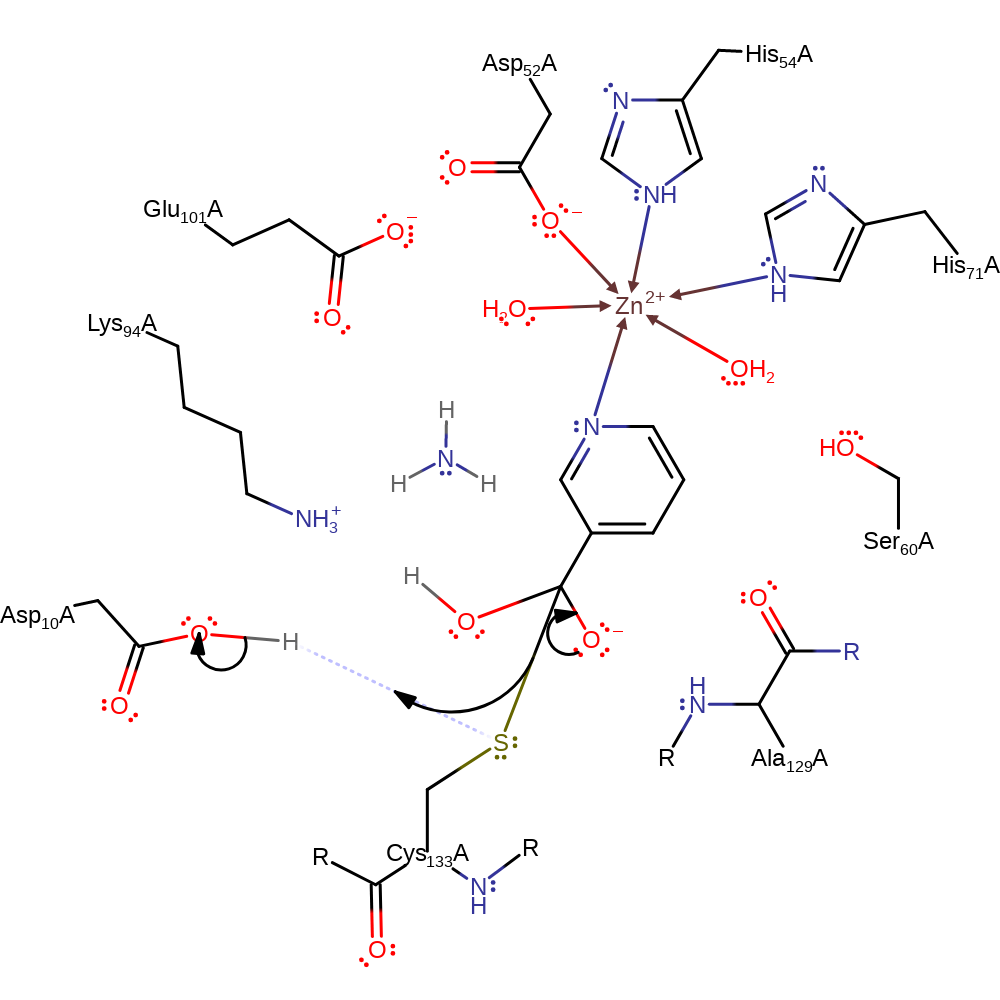
Step 4. The oxyanion initiates an elimination which results in the cleavage of the acyl-enzyme which releases Cys133 which then accepts a proton from Asp10 returning the active site to its native state.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Ser60A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Lys94A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Glu101A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Ala129A (main-N) | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Cys133A (main-N) | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asp52A | metal ligand |
| His54A | metal ligand |
| His71A | metal ligand |
| Cys133A | nucleofuge |
| Asp10A | proton donor |
| Cys133A | proton acceptor |




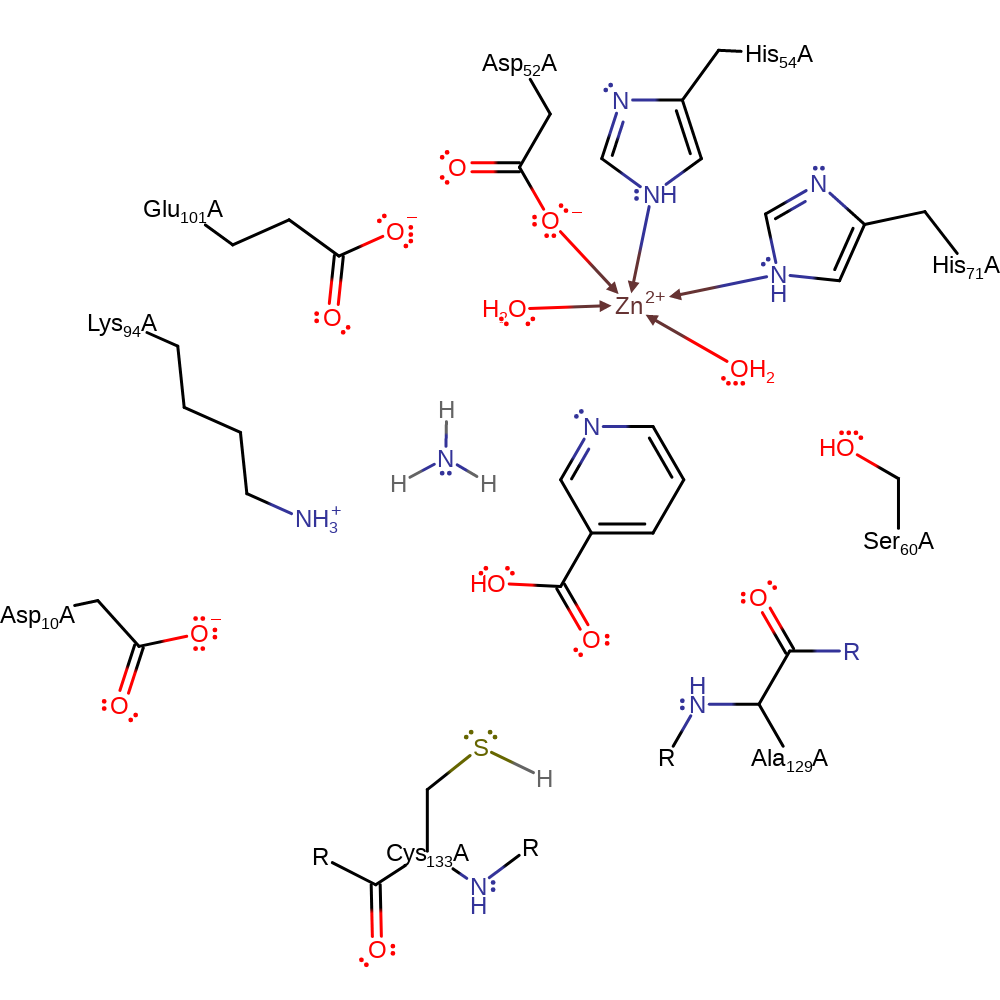 Download:
Download: