Cystathionine beta-synthase
Mammalian cystathionine beta-synthase (CBS) is a heme protein that catalyses the conversion of L-serine and L-homocysteine (L-Hcys) to give cystathionine in the first step in the transulfuration pathway. CBS is a member of the beta-family (Fold-type II) of pyridoxal 5'-phosphate (PLP) enzymes. These catalyse PLP-dependent, beta-replacement reactions in which the electronegative substituent in the beta-position of the amino acid substrate (in the case of CBS, the -OH group of L-Ser), is replaced by a sulphur-containing nucleophile (L-Hcys thiol group). Human CBS (hCBS) has three domains - the N-terminal domain where heme, which is not essential for catalysis and the function of which is still uncertain, is bound; the core catalytic dimeric domain where PLP is bound; and the C-terminal domain where the allosteric activator of the enzyme, S-adenosyl-L-methionine (AdoMet), is bound.
Reference Protein and Structure
- Sequence
-
P35520
 (4.2.1.22)
(4.2.1.22)
 (Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
(Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
- Biological species
-
Homo sapiens (Human)

- PDB
-
1m54
- CYSTATHIONINE-BETA SYNTHASE: REDUCED VICINAL THIOLS
(2.9 Å)



- Catalytic CATH Domains
-
3.40.50.1100
 (see all for 1m54)
(see all for 1m54)
- Cofactors
- Pyridoxal 5'-phosphate(2-) (1)
Enzyme Reaction (EC:4.2.1.22)
Enzyme Mechanism
Introduction
On addition of the first substrate, L-Ser, a transaldimination reaction takes place. The internal aldimine, formed by PLP bound to the enzyme via the amino acid residue Lys119, is converted into an external aldimine by replacing Lys with L-Ser. Following the binding of the second substrate, L-Hcys, to the enzyme the alpha-proton and beta-hydroxide of the external aldimine are abstracted and eliminated to form water and the alpha-aminoacrylate intermediate. The aminoacrylate intermediate undergoes nucleophilic addition by the thiolate of L-Hcys to form a quinonoid intermediate. A second transaldimination occurs where the resting enzyme is regenerated and the product (cystathionine) is released.
Catalytic Residues Roles
| UniProt | PDB* (1m54) | ||
| Lys119 | Lys119(76)A | Cofactor PLP is held in the active site as an internal aldimine via a Schiff base linkage formed with Lys119. | covalently attached, nucleofuge, nucleophile, proton acceptor, proton donor, proton relay, electron pair acceptor, electron pair donor |
Chemical Components
bimolecular nucleophilic addition, overall reactant used, intermediate formation, intramolecular elimination, schiff base formed, intermediate terminated, bimolecular elimination, proton transfer, proton relay, native state of cofactor regenerated, native state of enzyme regenerated, overall product formedReferences
- Taoka S et al. (2002), Biochemistry, 41, 10454-10461. Human Cystathionine β-Synthase Is a Heme Sensor Protein. Evidence That the Redox Sensor Is Heme and Not the Vicinal Cysteines in the CXXC Motif Seen in the Crystal Structure of the Truncated Enzyme†,⊥. DOI:10.1021/bi026052d. PMID:12173932.
- Tu Y et al. (2018), Biochemistry, 57, 3134-3145. Crystal Structures of Cystathionine β-Synthase from Saccharomyces cerevisiae: One Enzymatic Step at a Time. DOI:10.1021/acs.biochem.8b00092. PMID:29630349.
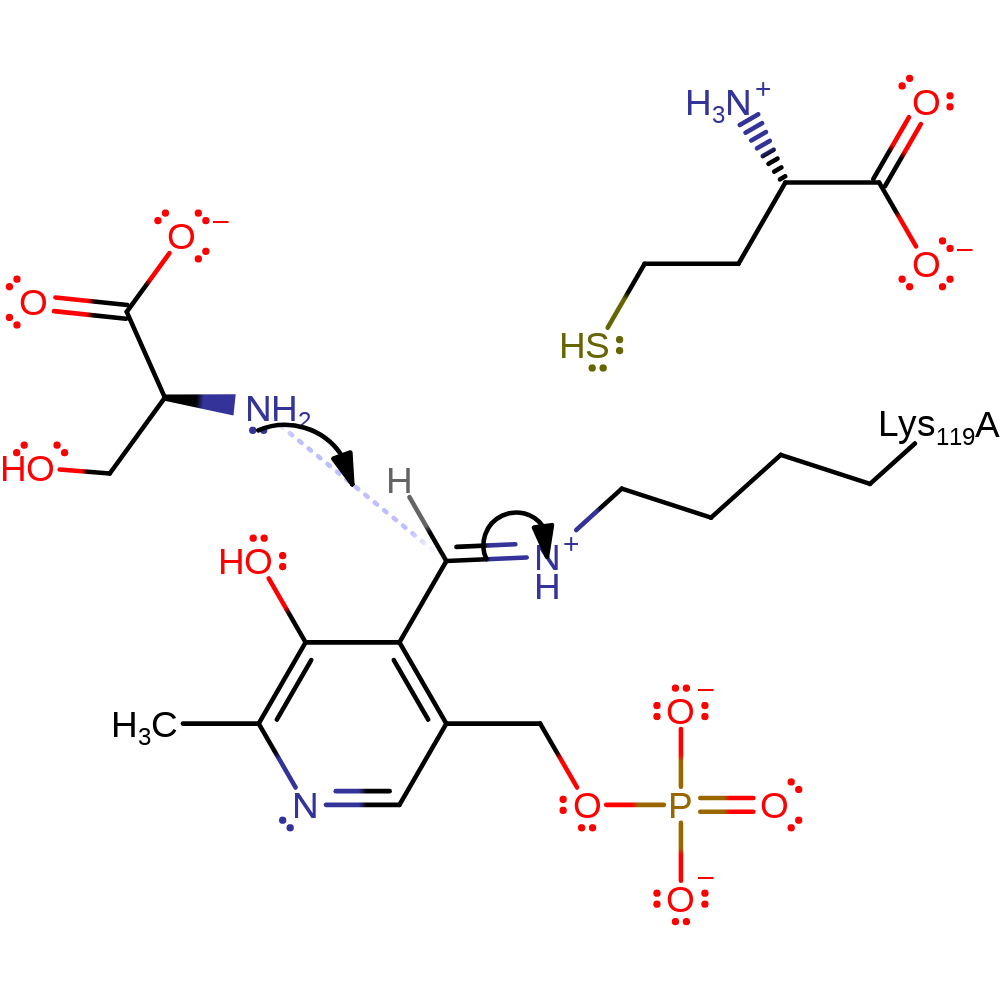
Step 1. The nitrogen of the substrate serine performs a nucleophillic attack upon the aldimine bond forming a tetrahedral intermediate.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Lys119(76)A | covalently attached |
| Lys119(76)A | electron pair acceptor |
Chemical Components
ingold: bimolecular nucleophilic addition, overall reactant used, intermediate formation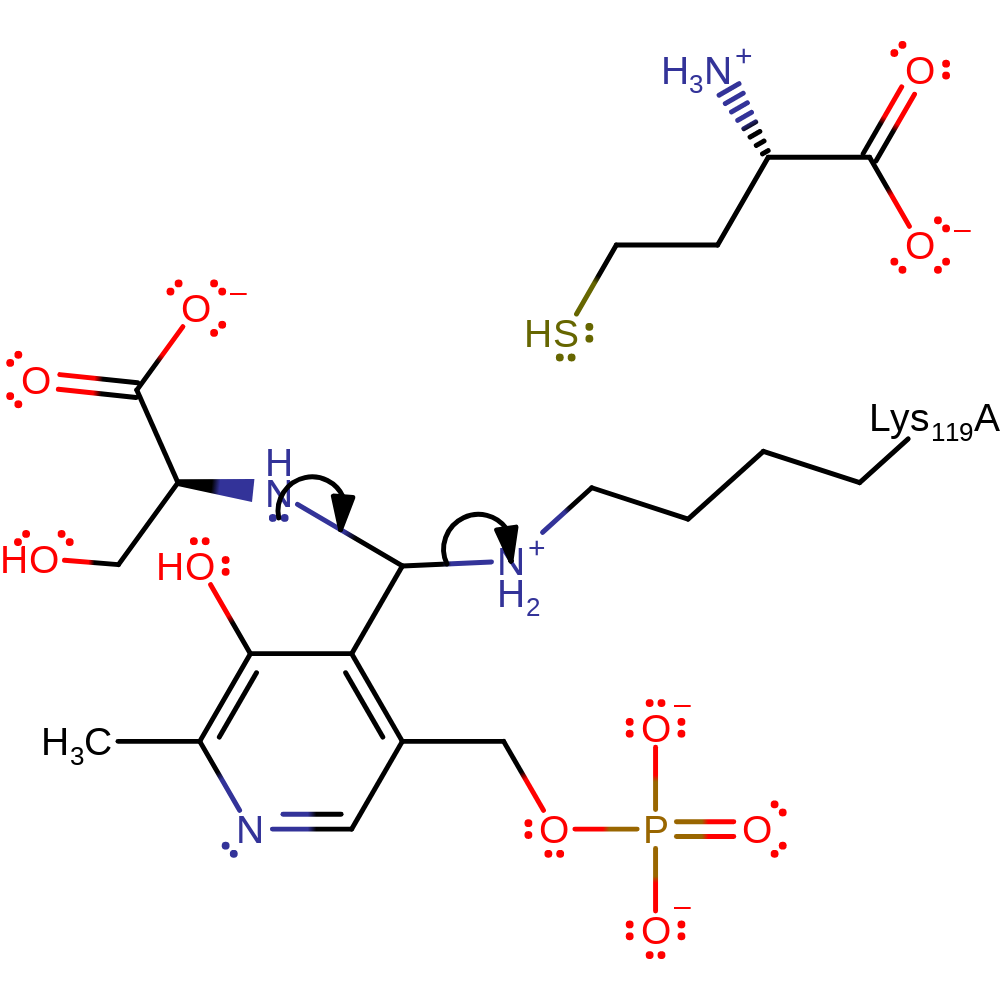
Step 2. Lys119 is eliminated and a new aldimine bond is formed between the serine and PLP.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Lys119(76)A | nucleofuge |
Chemical Components
ingold: intramolecular elimination, schiff base formed, intermediate terminated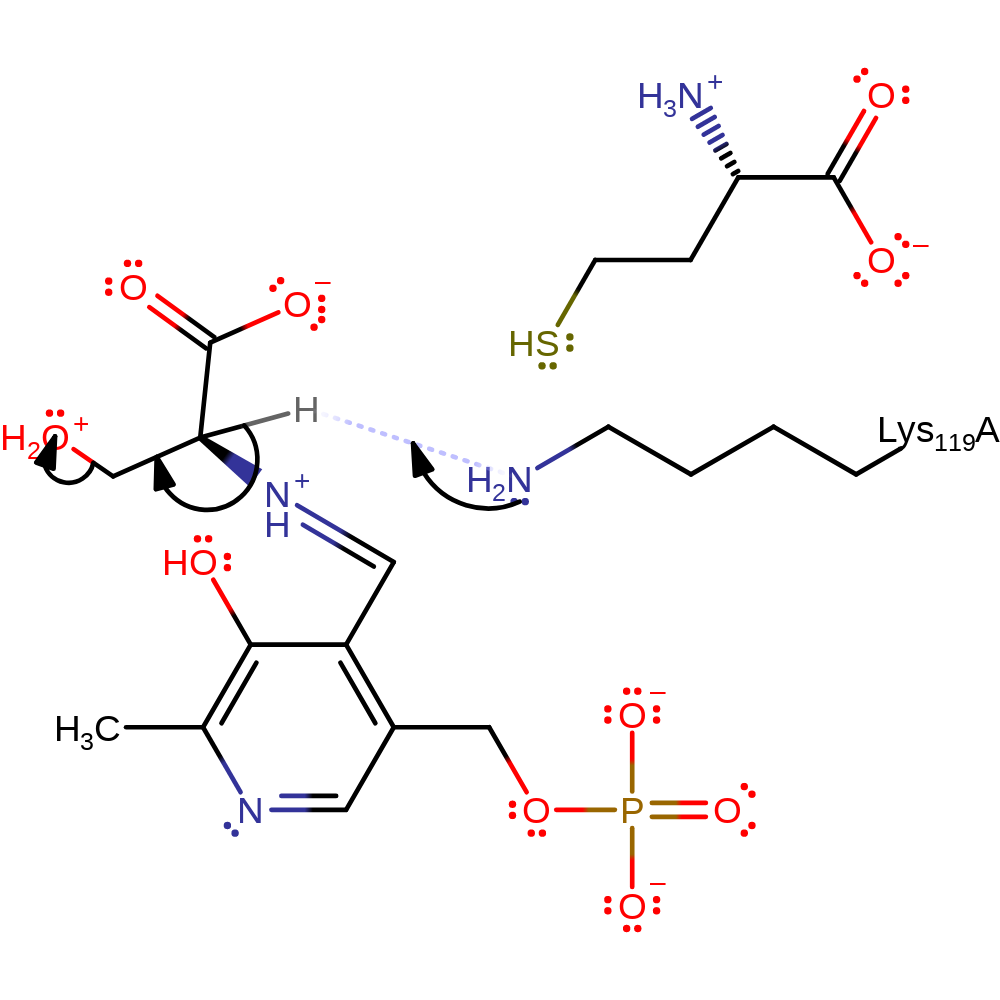
Step 3. Lys119 accepts a proton from the serine alpha carbon this leads to water being eliminated from the beta carbon forming an aminoacrylate intermediate.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Lys119(76)A | proton acceptor |
Chemical Components
ingold: bimolecular elimination, proton transfer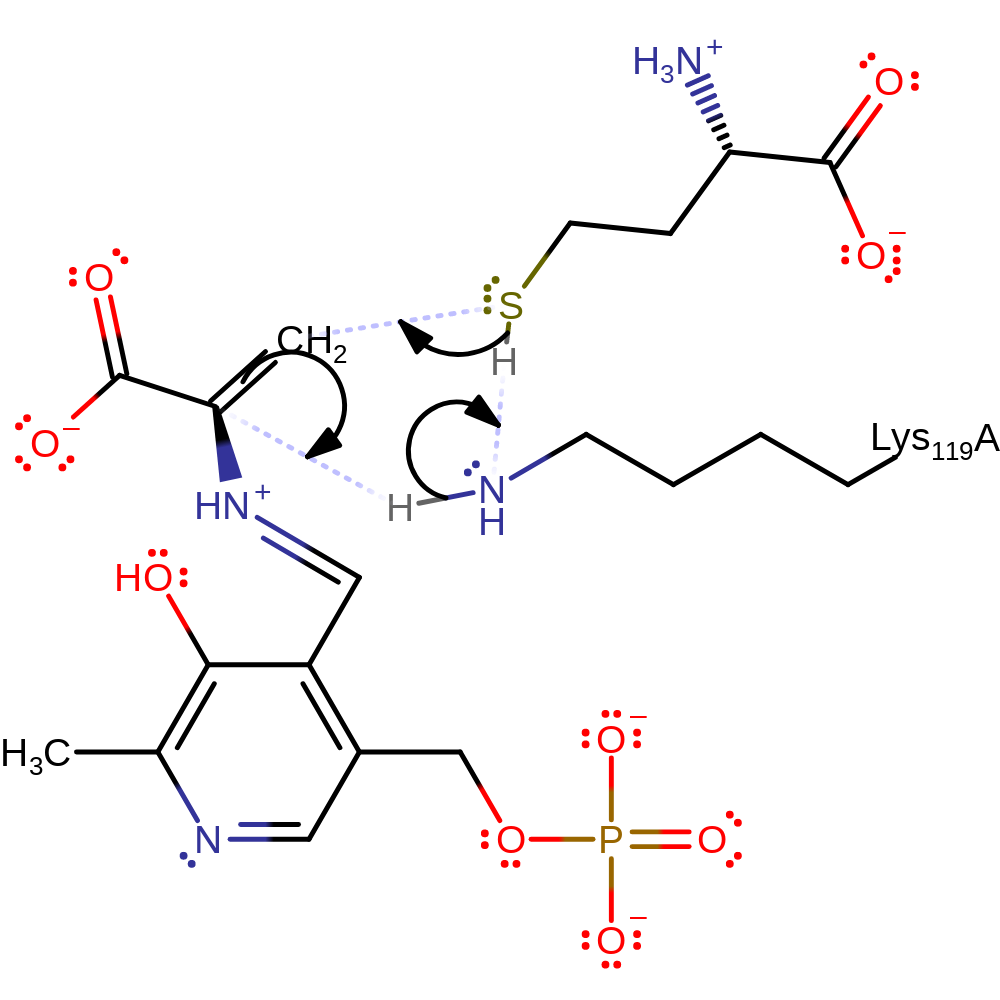
Step 4. The thiol group of the cysteine performs a nucleophilic attack on the C=C bond of the aminoacrylate forming a quinonoid intermediate, with Lys119 acting as a proton relay.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Lys119(76)A | proton relay |
| Lys119(76)A | proton acceptor, proton donor |
Chemical Components
ingold: bimolecular nucleophilic addition, proton relay
Step 5. Lys119 performs a nucleophilic attack on the aldimine bond in a second transaldimination reaction.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Lys119(76)A | covalently attached, nucleophile |
Chemical Components
ingold: bimolecular nucleophilic addition, intermediate formation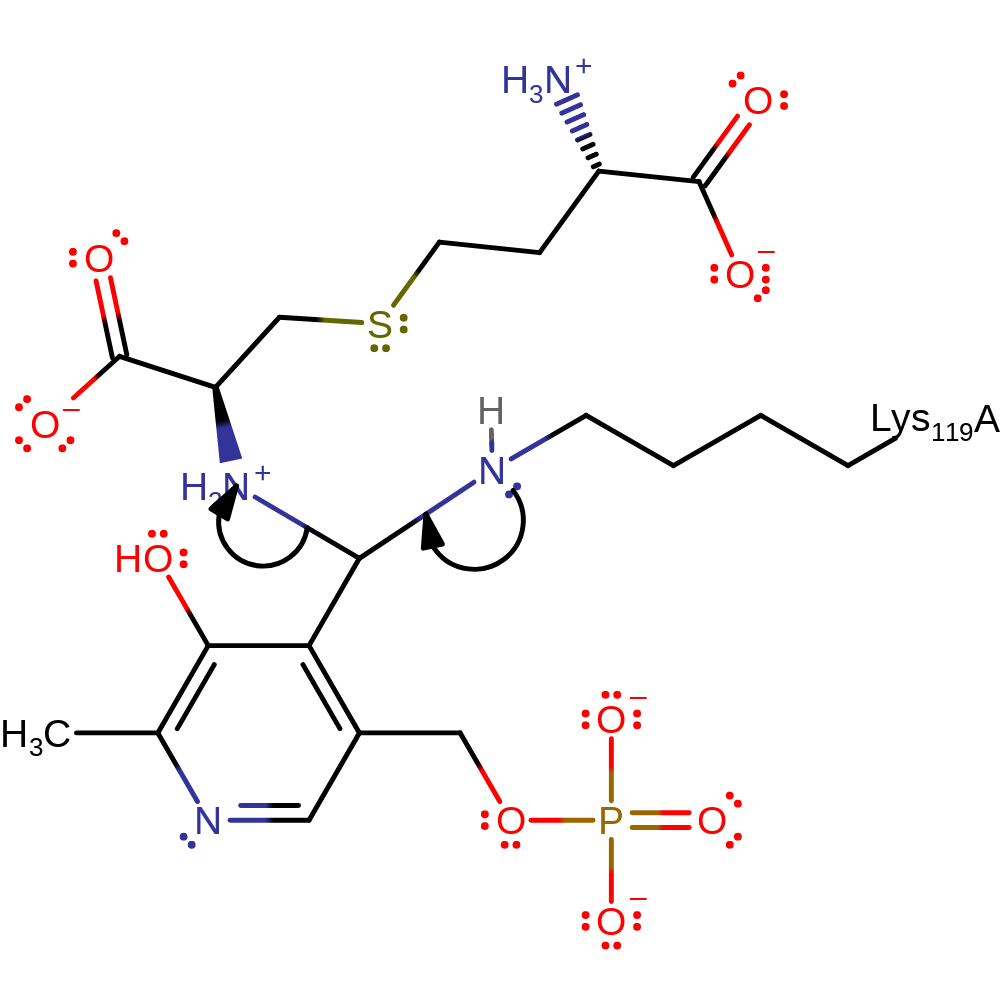
Step 6. The product is eliminated from PLP, regenerating the enzyme in its native state.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Lys119(76)A | covalently attached, electron pair donor |




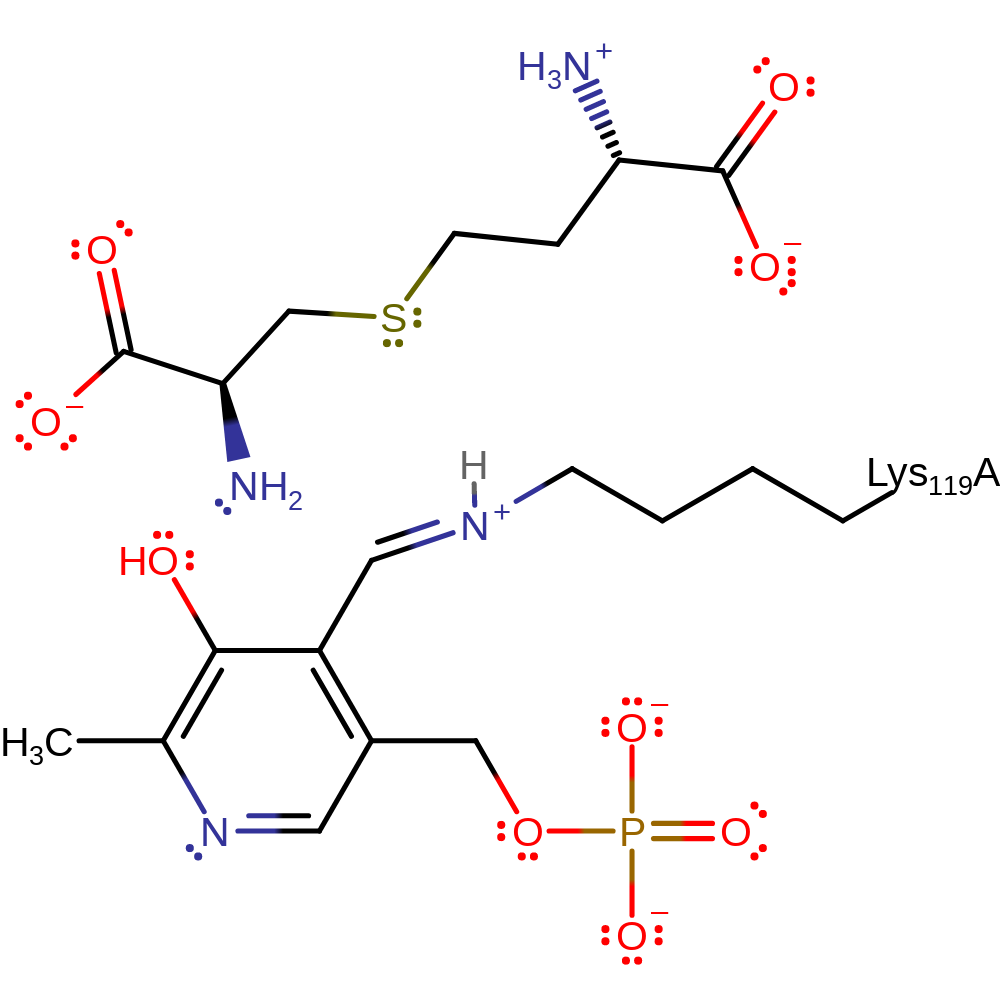 Download:
Download: